DNP3 Communication – Distributed Network Protocol 3
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communication protocols predominantly used between components in process automation systems. DNP 3 was initially developed to facilitate communication between various types of data acquisition and control equipment, with its primary use seen in the utilities sector, including electric and water companies.
History of DNP3
The DNP3 protocol was developed in 1993 by Westronic, Inc. (now GE Energy) as a robust, reliable, and efficient communication protocol for use in the electric utility industry. It was designed to optimize data transmission in challenging environments where reliability was paramount, such as electrical substations.
In the late ’90s, the DNP3 protocol was made an open standard, further accelerating its adoption. The DNP3 User Group maintains and promotes the protocol, ensuring it remains relevant and useful in modern applications.
Technical Aspects of DNP3
DNP3 is a layer 2 protocol that operates on either the physical and data link layers (Layers 1 and 2) of the OSI model or over TCP/IP network architectures (Layer 3 and above). It can support various types of hardware communication links, including serial (RS-232/RS-485) and Ethernet.
Features of Distributed Network Protocol 3
The DNP3 protocol includes several features to enhance reliability and functionality:
- Time synchronization: DNP3 allows for precise time-stamped data, which is crucial for event logging and post-event analysis.
- Multi-master support: It can accommodate multiple masters and peer-to-peer operations.
- Prioritization: Data can be classified according to priority, enabling essential data to be transmitted and processed first.
- Object-oriented data model: DNP3 uses a rich, object-oriented data model to represent various data types from real-world processes.
DNP3 Communication
In a DNP3 system, communication typically happens between a Master station (Control Center or SCADA system) and outstations (Remote Terminal Units, Intelligent Electronic Devices). The Master station initiates control actions or data requests, and the outstations respond to these commands.
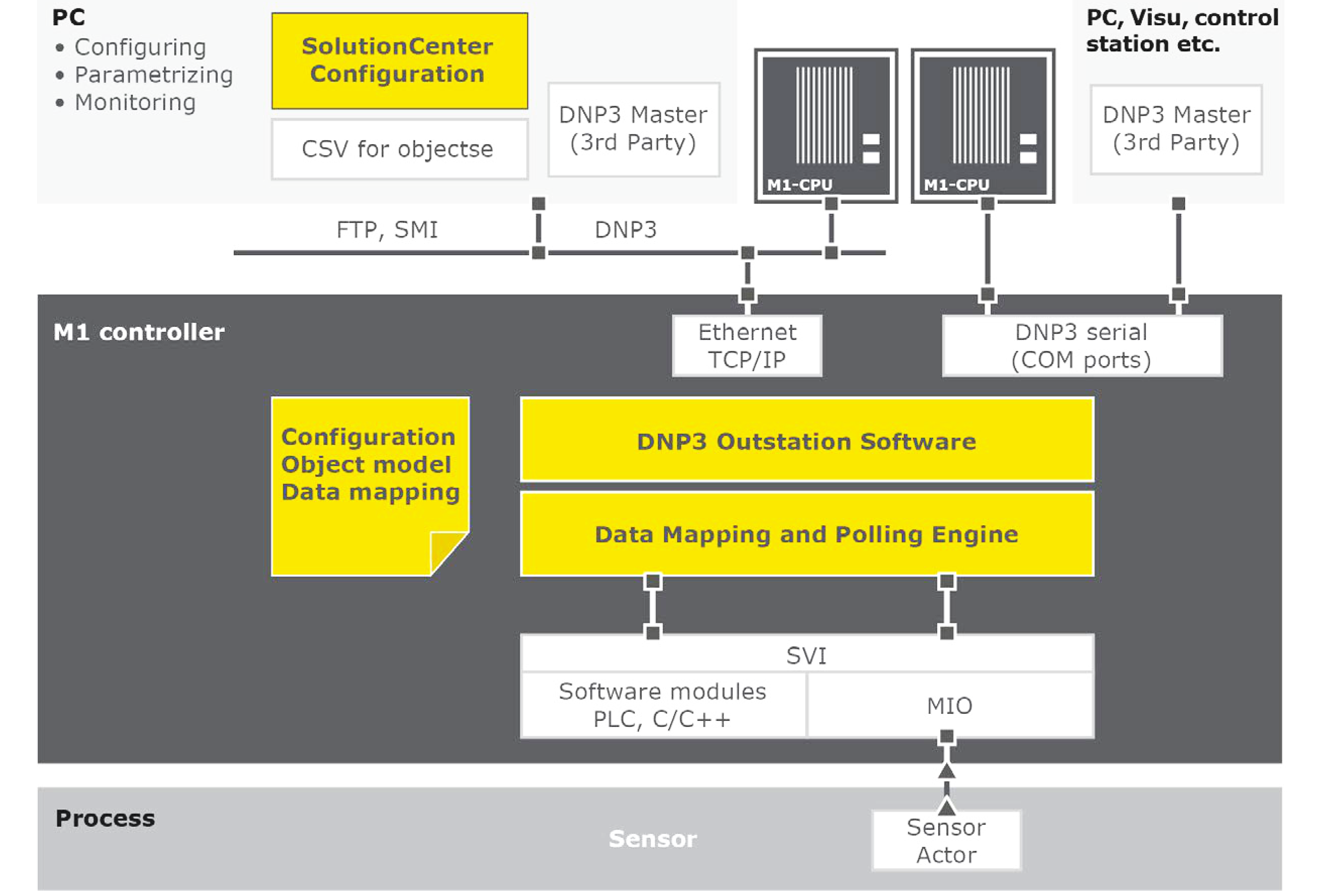
DNP3 in SCADA Systems
DNP3 has been widely adopted in Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, mainly due to its robustness, interoperability, and data integrity features. It’s used in critical infrastructure sectors worldwide, including water treatment facilities, gas and oil industries, and, most prominently, electrical utilities.
Security Concerns and Measures
As with all SCADA communication protocols, the security of DNP3 is of paramount concern, particularly because a successful attack could disrupt essential services. Despite DNP3’s inherent robustness, it was not initially designed with robust cybersecurity features.
However, over time, efforts have been made to improve its security. A secure authentication feature was added in DNP3 version 2.00, enhancing its ability to resist unauthorized control actions.
Yet, it’s essential to note that DNP3 security is also dependent on the broader cybersecurity infrastructure in which it’s embedded. A comprehensive security strategy should include network segregation, secure remote access, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
DNP3 Protocol Questions
The DNP3 protocol has remained a key communication protocol within SCADA systems and other process automation settings, offering a reliable, efficient, and flexible means of transmitting crucial data in real time.
As more industries continue to digitize and automate their processes, the importance of secure and efficient communication protocols like DNP3 will only continue to grow. Understanding DNP3 and its functions is fundamental to maintaining secure and efficient automation processes in industries worldwide.
What is DNP3?
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communication protocols used in utilities and process industries, primarily for electric, water, oil, and gas sectors. It’s used to enable communication between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It was designed to provide robust and efficient communication, even in harsh conditions where communication systems can be unreliable.
Who developed the DNP3 protocol?
The DNP3 protocol was initially developed by Westronic, Inc. (now GE Harris) in 1993. It was later handed over to the DNP Users Group which continues to maintain and develop the protocol.
Why was DNP3 developed?
DNP3 was developed to facilitate communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It provides robustness, efficiency, and compatibility in a wide range of applications, especially in environments where the communication systems may be unreliable or subject to harsh conditions.
How does DNP3 work?
DNP3 works as a layer 2 protocol that allows for reliable communication between many types of data acquisition and control devices. It uses a master/slave or client/server architecture where the master/client initiates transactions or requests for data, and the slave/server responds to the requests.
What is the importance of DNP3 in SCADA systems?
DNP3 is a critical communication protocol in SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. It allows for the reliable and efficient transmission of data between SCADA control centers and field devices such as sensors and actuators. DNP3 also provides advanced features not available in other protocols, such as time-stamping of events, which can be crucial for many SCADA applications.
What type of architecture does DNP3 use?
DNP3 uses a master/slave or client/server architecture. The master or client typically initiates transactions or requests for data. The slave or server, usually a remote device like a sensor, actuator, or intelligent electronic device, responds to these requests.
How is DNP3 different from Modbus?
While both DNP3 and Modbus are communication protocols used in industrial control systems, there are several differences between them. DNP3 provides more advanced features than Modbus, such as time-stamping, data classification, and exception-based reporting. These features make DNP3 a more efficient and reliable protocol for data communication in SCADA systems.
What are some of the key features of DNP3?
Key features of DNP3 include data fragmentation, time synchronization, event logging, and exception-based reporting. DNP3 also supports multiple data types, which allows for more flexible and efficient data communication.
Can DNP3 be used over Ethernet?
Yes, DNP3 can be used over Ethernet, and this is commonly done using the TCP/IP protocol. DNP3 over Ethernet offers several advantages, such as higher speed, better reliability, and improved diagnostics compared to serial communications.
Is DNP3 secure?
While DNP3 includes some security features, such as Secure Authentication, it’s not inherently secure against all types of cyber threats. For this reason, it’s often used in combination with other security measures, such as firewalls and VPNs, especially when used over public networks or the Internet.
What is DNP3 Secure Authentication?
DNP3 Secure Authentication is a feature that provides a means of authenticating command requests to prevent unauthorized control actions. It uses challenge-response authentication to ensure that command requests are only accepted from authorized sources.
What is DNP3 SAv5?
DNP3 SAv5, or Secure Authentication version 5, is the most recent version of DNP3 Secure Authentication. It provides strong, cyber-security industry-standard security for DNP3 communication sessions, ensuring that command requests are only accepted from authorized sources.
What is an outstation in DNP3?
In DNP3, an outstation refers to a remote terminal unit (RTU) or intelligent electronic device (IED) that collects data from sensors and implements control actions from the master station. The outstation communicates with the master station using the DNP3 protocol.
What does “unsolicited response” mean in DNP3?
An unsolicited response in DNP3 is a message sent from an outstation to a master station without a prior request from the master. This allows the outstation to inform the master of important events as soon as they occur, rather than waiting for a poll from the master.
What is a DNP3 master station?
A DNP3 master station is a device, typically a server in a SCADA system, that controls and monitors outstations or slaves. The master station initiates communication, sends control commands, and requests data from the outstations.
What is time synchronization in DNP3?
Time synchronization is a feature of DNP3 that allows a master station to synchronize the clocks of all outstations. This ensures that all events and data collected from the outstations are accurately timestamped, which is critical for analyzing and understanding the sequence of events in a system.
What is data fragmentation in DNP3?
Data fragmentation is a feature of DNP3 that allows large amounts of data to be split into smaller packets for transmission. This ensures that even if a communication link has a limited data capacity, large data sets can still be transmitted reliably.
What is DNP3 event logging?
DNP3 event logging is a feature that records changes in the process variables instead of their current values. This significantly reduces the amount of data to be transmitted and allows the master to receive updates only when actual changes occur.
What is DNP3 exception-based reporting?
DNP3 exception-based reporting is a feature that allows an outstation to report data to the master only when the data value changes or an event occurs, instead of continuously reporting the current value. This significantly reduces the amount of data to be transmitted and makes communication more efficient.
What is the DNP3 Users Group?
The DNP Users Group is a non-profit organization dedicated to ensuring the reliability and interoperability of DNP3. They maintain and develop the DNP3 specifications and provide resources and support to the DNP3 community.
How does DNP3 ensure data integrity?
DNP3 includes features such as CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) for error detection and control code functions for message control, ensuring the integrity of data transmitted over the network. In addition, DNP3 supports sequence numbers to ensure that all transmitted data packets are received in the correct order.
What types of data can DNP3 handle?
DNP3 supports multiple data types, including binary (status) inputs and outputs, analog (measurements) inputs and outputs, counter inputs, and file transfers. This variety allows DNP3 to be used in a wide range of applications.
How is DNP3 typically implemented in a SCADA system?
In a SCADA system, DNP3 is typically implemented between the SCADA control center (master station) and the field devices (outstations or slave stations). The master station sends control commands and requests data from the outstations. The outstations, in turn, send data and event notifications to the master station.
What is a DNP3 data link layer?
The DNP3 data link layer is responsible for reliable data transfer between the master and outstations. It uses frame-based communication, provides error checking with CRC, and manages the control functions such as link status, request link status, and reset link states.
What is a DNP3 application layer?
The DNP3 application layer is responsible for processing the data received from the data link layer. It manages the control functions, including the reading and writing of internal indications, counters, analog inputs and outputs, and binary inputs and outputs.
What is a DNP3 transport layer?
The DNP3 transport layer is responsible for segmenting and reassembling application layer messages. It ensures that large data sets can be transmitted reliably over networks that may have limitations on the size of individual data packets.
How is DNP3 used in the electric utility industry?
In the electric utility industry, DNP3 is commonly used for communications between a central SCADA system and substations, wind farms, or other remote sites. It enables efficient and reliable transmission of real-time data and control commands, helping utilities manage their operations and respond quickly to changing conditions.
Can DNP3 be used wirelessly?
Yes, DNP3 can be used over wireless communications. While it was originally designed for wired communications, DNP3 has been successfully implemented over various wireless technologies, including cellular and satellite networks.
How does DNP3 handle network failures or communication interruptions?
DNP3 includes several features to handle network failures or communication interruptions. These include error-checking mechanisms, retries, and support for data fragmentation and reassembly. Also, DNP3’s event-oriented nature ensures that important data is not lost, as changes in process variables are logged and transmitted when communication is re-established.
What programming languages are commonly used to implement DNP3?
DNP3 can be implemented using various programming languages. Commonly used languages include C, C++, and Java. There are also DNP3 libraries available for other languages, such as Python and .NET languages.
What are some common challenges when implementing DNP3?
Common challenges when implementing DNP3 can include dealing with the complexity of the protocol, ensuring robustness and reliability of communications, managing the large variety of data types and control codes that DNP3 supports, and ensuring compatibility with existing devices and systems.
What is the DNP3 Object model?
The DNP3 Object model is a collection of data types, control functions, and application services that DNP3 can handle. The object model includes binary and analog inputs and outputs, counters, and various control relay outputs, among other things.
What is DNP3 Class data?
DNP3 Class data refers to a mechanism for categorizing data based on its importance and frequency of change. DNP3 defines three classes (Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3) for event data. Class 1 data is for the highest priority events, while Class 3 is for the lowest priority.
What is the difference between DNP3 and IEC 60870-5-101/104?
While both DNP3 and IEC 60870-5-101/104 are communication protocols used in electric utilities, they were developed in different regions (DNP3 in North America, IEC in Europe) and have some differences in their features and capabilities. For example, DNP3 supports unsolicited responses and time synchronization, while IEC 60870-5-104 supports TCP/IP networks.
How can I test a DNP3 implementation?
Testing a DNP3 implementation can involve both functional testing (ensuring that the implementation behaves correctly according to the DNP3 specifications) and performance testing (ensuring that the implementation can handle the expected load and respond quickly enough). Various DNP3 testing tools are available, including simulators, protocol analyzers, and conformance testing suites.
What is a DNP3 simulation?
DNP3 simulation involves using software to emulate the behavior of DNP3 devices (either master or outstation). This can be used for testing, training, or development purposes, without the need for actual DNP3 hardware.
How does DNP3 support interoperability?
DNP3 supports interoperability by providing a standardized and comprehensive protocol for communication between devices from different manufacturers. The DNP3 specifications include detailed definitions of the protocol’s behavior, data types, control functions, and application services, which help ensure that all DNP3 devices can work together effectively.
Can DNP3 be used over serial communications?
Yes, DNP3 was originally designed to be used over serial communications and is still commonly used in this way, especially for communications with legacy devices or in situations where network infrastructure is not available.
What are the benefits of using DNP3 over TCP/IP?
Using DNP3 over TCP/IP offers several advantages, including higher communication speeds, better reliability, and improved diagnostics. In addition, TCP/IP networks are widely available and can support a large number of devices, making them a good choice for large-scale SCADA systems.
What are the limitations of DNP3?
While DNP3 is a powerful and flexible protocol, it does have some limitations. These include complexity (which can make DNP3 difficult to implement and manage), lack of built-in security features (requiring additional security measures to be implemented), and limited support for some types of data or control functions (compared to some other industrial protocols).
What is DNP3 Self-Addressing?
DNP3 Self-Addressing is a method that allows DNP3 devices to assign their own addresses automatically. This can simplify network configuration and help reduce the risk of address conflicts.
What is the use of confirmation messages in DNP3?
Confirmation messages in DNP3 are used to acknowledge the successful receipt of data. They play a crucial role in ensuring the reliable delivery of data and control commands, especially over unreliable or noisy communication channels.
Can DNP3 run on top of UDP?
While DNP3 is traditionally used over TCP/IP for network communications, it can also be used over UDP. However, this is less common because UDP does not provide the same level of reliability as TCP.
What is the role of DNP3 in substation automation?
In substation automation, DNP3 is used to enable communication between control centers and field devices such as circuit breakers, transformers, and protection relays. DNP3’s robustness and advanced features like time-stamping make it well-suited for this kind of application.
How does DNP3 handle control commands?
In DNP3, control commands are sent by the master station to an outstation. The outstation executes the command and sends a response back to the master, indicating whether the command was successful or not.
How does DNP3 support redundant communication paths?
DNP3 supports redundant communication paths by allowing for multiple physical layers. If one communication path fails, DNP3 can automatically switch to another available path, ensuring the continuous operation of the system.
What is the role of the DNP3 Link layer?
The DNP3 Link layer is responsible for the reliable transmission of frames over a physical medium. It uses error detection, address fields, and control fields to manage the communication between the master and outstations.
What are the benefits of using DNP3 in the water industry?
In the water industry, DNP3 is used to enable communication between central control systems and remote devices such as pumps, valves, and sensors. The robustness, reliability, and efficiency of DNP3 make it suitable for monitoring and controlling the widely distributed assets of water utilities.
What is DNP3 Deadband?
In DNP3, a Deadband is a value that determines when an analog input should be reported as an event. If the change in the analog input value exceeds the deadband, the new value is reported as an event to the master station.
Can DNP3 be used for distributed generation?
Yes, DNP3 can be used for distributed generation. It allows for the efficient and reliable communication of real-time data and control commands between the central control system and distributed generation resources like solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems.
What is the role of DNP3 in Smart Grid applications?
In Smart Grid applications, DNP3 is used for the communication between central control systems and various grid assets like substations, distributed energy resources, and smart meters. DNP3’s advanced features like time-stamping, event reporting, and secure authentication make it well-suited for the requirements of the Smart Grid.
How does DNP3 ensure the ordered delivery of data?
DNP3 ensures the ordered delivery of data by using sequence numbers. Each message sent from a master or outstation has a unique sequence number, which allows the receiving device to put the messages in the correct order.
Can DNP3 be used over radio communications?
Yes, DNP3 can be used over radio communications. While the speed and reliability may not be as high as with wired or network communications, radio can provide a cost-effective solution for communicating with remote or mobile devices.
How does DNP3 handle large amounts of data?
DNP3 can handle large amounts of data by using fragmentation and reassembly. Large data sets are split into smaller pieces (fragments), which are transmitted separately and then reassembled at the receiving end.
What is the difference between DNP3 and ICCP?
DNP3 and ICCP (Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol) are both communication protocols used in the electric power industry, but they serve different purposes. DNP3 is primarily used for communications between control centers and field devices, while ICCP is used for communications between control centers.
What is a DNP3 gateway?
A DNP3 gateway is a device that acts as an interface between a DNP3 network and a network using a different protocol. The gateway translates messages between the two protocols, allowing devices that do not support DNP3 to communicate with a DNP3 network.
What are the security risks associated with DNP3?
While DNP3 includes some security features, like secure authentication, it’s not inherently secure against all types of cyber threats. Potential security risks include unauthorized access, spoofing of control commands, and denial-of-service attacks. Therefore, additional security measures like firewalls, VPNs, and secure network design are typically required.
How is DNP3 used in the oil and gas industry?
In the oil and gas industry, DNP3 is used for communication between central control systems and remote assets like drilling rigs, pump stations, and storage facilities. DNP3 allows for efficient and reliable transmission of real-time data and control commands, enabling remote monitoring and control of these assets.
Can DNP3 be used in building automation systems?
While DNP3 is not typically used in building automation systems (where protocols like BACnet or Modbus are more common), there’s no technical reason why it couldn’t be used. However, it may not be the best choice due to its complexity and the lack of support for DNP3 in many building automation devices.
How does DNP3 handle time synchronization?
DNP3 supports time synchronization, which is important for accurate event logging and coordinated control actions. The master station can send a “delay measurement” command to an outstation, which responds with the time of receipt. This allows the master to calculate and correct any time offset at the outstation.
What is Secure Authentication in DNP3?
Secure Authentication in DNP3 is a feature that provides a method for verifying the identity of the devices in a DNP3 communication session. It helps to ensure that only authorized devices can participate in the communication, thus protecting against unauthorized access and control.
What is DNP3’s role in telemetry applications?
In telemetry applications, DNP3 is used to transmit real-time data from remote sensors to a central system. Its robustness, efficiency, and advanced features like time-stamping make it well-suited for this kind of application.
What is a DNP3 Outstation Simulator?
A DNP3 Outstation Simulator is a software tool that emulates the behavior of a DNP3 outstation. This can be useful for testing DNP3 master stations or for training purposes, without the need for actual hardware.
What are the benefits of using DNP3 over legacy protocols like Modbus?
While Modbus is simpler and easier to implement, DNP3 offers several advantages like better error checking, time-stamping, support for larger data sets, and event-oriented reporting. These features make DNP3 more suitable for complex and large-scale SCADA systems.
Can DNP3 be used for load-shedding applications?
Yes, DNP3 can be used for load-shedding applications. It allows for the real-time communication of system conditions and control commands between a central system and various load-shedding devices, enabling dynamic and coordinated load-shedding actions.
How does DNP3 support data classification?
DNP3 supports data classification through its concept of classes. It defines three classes (Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3) for event data, with Class 1 being the highest priority. This allows the master station to request different types of data based on its current needs or network conditions.
Can DNP3 be used in nuclear power plants?
While the use of DNP3 in nuclear power plants depends on the specific regulatory requirements in each country, technically DNP3 can be used in such environments. Its reliability, robustness, and advanced features make it suitable for the demanding conditions of nuclear power plants.
How does DNP3 support data concentration?
DNP3 supports data concentration through its use in devices known as data concentrators or remote terminal units (RTUs). These devices collect data from multiple local sensors or devices and transmit it to the master station, reducing the communication load on the master.
How is DNP3 used in microgrid applications?
In microgrid applications, DNP3 is used for the communication between the microgrid controller and various grid assets like distributed generation resources, energy storage systems, and load control devices. DNP3’s robustness and advanced features make it well-suited for the dynamic and decentralized nature of microgrids.
What are the main parts of a DNP3 message?
A DNP3 message consists of several parts, including a start character, a length field, a control field, a destination address, a source address, a transport layer, an application layer, and a CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) field for error detection.
What is the role of the DNP3 User Group?
The DNP3 User Group is an organization that maintains and promotes the DNP3 protocol. It provides technical support to users, develops enhancements to the protocol, organizes interoperability testing events, and maintains the DNP3 specifications and conformance testing process.
How is DNP3 used in renewable energy applications?
In renewable energy applications, DNP3 is used for communication between control systems and renewable energy resources like solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. DNP3 enables efficient and reliable transmission of real-time data and control commands, helping to manage and integrate these resources into the grid.
How does DNP3 support peer-to-peer communication?
While DNP3 is primarily a master-slave protocol, it also supports some forms of peer-to-peer communication. For example, an outstation can send unsolicited responses to the master station, and two outstations can communicate with each other through a process known as interposing.
How can I analyze DNP3 traffic on a network?
Analyzing DNP3 traffic on a network can be done using network monitoring tools and DNP3 protocol analyzers. These tools can capture and decode DNP3 messages, allowing you to inspect the details of the communication and troubleshoot any issues.
How does DNP3 handle network congestion?
DNP3 handles network congestion through its event-based reporting and data classification features. The master station can request different types of data based on network conditions, and the outstations can buffer event data until the network is able to handle it.
What is the role of unsolicited responses in DNP3?
Unsolicited responses in DNP3 are used by outstations to report event data to the master station without waiting for a poll. This can reduce network traffic and improve the timeliness of data reporting, especially for important or time-critical events.
Can DNP3 be used over cellular networks?
Yes, DNP3 can be used over cellular networks. This can provide a flexible and cost-effective solution for communicating with remote or mobile devices. However, the reliability and speed of the communication may depend on the quality of the cellular signal.
What is the role of RTU in a DNP3 system?
Remote Terminal Units (RTU) in a DNP3 system act as outstations. They interface with field devices, collect data, execute control commands from the master station, and report data back to the master.
What is the difference between DNP3 and Profibus?
DNP3 and Profibus are both communication protocols, but they are used in different applications. DNP3 is primarily used in the electric power industry for SCADA systems, while Profibus is used in a variety of industrial control systems.
What is DNP3 object grouping?
DNP3 object grouping is a way to efficiently structure and transmit data in DNP3. Each object group represents a type of data (like binary inputs, analog inputs, or counters), and each object variation represents a specific format of that data.
How does DNP3 handle device failures?
DNP3 handles device failures by providing mechanisms for error detection, retrying failed messages, and switching to redundant communication paths. Additionally, the master station can monitor the health of outstations through periodic polling.
Can DNP3 be used in Internet of Things (IoT) applications?
While DNP3 is not typically used in IoT applications (where protocols like MQTT or CoAP are more common), there’s no technical reason why it couldn’t be used. However, the complexity of DNP3 and the lack of support for it in many IoT devices might make it less suitable than other protocols.
How is DNP3 used in the mining industry?
In the mining industry, DNP3 is used for communication between control systems and mining equipment like conveyors, crushers, and drilling rigs. DNP3 enables efficient and reliable transmission of real-time data and control commands, helping to monitor and control these assets.
How does DNP3 handle the loss of communication?
When a DNP3 communication link fails, the outstation can buffer event data until the communication is restored. Meanwhile, the master station can switch to a redundant communication path if available, or it can continue operation with reduced functionality.
What is the difference between DNP3 and EtherNet/IP?
DNP3 and EtherNet/IP are both communication protocols, but they serve different purposes. DNP3 is used primarily for SCADA systems in the electric power industry, while EtherNet/IP is used for a wide range of industrial automation applications.
What is the role of timestamps in DNP3?
Timestamps in DNP3 are used to record the exact time when an event occurs. This is important for accurately logging events and for coordinating control actions between multiple devices. DNP3 supports high-precision timestamps, synchronized across all devices in a system.
What is the role of a DNP3 master simulator?
A DNP3 master simulator is a software tool that emulates the behavior of a DNP3 master station. This can be useful for testing DNP3 outstations or for training purposes, without the need for actual hardware.
Can DNP3 be used over satellite communications?
Yes, DNP3 can be used over satellite communications. This can provide a solution for communicating with remote or hard-to-reach locations. However, the reliability and speed of the communication may be affected by factors like satellite signal strength and latency.
How does DNP3 support system integration?
DNP3 supports system integration by providing a standardized, flexible, and robust protocol for communication between different devices and systems. With DNP3, devices from different manufacturers can interoperate smoothly, and new devices or systems can be added without disrupting existing operations.
Can DNP3 be used in transportation systems?
While DNP3 is not typically used in transportation systems (where protocols like CAN bus or NMEA 2000 are more common), technically DNP3 could be used in such systems. However, it may not be the best choice due to its complexity and the lack of support for DNP3 in many transportation devices.
What is the role of the DNP3 control field?
The DNP3 control field is part of the DNP3 link layer header. It contains several bits that indicate the type of the DNP3 message (e.g., data, acknowledgment, link status), control the flow of messages, and manage the communication between the master and outstation.
Can DNP3 be used over wireless networks?
Yes, DNP3 can be used over wireless networks. This can provide a flexible and cost-effective solution for communicating with remote or mobile devices. However, the reliability and speed of the communication may depend on the quality of the wireless signal.
What is the difference between DNP3 and OPC UA?
DNP3 and OPC UA are both communication protocols, but they serve different purposes. DNP3 is used primarily for SCADA systems in the electric power industry, while OPC UA is used for a wide range of industrial automation applications and supports a broader set of features, such as complex data types and secure communication.
How does DNP3 support cybersecurity?
DNP3 supports cybersecurity through features like Secure Authentication, which provides a method for verifying the identity of devices in a DNP3 communication session. Also, DNP3 messages can be transported over secure network protocols like TLS to provide encryption, data integrity, and confidentiality.
How is DNP3 used in the water treatment industry?
In the water treatment industry, DNP3 is used for communication between control systems and various water treatment assets like pumps, valves, and sensors. DNP3 enables efficient and reliable transmission of real-time data and control commands, helping to monitor and control these assets.
Can DNP3 be used in home automation systems?
While DNP3 could technically be used in home automation systems, it’s not typically the protocol of choice for such applications. Protocols like Zigbee, Z-Wave, or even Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are generally more suitable for home automation due to their simplicity, lower cost, and support for wireless communication.
What is the role of the DNP3 destination and source addresses?
The DNP3 destination and source addresses are part of the DNP3 link layer header. They identify the sender and receiver of a DNP3 message, allowing multiple devices to share the same communication link. The destination address is the address of the device that should receive the message, and the source address is the address of the device that sent the message.
How does DNP3 support multi-drop communication?
DNP3 supports multi-drop communication by providing a mechanism for addressing multiple devices on the same communication link. Each device is assigned a unique address, and the DNP3 messages include destination and source addresses to direct the communication to the correct devices.
What is the role of a DNP3 protocol analyzer?
A DNP3 protocol analyzer is a software tool that can capture and decode DNP3 messages. This allows users to inspect the details of the DNP3 communication, troubleshoot issues, and verify the correct operation of DNP3 devices.
Can DNP3 be used in aerospace applications?
While DNP3 could technically be used in aerospace applications, it’s not typically the protocol of choice for such applications. Aerospace applications often have very specific requirements for reliability, safety, and performance, which are typically met by specialized protocols like ARINC 429 or MIL-STD-1553.
Read Next:














