Exploring Wireless HART: Objective Questions with Detailed Explanations
Discover Wireless HART technology with clear explanations of objective questions. This detailed guide provides easy-to-understand insights, making it perfect for anyone interested in learning about industrial wireless communication protocols.
Which frequency band does Wireless HART operate in?
A. 5 GHz
B. 2.4 GHz
C. 900 MHz
D. 1.8 GHz
Answer: B
Explanation: Wireless HART operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, which is a globally available frequency band for industrial, scientific, and medical uses.
What type of network topology is used by Wireless HART?
A. Star
B. Ring
C. Mesh
D. Bus
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART uses a mesh network topology, which allows each device to communicate with multiple other devices, providing redundant communication paths and increasing network reliability.
What is the typical battery life of a Wireless HART device under normal operating conditions?
A. A few months
B. 1-2 years
C. 5-10 years
D. Over 20 years
Answer: C
Explanation: While the battery life can vary based on the device’s power consumption and operating conditions, a typical battery life for a Wireless HART device under normal conditions is around 5-10 years.
Which of the following security measures does Wireless HART use?
A. Encryption
B. Key management
C. Message integrity checks
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation: Wireless HART uses several security measures, including encryption of data, key management to ensure only authorized devices join the network, and message integrity checks to verify that data has not been tampered with.
Can a device be part of two Wireless HART networks simultaneously?
A. Yes, always
B. Yes, but only under certain conditions
C. No, never
D. It depends on the device manufacturer
Answer: C
Explanation: Typically, a device can only be part of one Wireless HART network at a time due to the unique network ID and join key requirements.
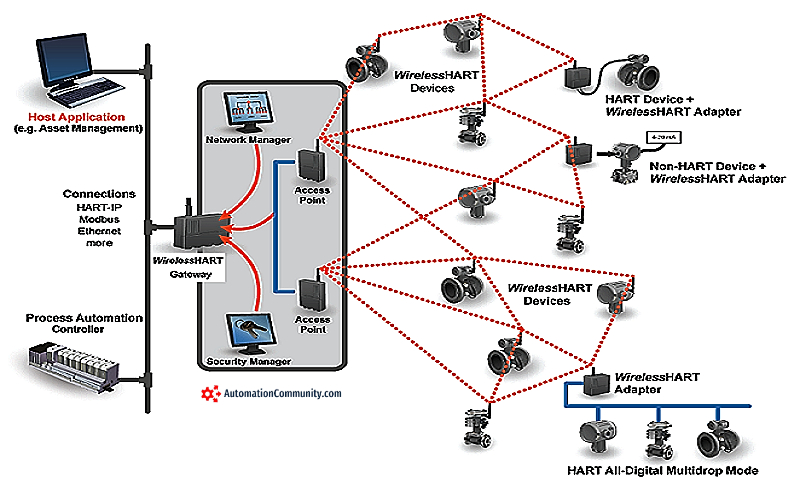
What does a Wireless HART Gateway do?
A. Converts wired HART signals to Wireless HART
B. Connects the Wireless HART network to a control system or network
C. Powers the Wireless HART devices
D. All of the above
Answer: B
Explanation: The primary function of a Wireless HART Gateway is to serve as the interface between the Wireless HART network and a control system or network, allowing data to be transferred to and from the devices on the Wireless HART network.
Which of the following is NOT a feature of Wireless HART?
A. Real-time control
B. Backward compatibility with wired HART devices
C. Bi-directional communication
D. Use of a proprietary frequency band
Answer: D
Explanation: Wireless HART uses the 2.4 GHz ISM band, which is a globally available and non-proprietary frequency band.
What type of encryption does Wireless HART use?
A. AES-128
B. RSA
C. DES
D. Blowfish
Answer: A
Explanation: Wireless HART uses AES-128 encryption, a strong and commonly used encryption standard.
Which of the following is a primary advantage of Wireless HART over traditional wired HART?
A. Lower installation cost
B. Higher data rates
C. Greater signal range
D. More devices per network
Answer: A
Explanation: One of the main advantages of Wireless HART is the significantly lower installation cost compared to traditional wired HART, as wireless networks don’t require costly and time-consuming cable runs.
How does a Wireless HART network manage data collisions?
A. By using a collision detection mechanism
B. By using a collision prevention mechanism
C. It doesn’t handle data collisions
D. By increasing the transmission power
Answer: B
Explanation: Wireless HART minimizes data collisions through careful scheduling of communications by the network manager and time synchronization among devices, essentially preventing data collisions.
Which organization is responsible for the standardization of Wireless HART?
A. IEEE
B. IETF
C. FieldComm Group
D. ISO
Answer: C
Explanation: The FieldComm Group, formerly known as the HART Communication Foundation, is the organization responsible for the standardization of Wireless HART.
What is the maximum transmission distance in a Wireless HART network under ideal conditions?
A. 30 meters
B. 100 meters
C. 225 meters
D. 500 meters
Answer: C
Explanation: Under ideal conditions, the maximum transmission distance in a Wireless HART network is approximately 225 meters.
Which technology does Wireless HART use to minimize the impact of radio frequency interference?
A. Frequency hopping
B. Beamforming
C. MIMO
D. CDMA
Answer: A
Explanation: Wireless HART uses frequency hopping, a technique that changes the communication frequency at regular intervals, to minimize the impact of radio frequency interference.
Can Wireless HART devices be used in hazardous locations?
A. Yes, but only with special protective casings
B. Yes, many Wireless HART devices are designed for use in hazardous locations
C. No, Wireless HART devices should not be used in hazardous locations
D. It depends on the local regulations
Answer: B
Explanation: Many Wireless HART devices are designed to be safe for use in hazardous locations. However, it’s important to check the specific certifications and ratings of the devices.
Which of the following is NOT a common use case for Wireless HART?
A. Remote monitoring
B. Asset management
C. High-speed data streaming
D. Process automation
Answer: C
Explanation: While Wireless HART is capable of many things, it is not typically used for high-speed data streaming due to its low data rate.
What is the role of a Network Manager in a Wireless HART network?
A. To schedule communication between devices
B. To facilitate frequency hopping
C. To encrypt and decrypt data
D. All of the above
Answer: A
Explanation: The Network Manager’s main role in a Wireless HART network is to schedule communication between devices and manage the routing of data.
How does a Wireless HART device join a network?
A. It automatically joins any nearby network
B. It must be manually configured with the network ID and join key
C. It sends a join request to the Network Manager
D. Both B and C
Answer: D
Explanation: To join a Wireless HART network, a device needs to be configured with the correct network ID and join key, and then it sends a join request to the Network Manager.
What type of antenna is typically used in Wireless HART devices?
A. Parabolic
B. Dipole
C. Yagi
D. Monopole
Answer: D
Explanation: Most Wireless HART devices use monopole antennas, which are compact and offer suitable performance for most applications.
What is the data rate of a Wireless HART network?
A. 250 kbps
B. 1 Mbps
C. 54 Mbps
D. 100 Mbps
Answer: A
Explanation: Wireless HART operates at a data rate of 250 kbps, which is sufficient for most industrial monitoring and control applications.
How many channels does Wireless HART use in the 2.4 GHz band?
A. 16
B. 10
C. 6
D. 3
Answer: A
Explanation: Wireless HART operates across 16 channels in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, providing multiple pathways for data transmission and aiding in the avoidance of interference.
What role does time synchronization play in a Wireless HART network?
A. It ensures devices communicate at the correct data rate
B. It reduces data collisions by coordinating communication times
C. It increases the network range by synchronizing transmission power
D. It’s not crucial in a Wireless HART network
Answer: B
Explanation: Time synchronization in a Wireless HART network aids in avoiding data collisions by ensuring devices communicate at scheduled times.
In which version of the HART protocol was Wireless HART introduced?
A. HART 5
B. HART 6
C. HART 7
D. HART 8
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART was introduced in the seventh version of the HART protocol, also known as HART 7.
Is it possible to upgrade a wired HART device to a Wireless HART device?
A. Yes, always
B. Yes, but only with certain devices
C. No, it’s not possible
D. It depends on the device manufacturer
Answer: B
Explanation: Some wired HART devices can be upgraded to Wireless HART with an adapter, but this may not be possible or practical for all devices.
What is a key benefit of the mesh network topology used by Wireless HART?
A. Higher data rates
B. More devices per network
C. Redundant communication paths
D. Greater transmission power
Answer: C
Explanation: The mesh network topology used by Wireless HART provides redundant communication paths, enhancing network reliability as there are multiple potential routes for data transmission.
How are lost or corrupted data packets handled in a Wireless HART network?
A. They are ignored
B. They are retransmitted
C. They are corrected using error correction codes
D. The network switches to a different frequency channel
Answer: B
Explanation: In a Wireless HART network, lost or corrupted data packets are typically retransmitted to ensure reliable data communication.
How are Wireless HART devices powered?
A. By a mains power supply
B. By Power over Ethernet (PoE)
C. By batteries
D. By solar power
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART devices are typically powered by batteries, allowing them to be installed in locations where a mains power supply may not be available.
Can Wireless HART devices communicate directly with each other?
A. Yes, always
B. Yes, but only under certain conditions
C. No, never
D. It depends on the network configuration
Answer: A
Explanation: Wireless HART devices can communicate directly with each other in a mesh network configuration, allowing data to be routed through multiple devices if necessary.
What is the primary role of a Wireless HART Gateway?
A. To manage the network schedule
B. To encrypt and decrypt data
C. To interface with a control system or network
D. To power the Wireless HART devices
Answer: C
Explanation: The primary role of a Wireless HART Gateway is to serve as an interface between the Wireless HART network and a control system or other network.
What happens if a Wireless HART device fails or is removed from the network?
A. The entire network stops functioning
B. Other devices can no longer communicate
C. The network automatically reconfigures to bypass the failed device
D. The failed device must be replaced immediately
Answer: C
Explanation: Due to the mesh network topology used by Wireless HART, if a device fails or is removed, the network can automatically reconfigure itself to bypass the failed device and maintain communication.
Which Wireless HART device typically holds the Network Manager role?
A. Field device
B. Gateway
C. Adapter
D. Router
Answer: B
Explanation: The Wireless HART Gateway typically fulfills the role of the Network Manager, responsible for managing the network schedule and routing.
Which error detection mechanism does Wireless HART use?
A. Parity Check
B. Checksum
C. Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
D. Hamming Code
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART uses CRC, a powerful error detection mechanism, to ensure data integrity.
How many neighbors can a Wireless HART device have in a network?
A. Up to 5
B. Up to 10
C. Up to 16
D. Up to 32
Answer: D
Explanation: A Wireless HART device can have up to 32 neighbors in a network, enhancing the robustness and flexibility of data transmission routes.
What kind of information is contained in a Wireless HART join key?
A. Network ID
B. Device address
C. Encryption key
D. All of the above
Answer: C
Explanation: The join key in Wireless HART contains an encryption key which is used to secure the initial communication between a device and the network manager during the joining process.
What type of modulation does Wireless HART use?
A. Frequency Modulation (FM)
B. Phase-Shift Keying (PSK)
C. Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying (QPSK)
D. Amplitude Modulation (AM)
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART uses QPSK, a type of phase modulation that is suitable for high-speed data transmission in environments with potential interference.
What is the purpose of Blacklisting in a Wireless HART network?
A. To exclude certain devices from the network
B. To prioritize data transmission for certain devices
C. To reserve bandwidth for future devices
D. To prevent certain devices from communicating with the Gateway
Answer: A
Explanation: Blacklisting in a Wireless HART network allows for certain devices to be excluded from the network for various reasons, including security concerns or network management.
Which type of application is Wireless HART NOT well-suited for?
A. Monitoring temperature in a large industrial facility
B. Streaming high-definition video
C. Tracking asset location within a factory
D. Detecting leaks in a pipeline system
Answer: B
Explanation: Due to its relatively low data rate, Wireless HART is not suitable for applications that require high-bandwidth data streaming, such as high-definition video.
In a Wireless HART network, which role is NOT typically performed by a Gateway?
A. Managing network schedule
B. Routing data packets
C. Providing power to the field devices
D. Acting as a bridge to the control system
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART Gateways do not provide power to field devices. The field devices in a Wireless HART network are typically battery-powered.
What does TDMA stand for in the context of Wireless HART?
A. Time Division Multiple Access
B. Transmit Data Multiple Access
C. Time Division Modulated Antenna
D. Transmit Data Modulated Antenna
Answer: A
Explanation: In the context of Wireless HART, TDMA stands for Time Division Multiple Access, a method of time-based multiplexing that allows multiple devices to share the same frequency channel.
What is the typical lifespan of the battery in a Wireless HART device?
A. Up to 1 year
B. Up to 2 years
C. Up to 5 years
D. Up to 10 years
Answer: D
Explanation: The batteries in Wireless HART devices are typically designed to last up to 10 years, reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
Which of the following statements about Wireless HART security is true?
A. The protocol doesn’t include built-in security features
B. All data transmissions are encrypted
C. Only sensitive data transmissions are encrypted
D. It relies solely on network-level security measures
Answer: B
Explanation: Wireless HART incorporates strong security measures, including encryption of all data transmissions, to protect against unauthorized access and interference.
What is the purpose of a Router in a Wireless HART network?
A. To provide power to the field devices
B. To act as a bridge to the control system
C. To forward data packets from one device to another
D. To manage the network schedule
Answer: C
Explanation: In a Wireless HART network, a Router’s primary role is to forward data packets from one device to another, facilitating communication within the mesh network.
Which of these statements about Wireless HART is FALSE?
A. It operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band
B. It is an open protocol developed by the FieldComm Group
C. It is only suitable for small-scale applications with less than 10 devices
D. It uses a mesh network topology
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART is designed for industrial applications and can support large networks with many devices. The protocol is not limited to small-scale applications with less than 10 devices.
What happens when a device receives multiple copies of the same packet in a Wireless HART network?
A. It responds to each copy
B. It discards all copies
C. It keeps the first copy and discards the rest
D. It forwards all copies to the Gateway
Answer: C
Explanation: If a device in a Wireless HART network receives multiple copies of the same packet, it will keep the first copy and discard the rest, reducing unnecessary traffic on the network.
What is the maximum number of devices that a Wireless HART network can support?
A. 100
B. 256
C. 500
D. 1000
Answer: B
Explanation: A Wireless HART network can support up to 256 devices, including the Gateway, field devices, routers, and other components.
What does DSSS stand for in the context of Wireless HART?
A. Dual Sideband Spectrum Spreading
B. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
C. Direct Signal Spectrum Sharing
D. Dual Sequence Signal Sharing
Answer: B
Explanation: In the context of Wireless HART, DSSS stands for Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum, a modulation technique used to spread the signal across a wider frequency band for increased reliability and resistance to interference.
In which year was the Wireless HART specification first released?
A. 2005
B. 2007
C. 2010
D. 2012
Answer: B
Explanation: The Wireless HART specification was first released in 2007 by the HART Communication Foundation, now known as the FieldComm Group.
How often does a Wireless HART device need to synchronize its clock with the Gateway?
A. Every second
B. Every minute
C. Every hour
D. Every day
Answer: A
Explanation: A Wireless HART device needs to synchronize its clock with the Gateway every second to maintain accurate timing for TDMA communication.
Which of these is a major disadvantage of Wireless HART?
A. Limited device compatibility
B. High power consumption
C. Vulnerability to interference
D. High cost of devices
Answer: C
Explanation: Like all wireless technologies, Wireless HART can be vulnerable to interference from other electronic devices and physical obstructions, which can potentially disrupt network communication.
How does Wireless HART handle network congestion?
A. By reducing the data rate
B. By increasing the transmission power
C. By changing to a different frequency channel
D. By throttling back the transmission of non-essential data
Answer: D
Explanation: Wireless HART can manage network congestion by throttling back the transmission of non-essential data, prioritizing critical communication.
Which of the following is NOT an application of Wireless HART?
A. Remote equipment monitoring
B. Real-time video streaming
C. Process automation
D. Asset tracking
Answer: B
Explanation: Wireless HART is not designed to handle applications requiring high data throughput, such as real-time video streaming.
Which field device power option is typically NOT available for Wireless HART devices?
A. Battery
B. Mains power
C. Solar power
D. Wind power
Answer: D
Explanation: While it’s technically possible, it’s typically impractical to power Wireless HART devices using wind power due to the size and location of these devices.
What is the maximum payload size for a Wireless HART message?
A. 128 bytes
B. 256 bytes
C. 512 bytes
D. 1024 bytes
Answer: A
Explanation: The maximum payload size for a Wireless HART message is 128 bytes. This is sufficient for most industrial automation data.
How many channels are available for communication in a Wireless HART network?
A. 8
B. 12
C. 16
D. 20
Answer: C
Explanation: A Wireless HART network has 16 channels available for communication. This helps to mitigate the effects of interference and allows for multiple devices to communicate simultaneously.
What is the role of a Superframe in Wireless HART?
A. It is used to schedule network-wide broadcasts
B. It is a data packet that contains all network traffic
C. It is used to group together a sequence of communication slots
D. It is used to coordinate the network routing
Answer: C
Explanation: A Superframe in Wireless HART is used to group together a sequence of communication slots, scheduling recurring communication events and allowing for efficient network operation.
Which statement about the Wireless HART network topology is FALSE?
A. It uses a mesh network topology
B. All devices can communicate directly with the Gateway
C. Devices can route messages through other devices
D. If a device fails, the network can reconfigure itself to maintain communication
Answer: B
Explanation: In a Wireless HART network, not all devices can directly communicate with the Gateway. Some devices may communicate indirectly with the Gateway by routing messages through other devices.
What is the typical update rate for a Wireless HART device?
A. Every second
B. Every minute
C. Every hour
D. Every day
Answer: B
Explanation: A typical update rate for a Wireless HART device is every minute. However, this rate can be adjusted based on the requirements of the application.
How does a Wireless HART device join a network?
A. It broadcasts a request to join, and any device can grant the request
B. It must be manually connected to the Gateway
C. It sends a request to join to the Gateway, which then grants the request
D. It automatically joins the network as soon as it is powered on
Answer: C
Explanation: A Wireless HART device sends a request to join the network to the Gateway. If the join key matches, the Gateway grants the request and the device becomes part of the network.
In the context of Wireless HART, what does RSSI stand for?
A. Relative Signal Strength Indicator
B. Received Signal Strength Indicator
C. Remote Signal Strength Index
D. Received Signal Strength Index
Answer: B
Explanation: In the context of Wireless HART, RSSI stands for Received Signal Strength Indicator. It is used to measure the power level being received by the antenna.
What technology does Wireless HART use to mitigate the effects of interference?
A. Frequency hopping
B. Signal amplification
C. Error correction
D. Channel bonding
Answer: A
Explanation: Wireless HART uses frequency hopping to mitigate the effects of interference. This means that the devices continuously change their communication frequency according to a known pattern.
What is the Network ID in a Wireless HART network?
A. It is the IP address of the Gateway
B. It is a unique identifier for each device
C. It is a unique identifier for the entire network
D. It is the MAC address of the Gateway
Answer: C
Explanation: The Network ID in a Wireless HART network is a unique identifier for the entire network. It is used to distinguish between different Wireless HART networks operating in the same area.
Which of the following is a mandatory device role in a Wireless HART network?
A. Router
B. Gateway
C. Field device
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation: All of these roles – Router, Gateway, and Field device – are mandatory in a Wireless HART network. Each plays a crucial role in network operation and communication.
What does the term “Blacklisting” mean in the context of a Wireless HART network?
A. It refers to blocking certain frequencies from being used
B. It refers to blocking certain devices from joining the network
C. It refers to blocking certain data packets from being transmitted
D. It refers to blocking certain channels from being used
Answer: A
Explanation: In the context of a Wireless HART network, “Blacklisting” refers to blocking certain frequencies from being used. This is done to avoid frequencies that are known to be a source of interference.
In a Wireless HART network, what happens when a device fails or becomes unreachable?
A. The entire network stops functioning
B. The failed device is automatically replaced by another device
C. The network reconfigures itself to bypass the failed device
D. The Gateway sends an alert, but the network continues to operate normally
Answer: C
Explanation: In a Wireless HART network, if a device fails or becomes unreachable, the network can reconfigure itself to bypass the failed device. This self-healing capability is a key feature of Wireless HART’s mesh network topology.
Which of the following is NOT a layer in the Wireless HART protocol stack?
A. Physical layer
B. Network layer
C. Data link layer
D. Application layer
Answer: D
Explanation: The Wireless HART protocol stack includes the Physical, Network, and Data link layers, but it does not define an Application layer. The Application layer is typically defined by the specific use case or software.
What happens if two devices in a Wireless HART network try to transmit on the same frequency at the same time?
A. The stronger signal overpowers the weaker one
B. Both transmissions fail
C. The devices automatically switch to a different frequency
D. The transmissions are combined and sent together
Answer: B
Explanation: If two devices in a Wireless HART network try to transmit on the same frequency at the same time, both transmissions would likely fail due to collision. This is why the protocol uses TDMA for time-based communication scheduling to avoid such scenarios.
Which of the following standards is Wireless HART based on?
A. IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi)
B. IEEE 802.15.4 (Zigbee)
C. IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet)
D. IEEE 802.16 (WiMAX)
Answer: B
Explanation: Wireless HART is based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, which is also the foundation for other low-rate wireless personal area network (LR-WPAN) technologies like Zigbee.
What does TDMA stand for in the context of Wireless HART?
A. Time Division Multiple Access
B. Time Delay Multiple Access
C. Time Division Multiplexing Access
D. Total Division Multiple Access
Answer: A
Explanation: In the context of Wireless HART, TDMA stands for Time Division Multiple Access, a method of enabling multiple devices to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots.
Which of these wireless protocols operates in the same frequency range as Wireless HART?
A. Bluetooth
B. LTE
C. Wi-Fi
D. Zigbee
Answer: D
Explanation: Both Wireless HART and Zigbee operate in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Therefore, they share the same frequency range.
How does Wireless HART handle network security?
A. It uses WEP encryption
B. It uses WPA2 encryption
C. It uses AES encryption
D. It doesn’t provide network security
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART uses AES encryption for network security. It helps to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data transmitted over the network.
What is the function of a Network Manager in a Wireless HART network?
A. It manages the network topology
B. It manages the frequency hopping schedule
C. It manages the encryption keys
D. All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation: A Network Manager in a Wireless HART network has multiple functions. It manages the network topology, the frequency hopping schedule, and the encryption keys, among other tasks.
Which part of the Wireless HART message contains the measurement data?
A. Header
B. Payload
C. Trailer
D. Checksum
Answer: B
Explanation: The payload part of a Wireless HART message contains the measurement data. The rest of the message is used for addressing, error checking, and other network-related information.
In a Wireless HART network, what is the maximum number of hops a message can take from source to destination?
A. 5
B. 10
C. 15
D. There is no maximum
Answer: C
Explanation: In a Wireless HART network, a message can take a maximum of 15 hops from the source to the destination. This is to ensure network efficiency and timely data delivery.
What kind of antenna does a typical Wireless HART device use?
A. Dipole antenna
B. Monopole antenna
C. Yagi antenna
D. Parabolic antenna
Answer: A
Explanation: A typical Wireless HART device uses a dipole antenna. This type of antenna is compact and efficient, making it suitable for use in small, low-power devices.
What happens when a new device is added to a Wireless HART network?
A. The Network Manager automatically detects and configures the device
B. The device must be manually configured by a network administrator
C. The network must be shut down and restarted to recognize the new device
D. The Gateway assigns the device a network address and join key
Answer: A
Explanation: When a new device is added to a Wireless HART network, the Network Manager automatically detects the device and configures it for the network.
What is the purpose of the join key in a Wireless HART network?
A. It is used to encrypt the network traffic
B. It is used to authenticate devices joining the network
C. It is used to identify the network
D. It is used to schedule the network traffic
Answer: B
Explanation: In a Wireless HART network, the join key is used to authenticate devices that are joining the network. Only devices with the correct join key are allowed to join the network.
Which of the following best describes the network topology of Wireless HART?
A. Star
B. Ring
C. Bus
D. Mesh
Answer: D
Explanation: Wireless HART uses a mesh network topology. In this topology, each device can communicate with multiple other devices, providing multiple paths for data transmission and increasing the reliability and resilience of the network.
In terms of network coverage, how does a Wireless HART network expand its reach?
A. By adding more gateways
B. By using signal boosters
C. By adding more devices
D. By using larger antennas
Answer: C
Explanation: A Wireless HART network expands its coverage by adding more devices. Each device in the network can act as a relay point, forwarding messages from other devices. This extends the network’s range beyond the direct communication range of the Gateway.
In the context of Wireless HART, what does DSSS stand for?
A. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
B. Digital Signal Spread Spectrum
C. Direct Signal Spread Spectrum
D. Digital Sequence Spread Spectrum
Answer: A
Explanation: In the context of Wireless HART, DSSS stands for Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum, a method used to spread the transmitted signal over a wide frequency band. This increases the signal’s resistance to interference and noise.
What is the main disadvantage of a Wireless HART network?
A. High power consumption
B. Limited range
C. High cost
D. Limited data rate
Answer: D
Explanation: The main disadvantage of a Wireless HART network is its limited data rate. The standard supports data rates of up to 250 kbps, which is adequate for many industrial applications, but may be insufficient for high data rate applications.
How does Wireless HART ensure reliable data transmission in an industrial environment with high levels of RF interference?
A. By using error correction codes
B. By using high power transmissions
C. By using frequency hopping
D. Both A and C
Answer: D
Explanation: Wireless HART ensures reliable data transmission in environments with high levels of RF interference by using error correction codes and frequency hopping. Error correction codes help to correct errors that occur during data transmission, while frequency hopping reduces the impact of interference by rapidly switching between different frequency channels.
What is the function of a Router in a Wireless HART network?
A. To manage the network topology
B. To forward messages between devices
C. To connect the network to the internet
D. To manage the network’s frequency hopping schedule
Answer: B
Explanation: In a Wireless HART network, a Router’s main function is to forward messages between devices. This enables devices that are out of direct communication range of each other to communicate via intermediate devices.
Which Wireless HART device role can join the network but not relay messages for other devices?
A. Router
B. Gateway
C. Handheld
D. Adapter
Answer: C
Explanation: Handheld devices in a Wireless HART network can join the network but cannot relay messages for other devices. This is because they are typically used for network configuration, maintenance, or troubleshooting, and do not participate in the regular network communication.
How does a Wireless HART network minimize the risk of message collisions?
A. By using CSMA/CA
B. By using TDMA
C. By using FDMA
D. By using CDMA
Answer: B
Explanation: Wireless HART uses Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) to minimize the risk of message collisions. With TDMA, each device in the network is assigned a specific time slot in which it can transmit, preventing simultaneous transmissions and thus avoiding collisions.
Which of the following network management tasks is NOT performed by the Gateway in a Wireless HART network?
A. Managing the network topology
B. Managing the network security
C. Managing the frequency hopping schedule
D. Managing the network’s IP address
Answer: D
Explanation: In a Wireless HART network, managing the network’s IP address is not a task performed by the Gateway. The Gateway does manage the network topology, network security, and the frequency hopping schedule, among other tasks.
What does the HART in Wireless HART stand for?
A. High Availability Radio Technology
B. Highway Addressable Remote Transducer
C. High Accuracy Radio Transmission
D. Hybrid Addressable Radio Technology
Answer: B
Explanation: The HART in Wireless HART stands for Highway Addressable Remote Transducer. This refers to the original HART protocol, which was developed as a standard for communication between intelligent field devices and controllers.
How many data channels are available for communication in a Wireless HART network?
A. 8
B. 16
C. 32
D. 64
Answer: B
Explanation: A Wireless HART network has 16 data channels available for communication. This provides a good balance between network capacity and the complexity of managing the frequency hopping schedule.
Which organization is responsible for the development and maintenance of the Wireless HART standard?
A. IEEE
B. IEC
C. ISA
D. FieldComm Group
Answer: D
Explanation: The FieldComm Group is responsible for the development and maintenance of the Wireless HART standard. This organization is dedicated to developing and promoting standards for the process industry.
Which of the following best describes the power consumption of a Wireless HART device?
A. High power consumption
B. Moderate power consumption
C. Low power consumption
D. No power consumption
Answer: C
Explanation: A Wireless HART device has low power consumption, which allows for battery-powered operation over long periods. This is an important characteristic for devices deployed in industrial settings where power sources may not always be readily available.
What kind of network path does a Wireless HART network use for data transmission?
A. Direct path
B. Indirect path
C. Multiple paths
D. Single path
Answer: C
Explanation: A Wireless HART network uses multiple paths for data transmission. The use of multiple paths improves the reliability of the network by providing alternate paths for data transmission in case of a failure of a particular path.
What is the primary application of Wireless HART technology?
A. Home automation
B. Industrial automation
C. Telecommunications
D. Mobile devices
Answer: B
Explanation: The primary application of Wireless HART technology is in industrial automation. It is used for process monitoring and control in various industries such as oil and gas, chemical, and manufacturing.
How does Wireless HART ensure secure communication?
A. By using public key encryption
B. By using private key encryption
C. By using symmetric key encryption
D. By not using any encryption
Answer: C
Explanation: Wireless HART ensures secure communication by using symmetric key encryption, specifically the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). This ensures that data transmitted over the network remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
Which part of the Wireless HART network is responsible for connecting the network to a host system?
A. Router
B. Gateway
C. Network Manager
D. Field device
Answer:
Explanation: The Gateway is the part of the Wireless HART network that is responsible for connecting the network to a host system. It serves as the interface between the wireless network and the wired host system.
Which of the following is NOT a function of a Wireless HART field device?
A. Transmitting measurement data
B. Relaying messages for other devices
C. Assigning network addresses
D. Receiving commands from the host system
Answer: C
Explanation: Assigning network addresses is not a function of a Wireless HART field device. This task is typically performed by the Network Manager or the Gateway in the network.
How does a Wireless HART network handle message collisions?
A. It uses a collision detection mechanism
B. It uses a collision avoidance mechanism
C. It uses a collision correction mechanism
D. It does not handle message collisions
Answer: B
Explanation: A Wireless HART network uses a collision avoidance mechanism to handle message collisions. This is accomplished through the use of Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), which assigns specific time slots for each device to transmit.
How does a Wireless HART device synchronize its clock with the network?
A. By using the Network Time Protocol (NTP)
B. By using the Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
C. By using time synchronization messages from the Gateway
D. Wireless HART devices do not synchronize their clocks with the network
Answer: C
Explanation: A Wireless HART device synchronizes its clock with the network by using time synchronization messages from the Gateway. This ensures that all devices in the network are operating with the same time reference, which is crucial for the correct operation of the network’s TDMA scheduling.
What is the maximum transmission distance of a Wireless HART device?
A. 100 meters
B. 200 meters
C. 500 meters
D. There is no maximum
Answer: A
Explanation: The maximum transmission distance of a Wireless HART device is approximately 100 meters. However, in a Wireless HART network, devices can relay messages for each other, allowing the network to cover larger distances.
Read Next: