Weld Pad Level Gauge (WFG) – Pune Techtrol
Description
The Weld Pad Level Gauge (WFG) is an instrument designed for indicating the level of liquid in vessels under conditions of high pressure and temperature. This gauge is installed directly onto the vessel through welding, making it an integral part of the structure.
Construction of Weld Pad Level Gauge
The weld pad level gauge comprises a weld pad block, reflex transparent gauge glass, sealing gasket, cushion gasket, and cover plate. These components are held together by bolts, ensuring a leak-proof assembly.
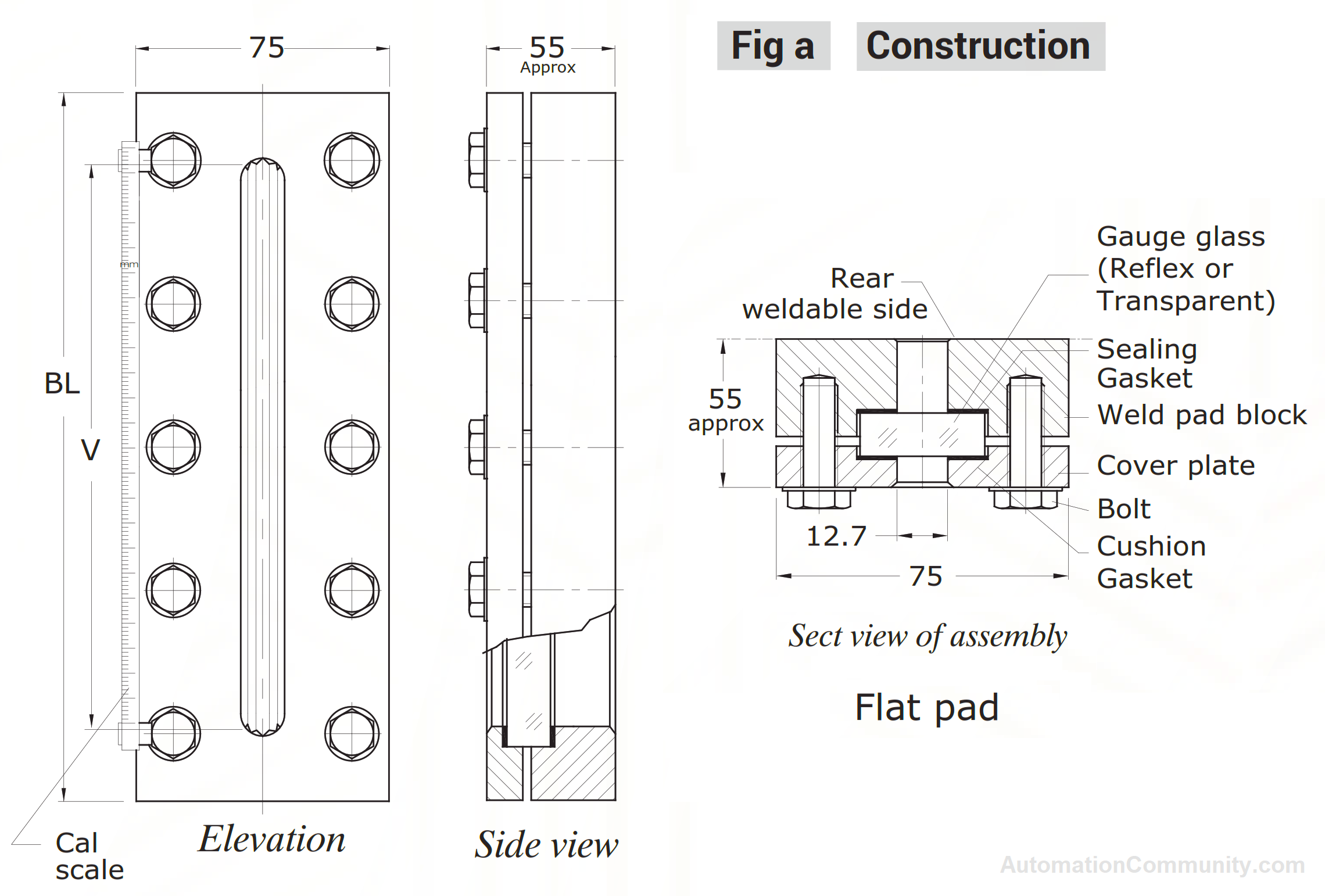
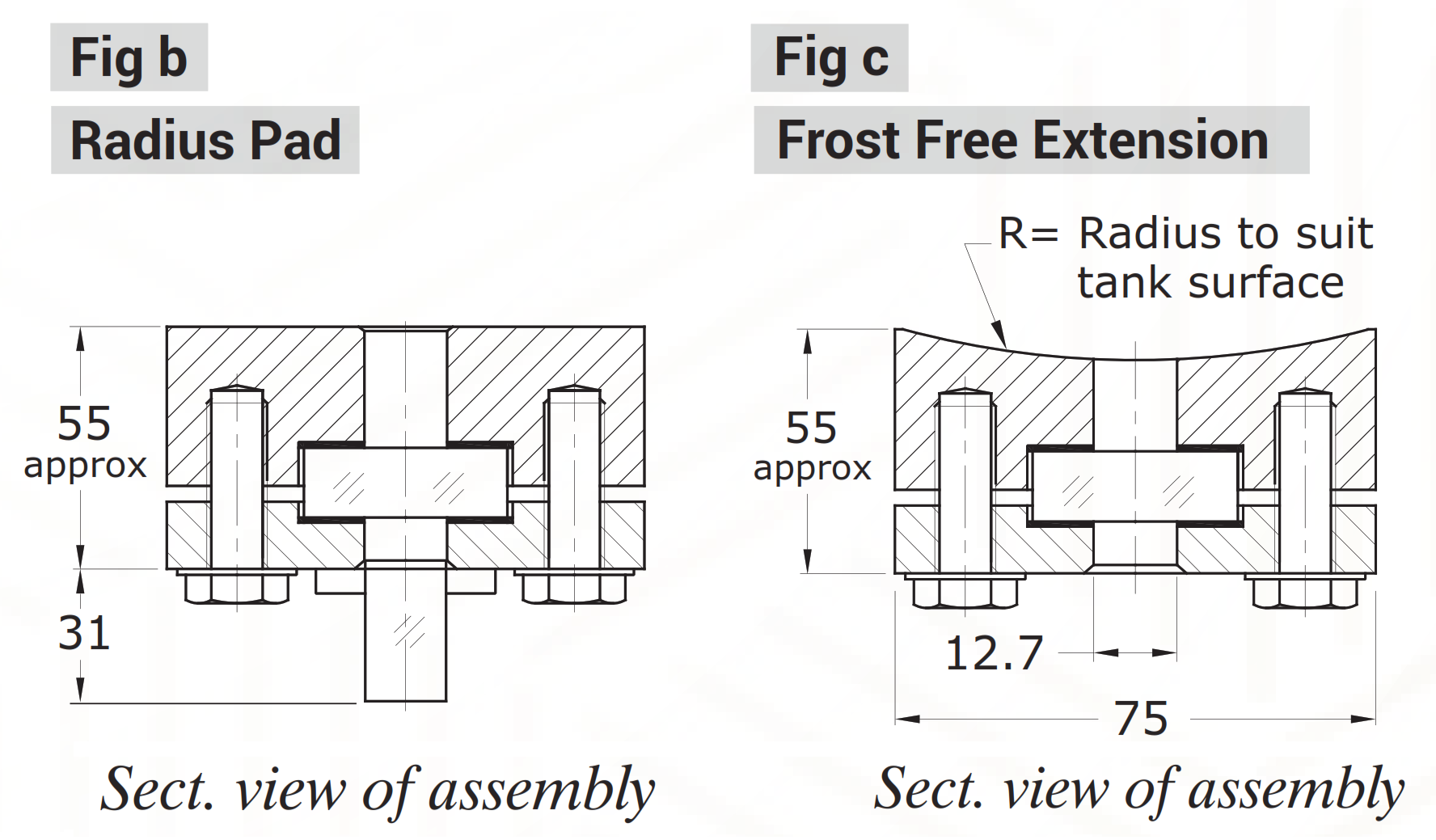
The level gauge glass, sandwiched between the sealing and cushion gasket, is placed on the front side for easy viewing of the liquid level. The weld pad block comes in different lengths ranging from 250 to 590 mm and can have either a flat or radius weldable side depending on the vessel’s surface.
The level gauge is equipped with an aluminum scale calibrated in millimeters (LC=10 mm) and can optionally include a frost-free extension to prevent frost formation on the outside surface of the gauge glass for clear visibility of the liquid level.
Materials
The weld pad block is typically constructed from either carbon steel (ASTM A 105) or stainless steel (SS316/SS316L), while the cover plate is made of ASTM A 105. However, if requested and in sufficient quantities, other materials can be used to construct the weld pad block.
Sealing Gaskets
The appropriate sealing gasket material for a Weld Pad Level Gauge depends on the temperature of the process and the contents of the vessel being monitored. Options for gasket materials include CAF, CNAF, and PTFE.
Ratings
The Weld Pad Level Gauge has a maximum pressure rating of 72 kg/cm2 and can handle temperatures up to 300°C when equipped with borosilicate glass. If equipped with soda ash glass, the gauge can handle pressures up to 20 kg/cm2 and temperatures up to 100°C. However, high-pressure models rated for pressures up to 150 kg/cm2 are available upon request.
Installation of Welded Level Gauge
During installation, Weld Pad Level Gauges can be installed in a single or staggered configuration based on the required visibility for the application. A flat pad should be employed for flat tank surfaces, while a radius pad should be used for curved tank surfaces.
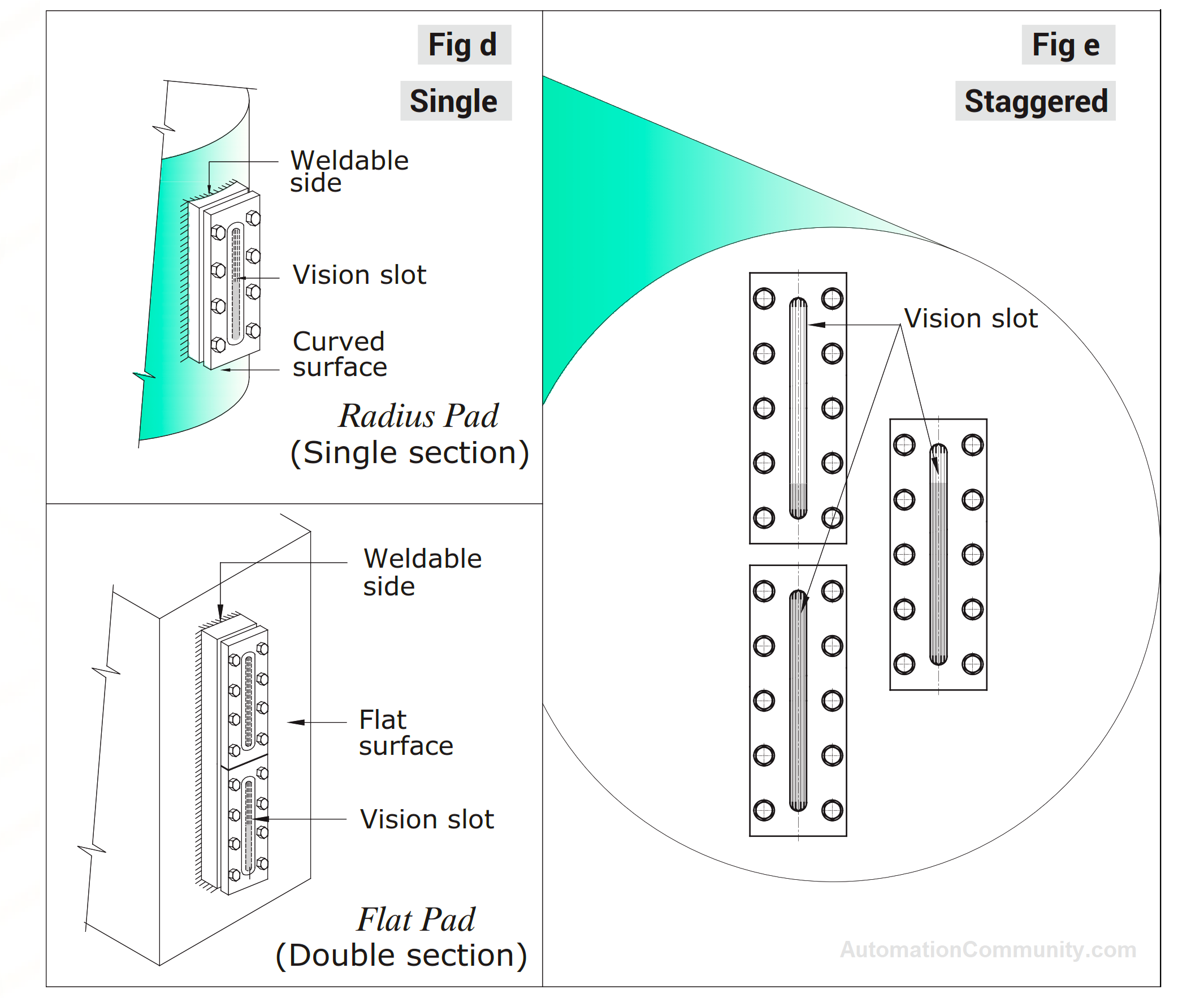
There are two methods for welding the weld pad to the vessel: cutting a slot in the tank wall equal to the vision slot of the gauge or drilling two holes in the tank wall located at the top and bottom of the visible range, ensuring their diameters are equivalent to the width of the vision slot of the gauge.
During the welding process, it is important to replace the level gauge glass with a welding insert to prevent warpage.
Precautions
Here are some guidelines to ensure the safe and optimal performance of your gauge:
- Adhere to the specified temperature and pressure limits and avoid exceeding them.
- It is not recommended to reuse any of the components, including glass, gaskets, cushions, and bolts, even if they appear to be in good condition. Stress is developed in the assembled position, and the gasket is deformed by compression. Therefore, it is best to use new glass and gaskets.
- When changing the gasket, make sure to smooth file the recessed area to remove any foreign particles and then install the new gasket.
Preventive Maintenance
Some of the maintenance tips are mentioned below.
- To prevent liquid loss and personnel injury, regularly check the gauge glass for cracks, scratches, or physical damage that may cause it to break under pressure.
- Use a soft cloth and commercial glass cleaner to keep the gauge glass clean, never use abrasive materials or wire brushes.
- Immediately take the gauge out of service if any damage is detected on the gauge glass.
- Check the gauge regularly for leakage at the gasket surface. If a leak is detected, repair it by verifying the tightness of bolts once the gauge has reached ambient temperature and pressure. If bolts are loose, tighten them in sequence, and if they are already tightened, replace the gasket.
- Bolts should be tightened in sequence after certain intervals.
- If any section of a multisection gauge is disturbed, check all sections for integrity and retorque or repair them as necessary.
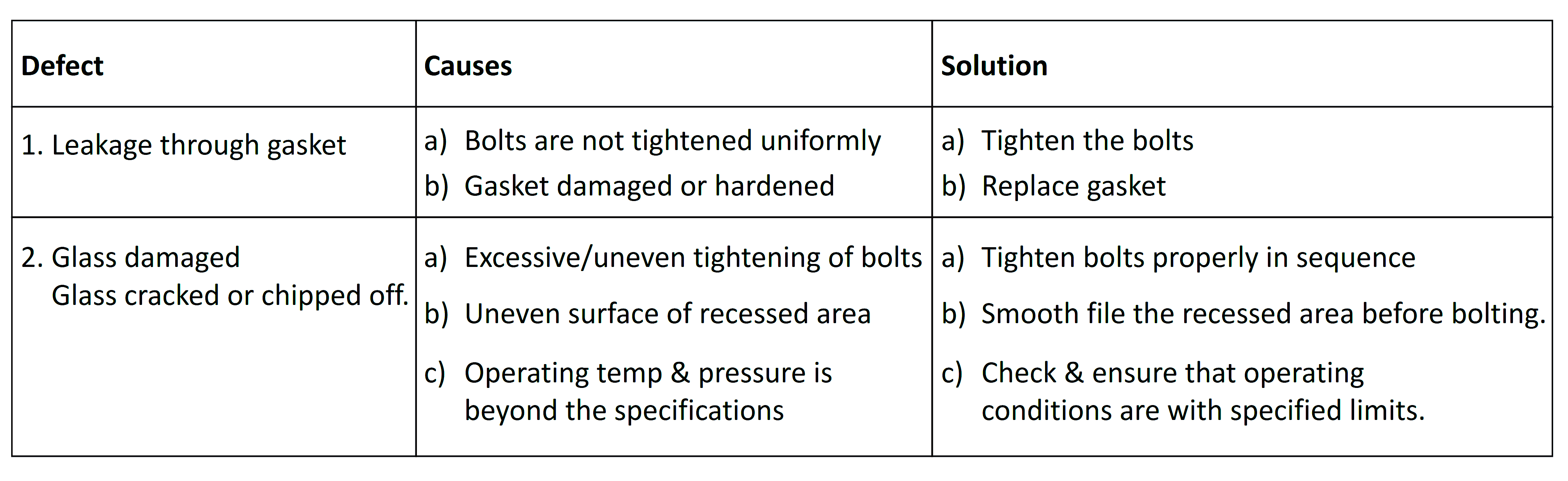
Troubleshooting of Weld Pad Level Gauge
Some of the common problems and solutions of weld pad level gauges are mentioned below.
Location
Report abuse
Report abuse
Featured






































