HART-IP: HART Communication over Internet Protocol
HART-IP stands for Highway Addressable Remote Transducer over Internet Protocol. That might sound a bit complex, but it’s actually a rather clever way of simplifying communication in industrial environments. HART-IP is an adaptation of the HART Protocol (a widely accepted industrial communication standard) to use IP networks. What this means is that HART-IP allows industrial devices like sensors, actuators, controllers, and more, to communicate over the same type of network your computer or phone uses to browse the internet.
HART-IP
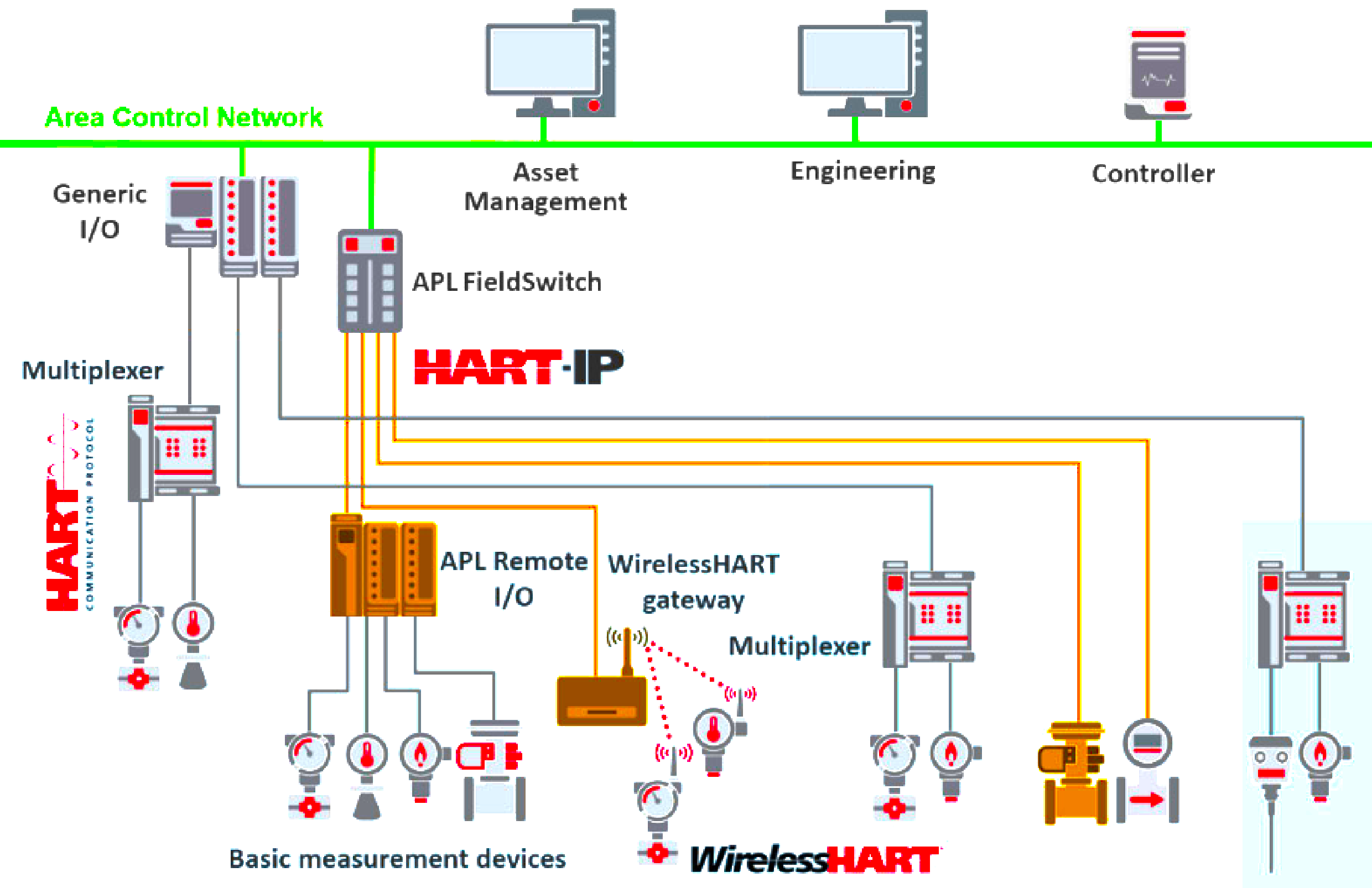
The beauty of HART-IP is that it enables easy, direct access to your HART-enabled devices from anywhere in the world, all over an IP network. This makes tasks like device configuration, system diagnostics, and data collection much simpler and more efficient. Plus, because it uses the internet, you don’t need any special cables or connectors to set it up!
What is HART-IP?
HART-IP is a protocol that provides a standard way to communicate with any HART-enabled device over an IP network. It facilitates the seamless integration of information from smart devices to higher-level systems and applications.
How does HART-IP differ from traditional HART?
Traditional HART communicates over a 4-20 mA analog signal, while HART-IP uses Internet Protocol for communication. This allows HART-IP to transmit more data, faster, and over larger distances compared to traditional HART.
What are the advantages of using HART-IP?
HART-IP offers several advantages including the ability to transmit large amounts of data quickly, long-distance communication, integration with standard network technology, and the capability of utilizing existing plant Ethernet infrastructure.
How does HART-IP support system integration?
By utilizing IP networks for communication, HART-IP can seamlessly integrate into system architectures, allowing process data to be easily accessible by asset management systems, process control systems, and other applications.
What kind of data can be transferred using HART-IP?
HART-IP can transmit a range of data including process variables, device status, diagnostic data, and device parameters. Essentially, it provides access to all device data.
What is a HART-IP Device Server?
A HART-IP Device Server is a device that connects HART devices to an IP network, allowing them to communicate using the HART-IP protocol.
What types of HART devices can be used with HART-IP?
Any HART-enabled device can potentially be used with HART-IP, provided that it is connected to the network via a HART-IP gateway or device server.
What is a HART-IP Adapter?
A HART-IP Adapter is a device that enables a HART device to communicate over an IP network using the HART-IP protocol.
What is a Gateway in HART-IP?
A Gateway in HART-IP is a device that connects a HART-IP network to other networks (like an Ethernet network), allowing for communication between HART-IP devices and systems on other networks.
Can multiple HART-IP devices share the same IP address?
No, each HART-IP device must have a unique IP address on the network to ensure accurate communication and data retrieval.
How does HART-IP support device diagnostics?
HART-IP provides access to all device data, including diagnostic data. This allows systems to monitor the health and performance of HART-IP devices and detect potential issues.
What tools are available for troubleshooting a HART-IP network?
Troubleshooting tools for a HART-IP network can include network monitoring tools, network analyzers, and HART communication software that supports HART-IP.
What is the HART-IP Application Layer?
The HART-IP Application Layer is the highest layer in the HART-IP protocol stack. It is responsible for the formatting and interpretation of data communicated between HART-IP devices and systems.
What is a HART-IP Multi-drop network?
A HART-IP Multi-drop network is a network configuration where multiple HART-IP devices are connected to the same physical network segment. This can be accomplished with the use of a HART-IP gateway or device server.
What types of physical media can be used for a HART-IP network?
HART-IP can be used with any physical media that support IP networking. This includes Ethernet cables, fiber optic cables, and wireless networks.
How does HART-IP improve device access and configuration?
HART-IP allows for direct access to all HART-enabled devices from any location with network access. This enables easy device configuration, troubleshooting, and data analysis without the need for handheld communicators or other additional tools.
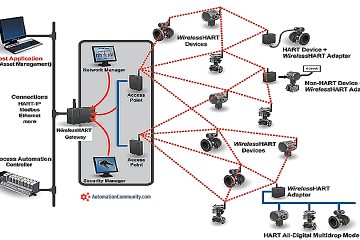
What is the role of WirelessHART in HART-IP networks?
WirelessHART provides a wireless communication method for HART-IP. It allows for the collection of data from devices in hard-to-reach locations or where traditional cabling isn’t feasible, enhancing the overall reach and flexibility of HART-IP networks.
What are the security considerations for HART-IP networks?
Like any network-based communication, HART-IP networks need to be secured to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity. Security measures can include firewalls, network segmentation, encryption, and authentication protocols.
What type of Ethernet infrastructure is required for HART-IP?
HART-IP can be used with standard Ethernet infrastructure, including switches, routers, and cables. It can also be used with existing plant Ethernet networks.
What is the relationship between HART-IP and FDI (Field Device Integration)?
Field Device Integration (FDI) is a standard that makes it easier to manage field devices during their entire lifecycle. HART-IP is one of the protocols supported by FDI, allowing HART-IP devices to be integrated and managed within the FDI framework.
What is a Device Description (DD) in HART-IP?
A Device Description (DD) is a software description of a HART-IP device’s data and functions that allows a host system to correctly interpret the device’s data and control the device’s operations.
What role does the HART Communication Foundation play in HART-IP?
The FieldComm Group, formerly known as the HART Communication Foundation, is responsible for the development, maintenance, and promotion of the HART-IP standard. It also ensures the interoperability of HART-IP devices by certifying them.
What are the benefits of using HART-IP in a Wireless HART network?
Using HART-IP in a WirelessHART network enables the wireless transmission of device data over IP networks. This makes it easier to access device data from any location with network access, reducing the need for onsite visits.
What is the transmission speed of HART-IP?
The transmission speed of HART-IP depends on the underlying network infrastructure. As HART-IP utilizes standard Ethernet and TCP/IP, it can potentially reach speeds up to 100 Mbps or higher depending on the Ethernet infrastructure.
Can HART-IP be used with both wired and wireless devices?
Yes, HART-IP can be used with both wired and wireless HART-enabled devices, allowing for flexible network configurations.
What network protocols are used by HART-IP?
HART-IP uses standard Internet and Ethernet protocols, including TCP/IP and UDP for data transmission.
What types of applications can benefit from HART-IP?
HART-IP can benefit a wide range of applications, particularly those requiring real-time access to field device data. These can include process control, asset management, preventive maintenance, and condition monitoring applications.
What is the difference between HART-IP and Modbus TCP?
Both HART-IP and Modbus TCP are protocols for communication over IP networks. HART-IP is designed specifically for HART devices and supports both analog and digital data, whereas Modbus TCP is a more general-purpose protocol that supports digital data only.
How can a HART-IP network be configured?
A HART-IP network can be configured using network configuration software that supports HART-IP. The configuration would typically involve setting up the network parameters and configuring the HART-IP devices on the network.
Can HART-IP and traditional HART devices coexist on the same network?
Yes, with the use of a HART-IP gateway, traditional HART devices can be incorporated into a HART-IP network. This allows for a gradual upgrade to HART-IP without replacing all existing devices.
What is the function of a HART-IP Server?
A HART-IP Server is a software application that provides a connection point for clients to access data from HART-IP devices. It handles client requests and communicates with the HART-IP devices to retrieve or update data.
What is the impact of network latency on a HART-IP network?
Network latency can affect the speed and efficiency of communication in a HART-IP network. However, because HART-IP utilizes standard Ethernet and IP protocols, techniques like network optimization and quality of service (QoS) can be used to manage and mitigate latency.
What factors can affect the reliability of a HART-IP network?
Factors that can affect the reliability of a HART-IP network include network infrastructure quality, network configuration, device compatibility, and environmental factors like electrical interference.
How can redundancy be achieved in a HART-IP network?
Redundancy in a HART-IP network can be achieved by using redundant network components (like switches and routers) and designing the network topology to have multiple paths between devices. This ensures that if one path fails, communication can continue via an alternate path.
How does HART-IP support real-time communication?
HART-IP utilizes TCP/IP and Ethernet protocols, which are capable of high-speed data transfer. This allows for near real-time communication between devices and systems.
What is a HART-IP Client?
A HART-IP Client is a software application or system that connects to a HART-IP Server to access data from HART-IP devices. Clients can include control systems, asset management systems, and custom software applications.
What are some of the challenges when implementing a HART-IP network?
Challenges can include ensuring network security, managing network traffic to prevent latency, ensuring device compatibility, and maintaining network infrastructure.
Can HART-IP be used over the Internet?
Technically, HART-IP can be used over the Internet. However, due to security concerns, it’s typically used over a private network or a secure virtual private network (VPN).
What is the impact of packet loss on a HART-IP network?
Packet loss can disrupt communication in a HART-IP network, potentially resulting in data loss or delays. However, because HART-IP utilizes TCP/IP, it has built-in mechanisms for detecting and retransmitting lost packets.
How is device compatibility ensured in a HART-IP network?
Device compatibility is ensured through the FieldComm Group’s product registration program, which verifies that devices correctly implement the HART-IP standard and are interoperable with other HART-IP devices.
How does HART-IP support device configuration?
HART-IP enables direct access to all device parameters from any location with network access. This allows systems or users to easily configure device settings without needing to visit the device location physically.
What’s the significance of HART-IP for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
HART-IP plays a crucial role in IIoT by providing a standard protocol for transmitting device data over IP networks. This enables easy integration of HART devices into IIoT systems and facilitates real-time access to device data for IIoT applications.
Can HART-IP be used in hazardous environments?
Yes, HART-IP can be used in hazardous environments, provided that the network infrastructure and devices meet the required safety standards for such environments.
What are some common use cases for HART-IP?
Common use cases for HART-IP include process control, asset management, condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
How does HART-IP enable predictive maintenance?
By providing real-time access to all device data, including diagnostic data, HART-IP enables systems to monitor device health and predict potential failures, facilitating predictive maintenance strategies.
What is a HART-IP Network Manager?
A HART-IP Network Manager is a software application or system that manages communication and data exchange within a HART-IP network.
What are some best practices for implementing a HART-IP network?
Best practices can include using certified HART-IP devices, designing the network topology for optimal performance and redundancy, implementing appropriate network security measures, and regularly monitoring and maintaining the network.
Can HART-IP networks be used in a redundant configuration?
Yes, HART-IP networks can be designed with redundancy to ensure continued operation in case of a network failure. This can involve redundant network paths, redundant network components, and possibly redundant HART-IP devices.
How can HART-IP facilitate digital transformation in industrial settings?
HART-IP can facilitate digital transformation by providing a standard method for integrating HART devices into digital systems and applications. This allows industrial plants to easily access and utilize device data for digital applications like real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
What is the maximum number of HART-IP devices that can be connected to a network?
The maximum number of HART-IP devices on a network primarily depends on the network’s IP address range and the network infrastructure capacity.
How does HART-IP handle communication errors?
HART-IP relies on the underlying TCP/IP protocol for error handling. TCP/IP has built-in error detection and retransmission capabilities to ensure reliable communication.
What types of data types are supported by HART-IP?
HART-IP supports a range of data types consistent with the HART protocol, including process variables, device parameters, device status information, and diagnostic data.
What is the role of HART-IP in asset management?
HART-IP enables real-time access to all data from HART devices, which can be used for comprehensive asset management. This includes monitoring device performance, planning maintenance activities, and diagnosing device issues.
How can HART-IP facilitate remote monitoring?
By utilizing IP networks, HART-IP allows for remote access to device data from any location with network access. This enables remote monitoring of device performance and status.
Can HART-IP be used with other industrial communication protocols?
Yes, HART-IP can coexist with other industrial communication protocols on the same network, provided that appropriate network infrastructure and gateways are in place.
What is the process to upgrade a traditional HART network to HART-IP?
Upgrading to HART-IP involves implementing an Ethernet infrastructure (if not already present), installing HART-IP gateways or device servers to connect HART devices to the IP network, and configuring the network and devices for HART-IP communication.
What are the considerations for power supply in a HART-IP network?
Power supply considerations depend on the specific devices and network infrastructure used. Some devices may receive power over Ethernet (PoE), while others may require separate power sources.
What kind of network topology can be used for a HART-IP network?
Any network topology supported by IP networks can be used for a HART-IP network, including star, ring, mesh, and tree topologies.
What is the role of the Universal Command set in HART-IP?
The Universal Command set is a set of standard commands defined by the HART protocol. These commands are used for basic communication with HART devices, including reading and writing device variables and accessing device status information. They are supported by all HART and HART-IP devices.
What are the different data formats used in HART-IP?
HART-IP supports multiple data formats including integer, floating-point, and character string formats, allowing it to handle a wide variety of data types.
Can HART-IP networks be secured against cyber threats?
Yes, like any other IP network, HART-IP networks can and should be secured using standard network security measures such as firewalls, network segmentation, secure authentication methods, encryption, and regular network monitoring.
What are the differences between HART-IP and HART-7?
HART-7 is a version of the HART protocol, while HART-IP is a way of implementing the HART protocol over IP networks. Thus, HART-IP incorporates all the features of HART-7, but adds the ability to transmit data over Ethernet networks using the TCP/IP protocol stack.
How is fault detection managed in a HART-IP network?
Fault detection in a HART-IP network is typically managed through network monitoring tools and the built-in diagnostic capabilities of HART-IP devices. Network monitoring tools can detect network issues like connectivity problems or high latency, while device diagnostics can identify device-specific issues.
How can you test a HART-IP device?
Testing a HART-IP device can involve checking network connectivity, verifying device communication with a HART-IP client or server, and checking the device’s functionality and data using a HART communication tool that supports HART-IP.
What is the significance of the HART-IP Device Specification?
The HART-IP Device Specification provides a detailed description of a device’s data and functions, including its command set, device variables, and device functions. This specification is used by HART-IP clients and servers to correctly interpret and use the device’s data.
What is Device Revision in HART-IP?
The Device Revision is a number assigned by the device manufacturer that indicates the version of the device’s firmware or software. It helps to identify the device’s capabilities and compatibility with different versions of the HART-IP protocol.
How does HART-IP support the interoperability of devices from different manufacturers?
HART-IP supports interoperability by adhering to a standardized protocol. All HART-IP devices are required to comply with the HART-IP standard, ensuring that they can communicate with any HART-IP client or server, regardless of the manufacturer.
What kind of devices typically serve as HART-IP Clients?
HART-IP clients can be any system or software application that needs to access data from HART-IP devices. This can include control systems, asset management systems, data acquisition systems, and custom software applications.
How are software updates handled in a HART-IP network?
Software updates in a HART-IP network depend on the specific devices and systems used. Some devices may support remote firmware updates over the network, while others may require manual updating.
What role does the FieldComm Group play in the development and maintenance of HART-IP?
The FieldComm Group is responsible for the development, maintenance, and promotion of the HART-IP protocol. They provide specifications, technical resources, and product certification programs to ensure the interoperability and quality of HART-IP devices and systems.
How can HART-IP be integrated with an existing control system?
Integration of HART-IP with an existing control system generally involves connecting the control system to the HART-IP network, configuring the control system to communicate with HART-IP devices, and mapping the device data to the control system’s data model.
What is HART-IP Device Description (DD)?
A HART-IP Device Description (DD) is a software file that provides a detailed description of a device’s capabilities and how to access its data. The DD is used by HART-IP clients and servers to correctly interpret and use the device’s data.
How is data integrity ensured in a HART-IP network?
Data integrity in a HART-IP network is ensured through the built-in error detection and correction mechanisms of the TCP/IP protocol. In addition, device diagnostics and network monitoring tools can be used to identify and resolve data integrity issues.
What is Burst Mode in HART-IP?
Burst Mode is a feature of the HART protocol where a device continuously broadcasts a set of data without waiting for a specific request. This feature is supported by HART-IP and can be used for real-time monitoring and control applications.
What are the typical data rates for a HART-IP network?
The data rates for a HART-IP network depend on the underlying Ethernet network. Standard Ethernet networks can support data rates up to 100 Mbps or 1 Gbps, while advanced networks can support higher data rates.
What is a Device Variable in HART-IP?
A Device Variable is a specific piece of data provided by a HART-IP device, such as a process variable, device parameter, or diagnostic data. Device Variables are defined in the device’s Device Description and can be accessed by HART-IP clients and servers.
What types of applications can benefit from using HART-IP?
Applications that can benefit from HART-IP include process control, asset management, predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, condition-based monitoring, process optimization, and IIoT applications.
What are Dynamic Variables in HART-IP?
Dynamic Variables in the context of HART and HART-IP are sets of variables that a device can continuously update and broadcast. This typically includes the device’s primary process variable and three other variables that can be chosen based on the needs of the application.
How can a HART-IP network be troubleshot?
Troubleshooting a HART-IP network involves diagnosing network connectivity issues using network monitoring tools, checking device communication with a HART-IP client or server, and diagnosing device functionality using a HART communication tool.
What is the role of a Device Server in a HART-IP network?
A Device Server in a HART-IP network is a hardware device that connects one or more HART devices to the IP network, enabling communication between the HART devices and HART-IP clients.
What are some limitations of HART-IP?
Some potential limitations of HART-IP could include the need for an Ethernet infrastructure, potential issues with network latency for real-time applications, and the need for appropriate network security measures due to the use of IP networks.
Can HART-IP support mobile devices?
Yes, HART-IP can support mobile devices provided the devices have the necessary network connectivity and software capabilities to communicate with the HART-IP network.
What does it mean for a HART-IP device to be “multidrop”?
A “multidrop” HART-IP device is one that can share a single network connection with multiple other HART devices. This feature, which is common in traditional HART networks, can also be supported in HART-IP networks using appropriate network infrastructure and device servers.
What type of security measures should be implemented in a HART-IP network?
Security measures for a HART-IP network should include firewall rules to control network traffic, secure authentication methods to prevent unauthorized access, network segmentation to limit the impact of potential security breaches, encryption to protect data in transit, and regular network monitoring to detect potential security threats.
What type of documentation should be maintained for a HART-IP network?
Documentation for a HART-IP network should include network diagrams, device specifications and configurations, IP address assignments, network security policies, and records of network maintenance activities.
What factors should be considered when designing a HART-IP network?
Designing a HART-IP network involves considering factors such as the number and types of devices to be connected, the required data rates and latency, the network topology, the available network infrastructure, the need for network redundancy, and the requirements for network security.
How does HART-IP support device diagnostics?
HART-IP supports device diagnostics by providing access to a wide range of device data, including status information and diagnostic data. This data can be used by systems or users to monitor device health and performance, diagnose issues, and plan maintenance activities.
What are some common issues that might occur in a HART-IP network and how could they be resolved?
Common issues could include network connectivity problems, device communication errors, and data integrity issues. These can often be resolved by checking network connections, testing device communication with a HART-IP client or server, and using network monitoring tools to identify and resolve network issues.
When encountering communication issues with a HART-IP device, what would be your first steps to diagnose the problem?
The first steps would include checking the network connection to the device, verifying the device’s IP address and network settings, and testing communication with the device using a HART-IP client or communication tool.
What tools might you use to monitor network traffic in a HART-IP network?
Tools for monitoring network traffic in a HART-IP network could include network monitoring software, network analyzers, and packet sniffers. These can provide information about network usage, data rates, error rates, and other important network parameters.
How would you go about resolving a data integrity issue in a HART-IP network?
Resolving a data integrity issue could involve checking the network for errors or interference, testing device communication to ensure that data is being correctly transmitted and received, and checking the device’s diagnostics to identify any potential device issues.
If a HART-IP device is not responding, what could be the potential reasons and how would you troubleshoot it?
Potential reasons could include network connectivity issues, incorrect device settings, or device faults. Troubleshooting could involve checking the network connection, verifying the device’s settings and status, and possibly resetting or power-cycling the device.
How would you go about identifying and resolving network latency issues in a HART-IP network?
Identifying network latency issues would typically involve using network monitoring tools to measure latency and identify any patterns or issues. Resolving these issues might involve optimizing network configurations, increasing network bandwidth, or possibly redesigning the network for better performance.
If a HART-IP client is unable to connect to a HART-IP device, what would be your troubleshooting steps?
Troubleshooting steps could include checking the network connection between the client and the device, verifying the client’s network settings and HART-IP settings, checking the device’s settings and status, and possibly testing the device with a different HART-IP client to isolate the issue.
If a HART-IP network is experiencing high error rates, what could be the causes and how would you address them?
High error rates could be caused by network congestion, interference, poor network quality, or device issues. Addressing these issues could involve optimizing network configurations, increasing network bandwidth, troubleshooting individual devices, or possibly redesigning the network for better reliability.
What considerations should be made when troubleshooting a HART-IP network that’s used in a hazardous environment?
When troubleshooting a HART-IP network in a hazardous environment, safety must be the top priority. This might include adhering to safety procedures, using intrinsically safe tools, and possibly coordinating with safety personnel or shutdown processes.
How would you go about verifying the integrity of the HART-IP data received from a field device?
Verifying the integrity of HART-IP data could involve comparing the received data with expected values or ranges, checking the device’s status and diagnostics for any reported issues, and possibly verifying the data with a separate tool or method.
Read Next: