H2S Gas Detector Calibration Procedure
In this article, you will learn the detailed H2S gas detector calibration procedure, the basics of H2S detectors, required tools, types of tests, and zero & span calibrations.
What is an H2S Gas Detector?
H2S portable gas detector is part of the monitoring system. It is designed for applications where protection against high levels of toxic gases is the utmost priority. A gas detector is a portable instrument that a person carries during plant visits for detecting gas leakages.
As hydrogen sulfide is a toxic gas, the detector is used to identify pipeline leakages. Also, gas accumulations in confined areas, pits, and low-lying areas can be detected. Thereby, the safe operation of the work site is possible.
Upon detection of unsafe conditions, the H2S detector alerts by alarms in the form of visual, sound, vibration, and also reading in the display. A vibrating module that warns even in noisy environments.
What is H2S gas?
In the oil and gas industries, hydrogen sulfide is a gas that is commonly found during exploration and production.
The following are characteristics of H2S gas
- It is heavier than air
- Settles in low-lying areas
- It is colorless, flammable
- Poisonous, and Corrosive
- Spreads fast with the wind.
Perception of H2S presence can be by inhalation and smells of rotten eggs. Exposure to low concentrations for a long time causes headaches, skin, and eye irritation. Higher concentrations lead to a dull sense of smell, thereby suffocation. Inhalation of H2S gas, in high concentrations, is deadly.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) directives must be followed to overcome the effects of exposure.
Basics of Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Detector
Gas detectors should be calibrated regularly because sensors can drift over time and contaminates affect the gas readings. Using the wrong or expired calibration gas can lead to improper calibration, and the gas detector will not give accurate readings. Life-threatening consequences can result from these simple mistakes.
Hence, calibration gas cylinders should always be checked for contents and expiration dates. Do not use expired bottles, as chemical reactions can occur inside the bottle, altering the contents.
Why Calibrate the Gas Detector?
As the sensor “wears out”, it reacts with the gas to be detected differently. Therefore, the signal it sends to the detector is different. Periodically, the detector must be taught to interpret the sensor signal through calibration, that is, to read just that response.
Most of the sensors that the gas detectors carry, deteriorate over time. Long exposure to the gas, humidity, very high or very low temperatures, etc. are the reason for the deterioration.
Tools Required for Calibration
The following tools and equipment are required for the calibration of H2S gas detectors.
- Span gas cylinder
- Zero gas cylinder
- Gas regulator
- Rotameter
Calibration Setup
The following image shows the calibration setup for carrying out the calibration of the gas detector.
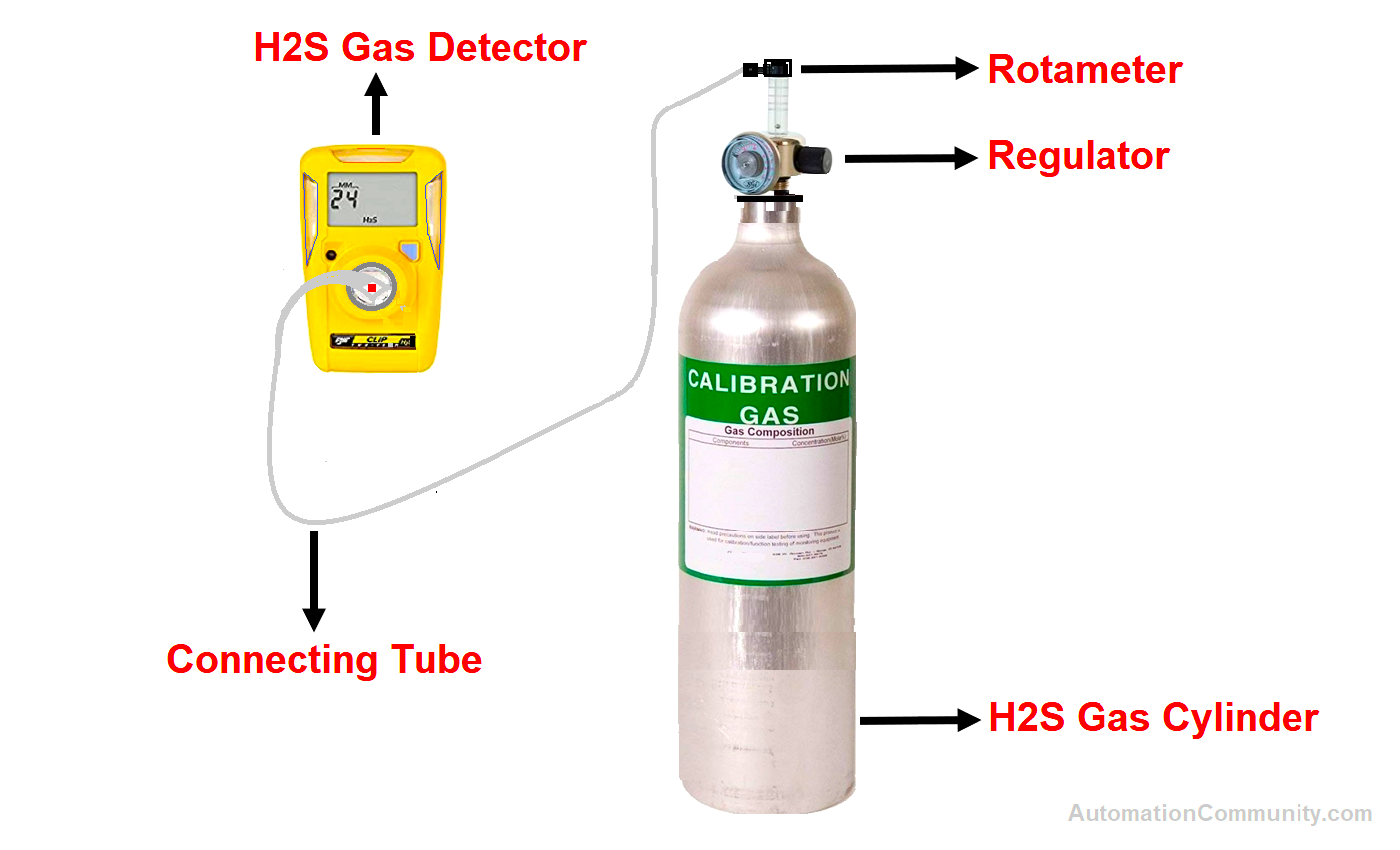
Calibration Procedure of Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Detector
As part of occupational health safety, take necessary safety measures. Wear the PPE before proceeding with calibration. There are two ways to test a hydrogen sulfide detector.
- Bump test
- Test with calibration gas
Bump Test
In the bump test, the gas detector sensor is briefly exposed to a concentration that is higher than the alarm set points. This test verifies that our gas detector’s sensor responds and alarms as expected. It is important to note that the bump test does not verify the accuracy of the gas reading, but rather the operation of the sensors and alarms. The only way to know your gas detector is working is to bump-test before every shift.
So users can trust the gas detector to warn them of unseen dangers. Bump tests protect the wearer on the job by verifying that the gas monitors issue an alert if hazardous gas levels are present.
This test verifies that our gas detector’s sensors will respond and an alarm will sound as expected.
Calibration with Known Gas Concentration (PPM)
Calibrating the monitor means exposing it to a known concentration of a calibration gas or test gas for a set amount of time. One-point calibration means it is carried out from clean air in the atmosphere.
A two-point calibration is usually done from a bottle with the gas of known concentrations. With these two points, determine the response of the detector to the different concentrations to which it is exposed.
The usual measurement ranges for H2S gas detectors are
- 0 to 20 ppm of H2S
- 0 to 30 ppm of H2S
- 0 to 50 ppm of H2S
- 0 to 100 ppm of H2S
- 0 to 500 ppm H2S
Zero Calibration
The following steps show the H2S gas detector zero calibration procedure.
- From the menu, select zero adjustments.
- Zero adjustments can be performed by making sure that the calibration is performed in uncontaminated clean environments.
- After performing the above step, if still an error is found, follow the step below.
- Put the zero gas cylinder and select the zero adjustments in the device program.
- Repeat to check the zero.
Span Calibration
The following steps describe the span gas calibration procedure for an H2S gas detector.
- In the device, from the program menu, chose span adjustment.
- Slowly open the calibration gas with the help of a pressure regulator/rotameter.
- The detector is exposed to the required gas concentration.
- Adjust the span accordingly.
- Repeat the above steps for confirmation.
Keywords
TLV: Threshold Limit Value of occupational exposure value. It is used as a guideline to assist in the control of health hazards when exposed to toxic gases.
TWA: Time-weighted average, related to exposure to harmful substances by the workforce.
STEL: Short-term exposure limit is a time-weighted average gas concentration. Usually, 15 minutes of safe acceptable limit for average exposure, do not cause a health risk.
LTEL: Long-term exposure limit is a time-weighted average gas concentration. Usually, it is 8 hours per day, 40 hours per week without causing health risks to the exposed person.
REL: It is recommended exposure limit, be followed by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Recommended limits are 10 hours per day, and 40 hours a week.
PEL: Permissible exposure limit, same as STEL. Mostly followed in the United States for safe exposure of a person to the gas concentration.
Read Next:













Comments
3
Thank you for sharing
Good information given
valuable information, thank you.