What is a Network Topology? Types, Advantages, Disadvantages
In this article, you will learn about the network topology, types of topologies, and their advantages & disadvantages in detail explanation.
What is a Network Topology?
The topology defines how the different nodes are placed and interconnected with each other. The overall topology of a network is usually depicted by a line and an object.
As shown in the below figure, the topology of a network can be divided into two types.
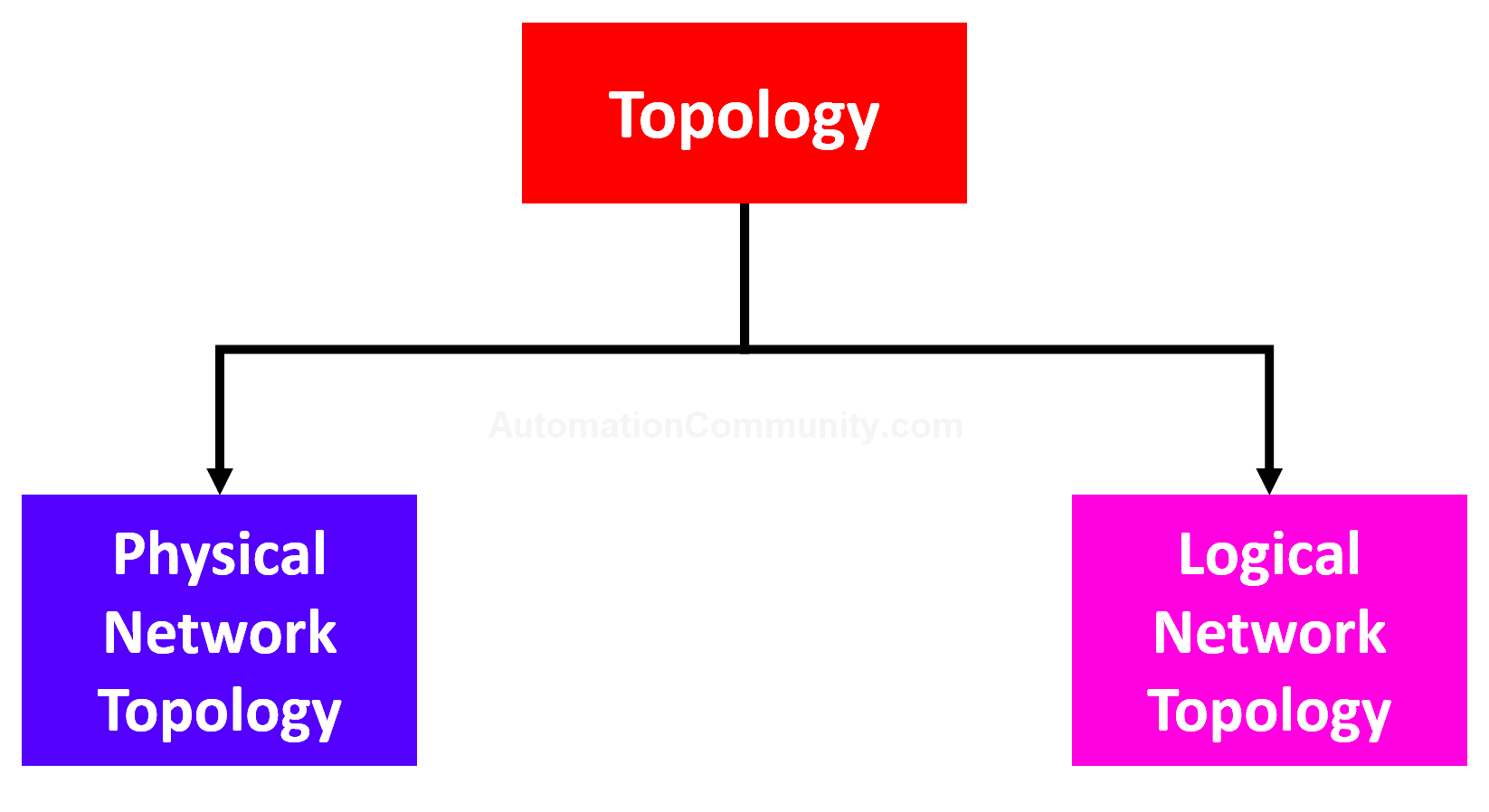
Physical network topology determines how its various components are arranged. The various connectors represent the physical network cables, and the nodes represent the physical network devices on the network (such as switches).
The logical network topology illustrates, at a higher level, the flow of data within a network. It focuses on the data transfer pattern between network nodes.
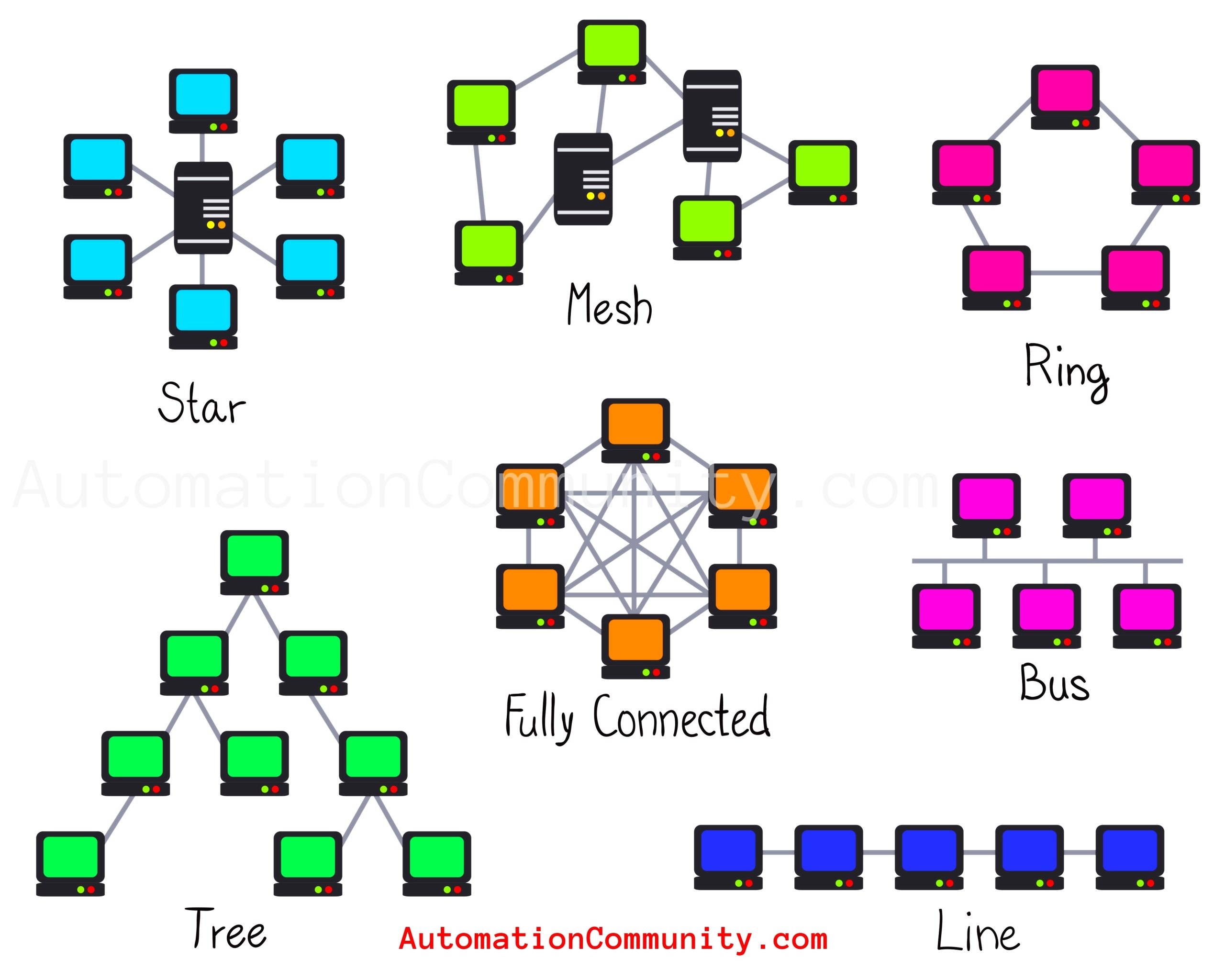
Typical Topologies
The following architectures are or have been used in consumer or enterprise computer networks. Physical architecture corresponds to the topology of a network.
They are classified by their structure.
There are two propagation modes for classifying topologies:
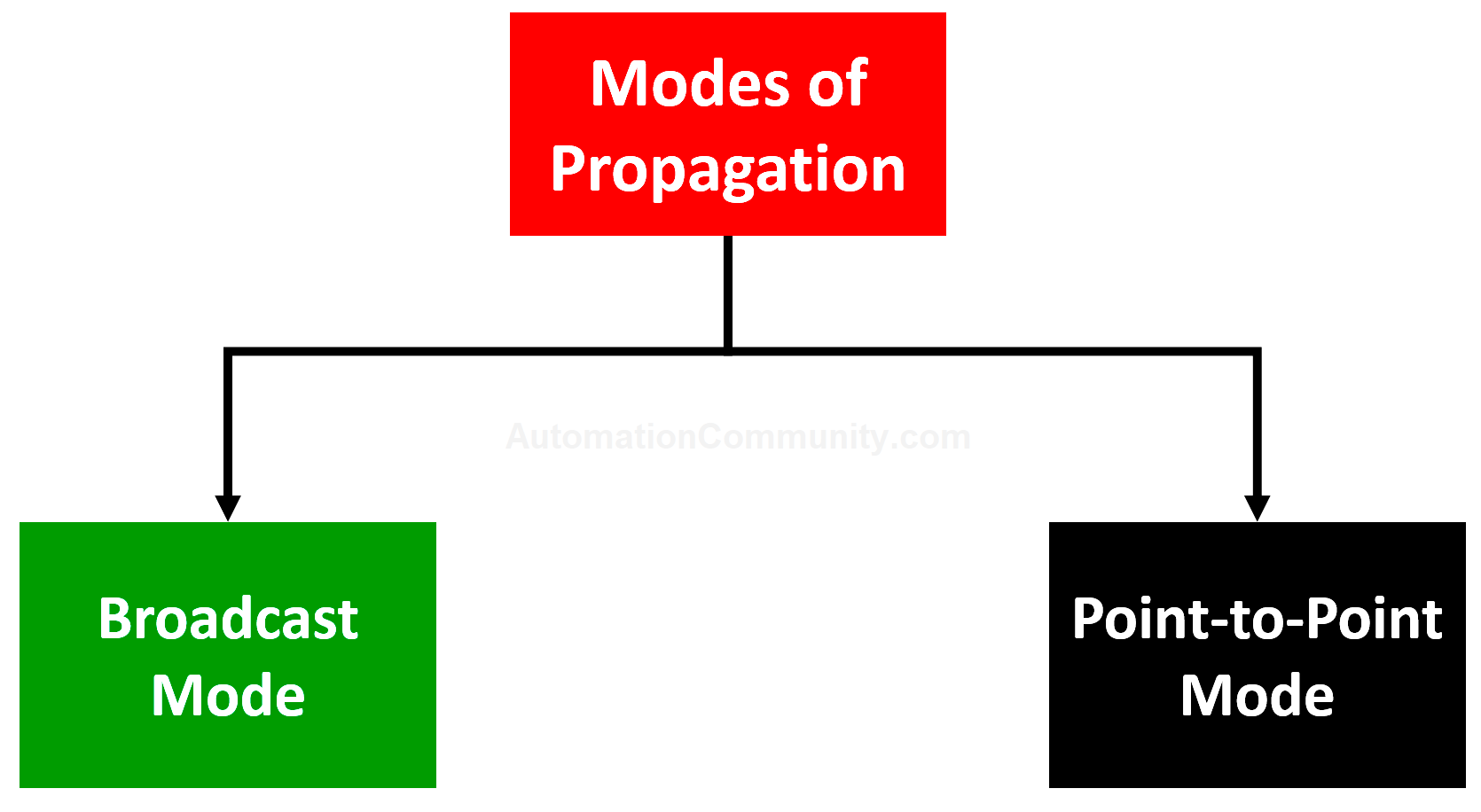
The broadcast mode of operation consists in using only one transmission medium. The principle is that the message is sent over the network, so any network unit can see the message and analyze according to the recipient’s address whether the message is intended for him or not. For example Bus or Ring topology.
In Point-to-Point mode, the physical medium connects only one pair of units. For two network units to communicate, they necessarily pass through an intermediary (the node). Typical topologies are Star or Mesh.

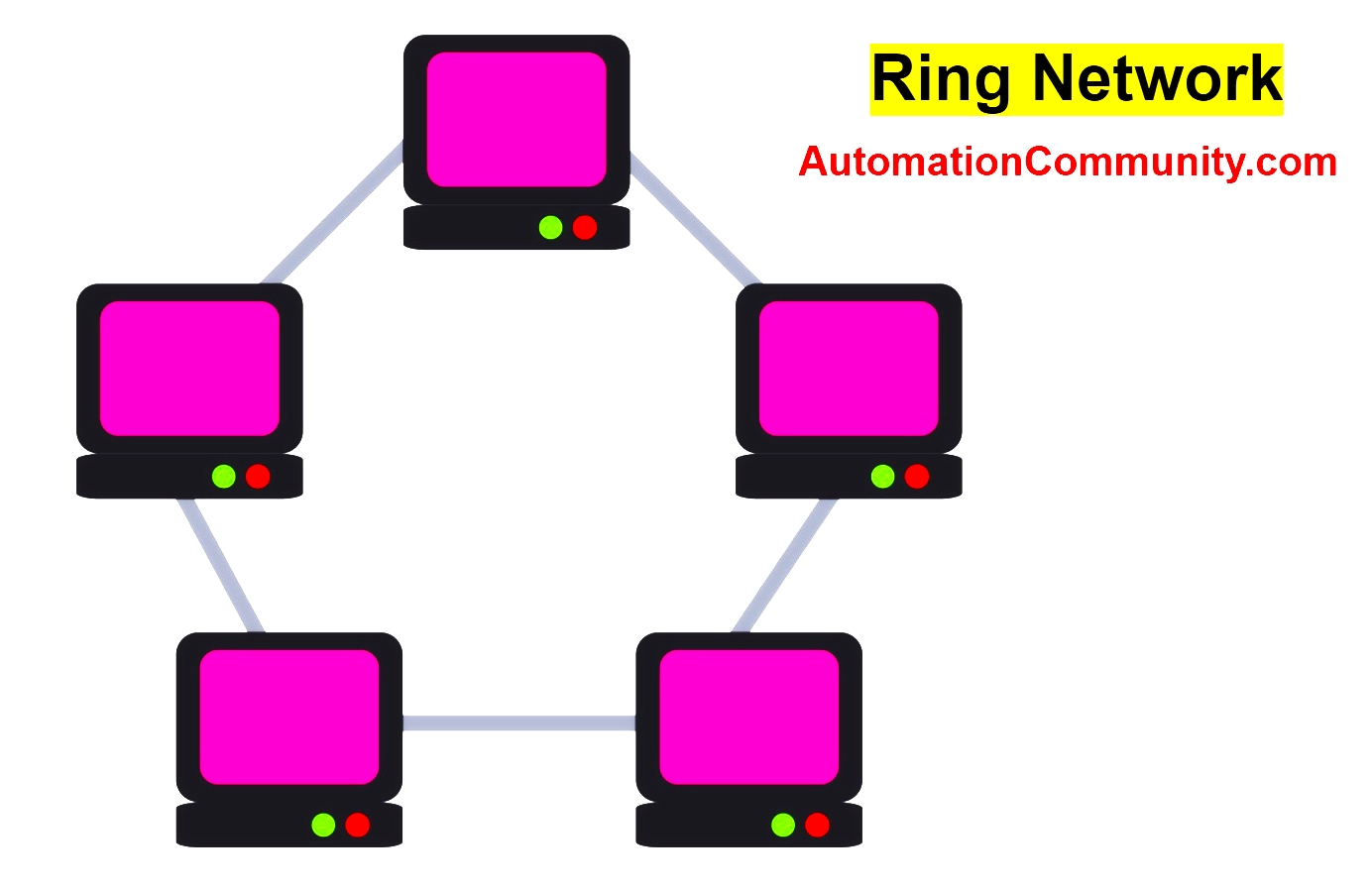
Ring Network Topology
The ring topology is to be preferred in mission-critical applications when network security and monitoring are essential. This is because the topology allows automatic failover to ensure continuity of service.
Data travels from one device to another until it reaches its final destination and then returns to the data center. This configuration is less demanding in wiring than star topologies.
To guarantee rock-solid reliability, this topology should be combined with industrial Ethernet switches capable of transmitting data at very high speeds, even under the most extreme conditions.
Advantages of Ring Topology
- Ring topologies allow us to connect all the devices in our network in series.
- The topology is easier to implement and at a lower cost.
- In a ring network topology, all its nodes are connected in a chain to each other by a two-point link and the last to the first.
- Monitoring and Control of critical applications.
- Dual-ring network can be implemented to create two directions for data travel.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
- Faced with traditional star topologies, if a device fails, the entire network suffers the consequences and risk of losing the network.
- A system allowing centralized traffic management in metropolitan areas.
- Gigabit fiber optic network and Ethernet switches with multiple nodes spread over multiple metropolitan areas, over long distances, and at high speed.
- The failure of a node breaks the ring structure if the communication is unidirectional.
Tree Network Topology
Among the network topologies, the tree topology is the most popular. Tree topology is a topology, that has a tree structure or hierarchy-based network topology. As can be seen in the below figure, the network is divided into different hierarchical levels, and an element of the network is connected to other lower-level positions.
Flexibility and scalability are the main advantages of this topology. Tree network topology is considered the simplest topology of all. The tree topology in a computer network is a combination of the bus and star topologies.
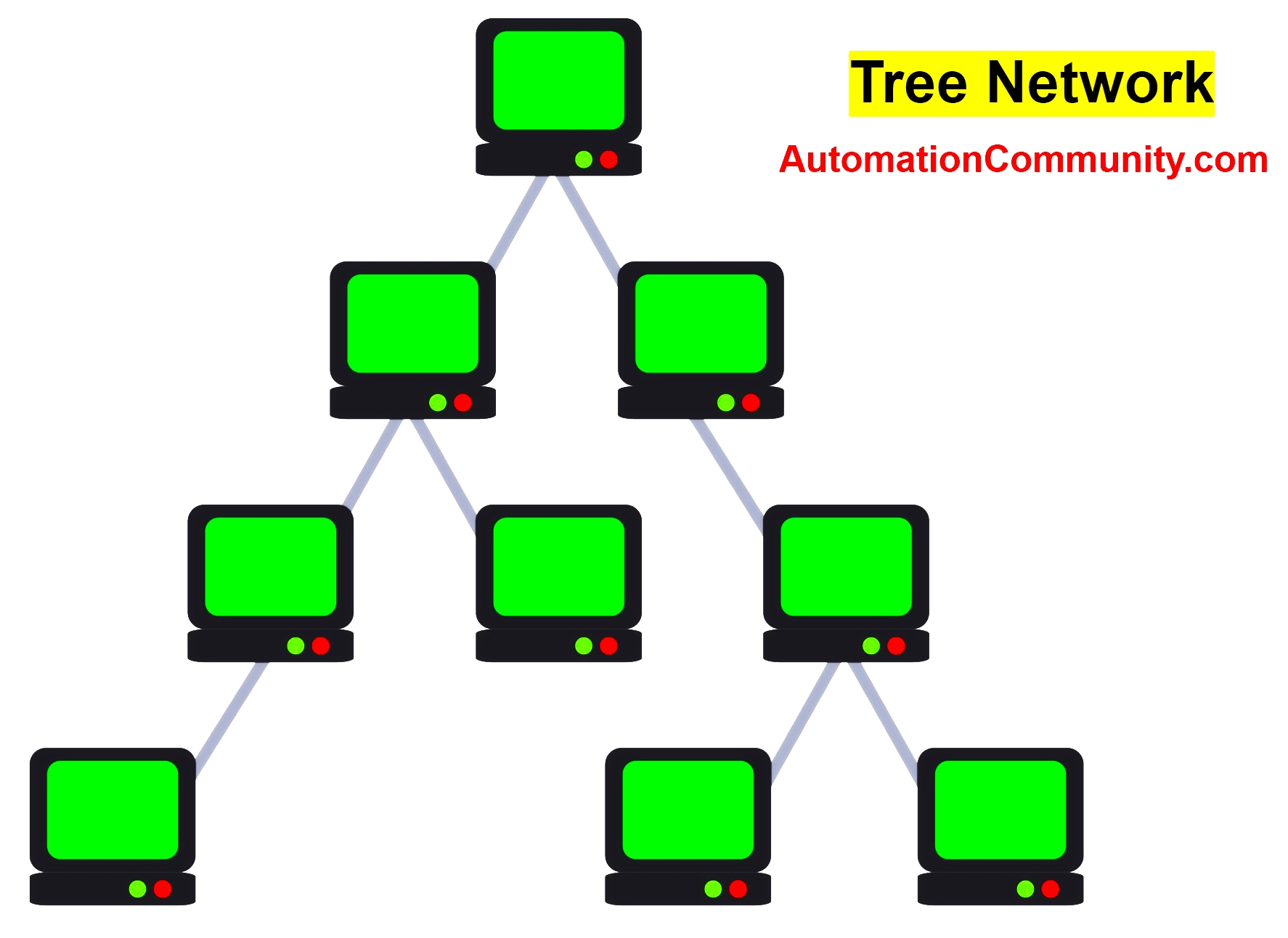
Of all topologies which have only one route between two nodes in the network. The connection model looks like a tree in which all branches spring from a root (Tree Topology).
Advantages of Tree Topology
- Tree topology is best suited for large networks, it is a combination of bus and star topology.
- This topology provides a hierarchical as well as a central layout of node data.
- The leaf nodes can add any number of nodes to the hierarchical string, this topology is highly scalable.
- Other nodes in a network are not affected if one of their nodes is damaged or not functioning.
- The tree topology allows for easy maintenance and easy fault identification can be performed.
- Point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
- The tree topology is reliable and highly secure.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
- This network is very difficult to configure compared to other network topologies.
- The length of a segment is limited and the segment limit depends on the type of cabling used.
- As a result of a large number of nodes in tree topology, the network performance becomes somewhat slow.
- In comparison to star and ring topology, tree topology requires a large number of cables.
- As the data has to travel from the core wire, this creates heavy network traffic.
- The Backbone appears as the point of failure of the entire network segment.
- The topology processing is quite complex, and the establishment cost is high but easier to manage the network by defining access rights for each branch of the network.
- If the bulk of nodes is added to this network, maintenance will become complicated.
Bus Network Topology
A bus topology refers to the configuration of a network in which all devices are connected to a single cable or network backbone. Network cards are connected by coaxial cable with RJ-45 connectors.
When a station is defective and no longer transmits on the network, it does not disturb the network. The signal transmitted by a station propagates in one direction only or in both directions.
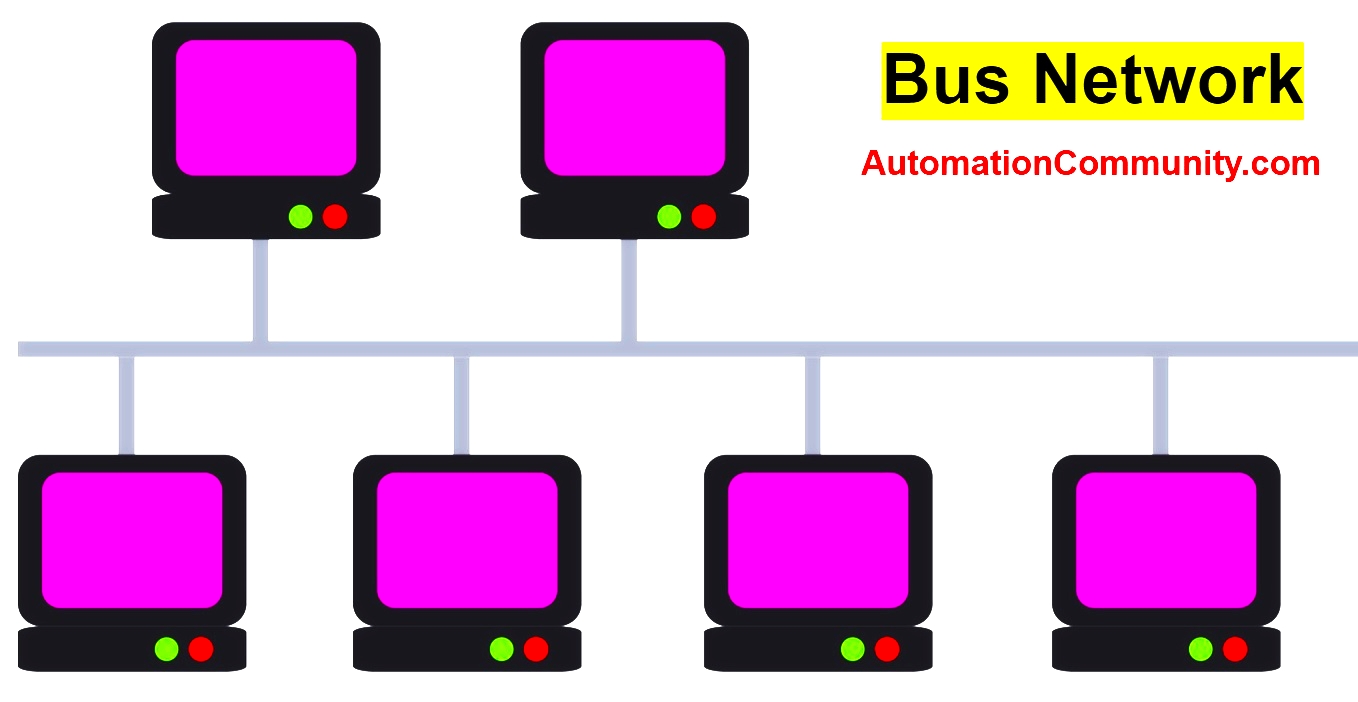
If the transmission is bidirectional, all the connected stations receive the signals emitted on the bus at the same time (to the nearest propagation delay).
Advantages of Bus Topology
- It works well in small networks.
- This topology connects all devices linearly.
- Less cable is required compared to a star topology.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
- Troubleshooting can be difficult when the entire network shuts down.
- It can be challenging to address issues related to individual devices.
- Bus topologies are not recommended for large networks.
- To avoid cable noise, terminators are required at both ends of the trunk (main) cable.
- There is a slowdown in the network when additional devices are connected.
- If the main cable is damaged the entire network breaks down.
Star Network Topology
This is the most common topology at present. The star topology is widespread and very flexible in terms of network management and troubleshooting.
The failure of a node does not disrupt the overall operation of the network. On the other hand, the central equipment is a hub, and more often on modern networks, a switch that connects all the nodes constitutes a single point of failure.
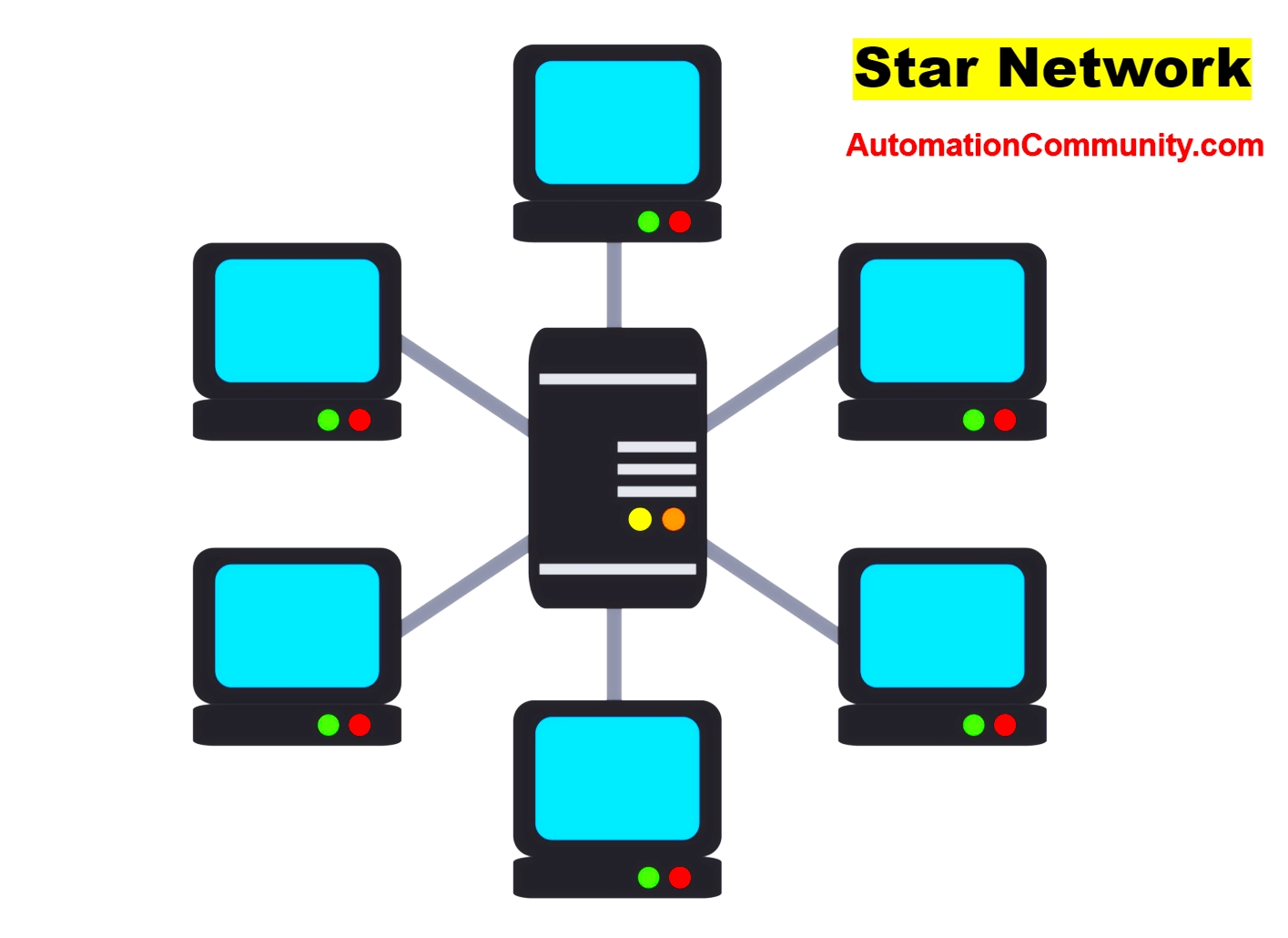
A failure at this level renders the network completely unusable. The Ethernet network is an example of a star topology. The main drawback of this topology lies in the length of the cables used.
This is the linear network
Advantages of Star Topology
- It has the advantage of low deployment cost.
- Network issues can be solved easily.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
- Consumption of lengthy cable is required for its implementation.
Mesh Network Topology
The mesh topology is an enhanced star network. In this, every workstation is connected to all the others.
Mesh topology consists of network nodes that are all connected. In a mesh topology, there are several point-to-point links.
For message transmission, there is no concept of a central switch, hub, or computer that serves as a central communication point as can be seen in the below figure.
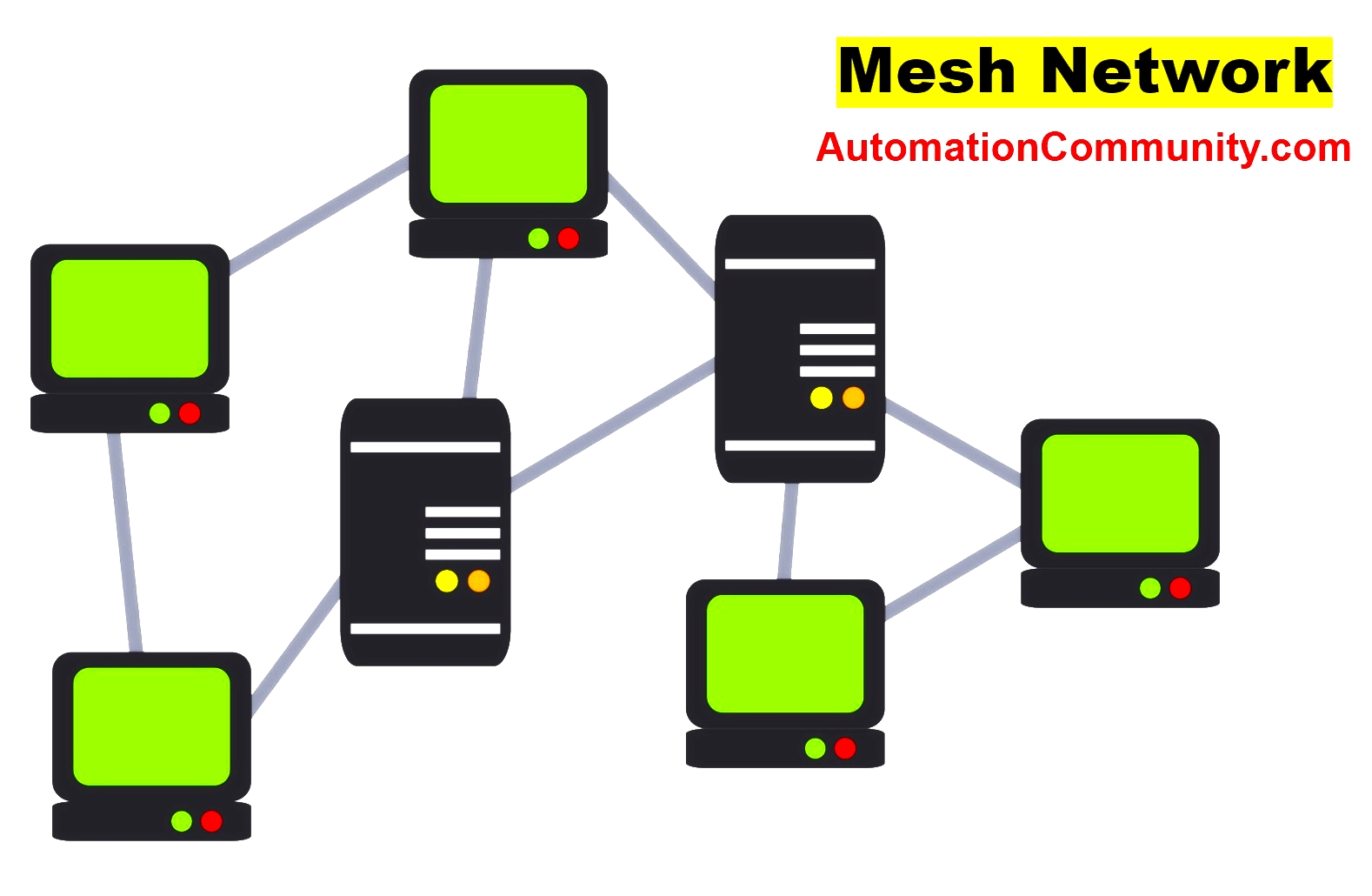
Large distribution networks like the internet use this topology. A network can transport information along different routes, under the control of powerful network supervisors, or by using distributed routing.
The Mesh topology can be divided into two types:
- Fully Connected Mesh Topology
- Partially connected mesh topology
Fully connected mesh topology:
In this category, all nodes are connected. It is just like graph theory, it is a fully connected graph in which all nodes are connected to all other nodes.
Partially connected mesh topology:
It does not have all nodes connected.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
- Mesh network offers the highest level of good security and unmatched performance once they are implemented.
- The workstations are independent of one another. Failure at a particular station does not prevent other stations from communicating with each other.
- A connection can carry its load of data.
- It is easy to diagnose a fault.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- The main drawback of this topology is that its implementation becomes more and more difficult depending on the number of stations to be installed.
- The resources required are enormous, whether in terms of connection equipment or cabling.
- As connectivity becomes more critical, installation and configuration become more challenging.
- A fully connected mesh network increases the cost of cabling.
- It is necessary to ground the system.
Read Next:













