Foundation Fieldbus Questions and Answers
Discover valuable insights into Foundation Fieldbus with our comprehensive collection of questions and answers. This resource provides a wealth of knowledge on Foundation Fieldbus technology, protocols, devices, configurations, troubleshooting, and more.
Foundation Fieldbus Questions
Explore a wide range of topics to enhance your understanding and stay up to date with the latest advancements in industrial automation and control. Get ready to expand your expertise in Foundation Fieldbus with our reliable Q&A resource.
What is Foundation Fieldbus (FF)?
Foundation Fieldbus is a digital multi-drop communication protocol used in process automation industries. It’s designed for real-time distributed control of manufacturing instrumentation such as sensors and actuators.
What are the key features of Foundation Fieldbus?
Key features of Foundation Fieldbus include bi-directional communication, device interoperability, digital signal quality, and the ability to carry multiple variables.
What are the main types of Foundation Fieldbus?
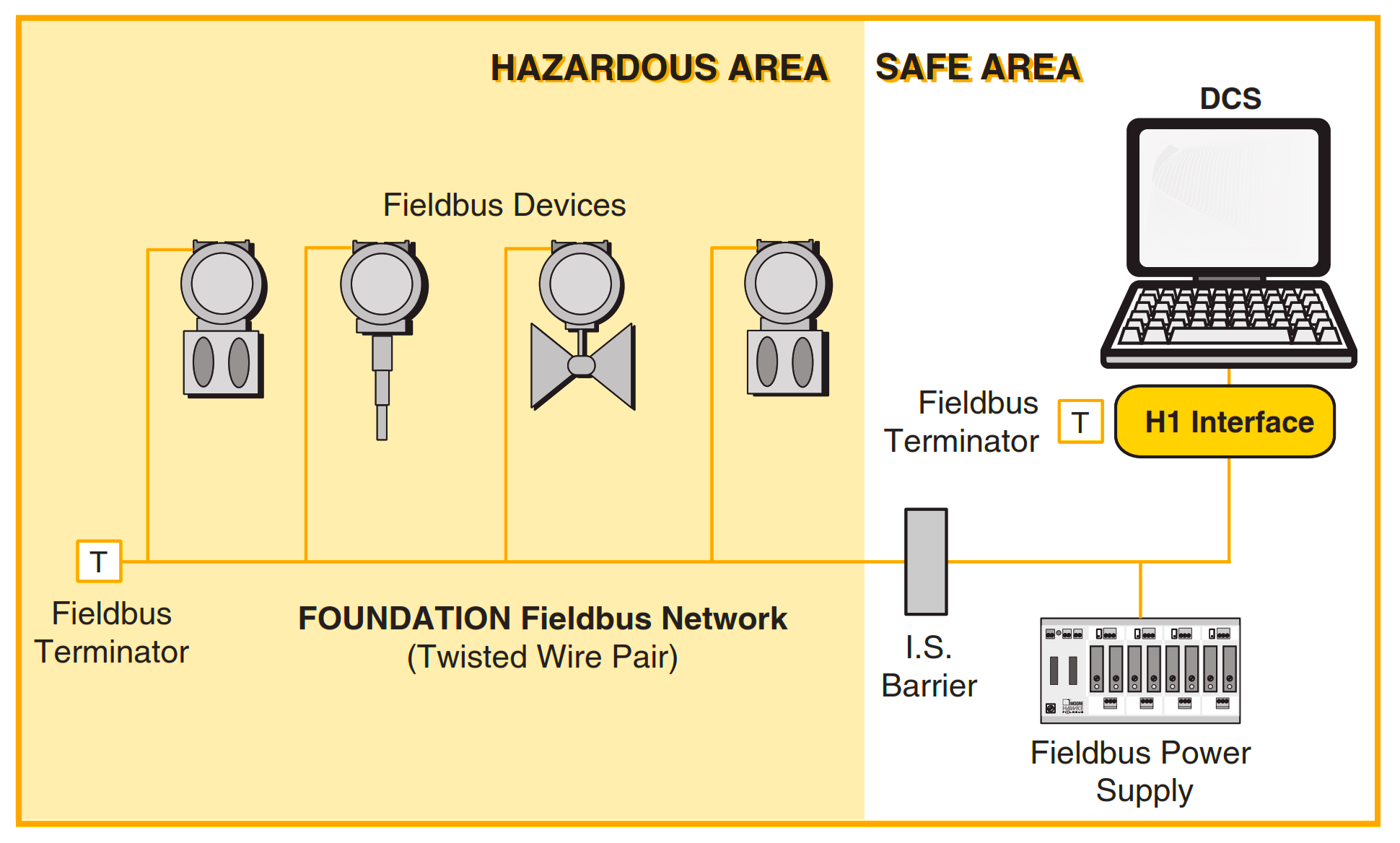
The main types of Foundation Fieldbus are H1 Fieldbus, operating at 31.25 kbit/s and used for connecting field devices, and HSE Fieldbus (High-Speed Ethernet), operating at 100 Mbit/s and used for control and information viewing.
How many devices can be connected to a Foundation Fieldbus H1 segment?
Up to 32 devices can be connected to a Foundation Fieldbus H1 segment, depending on the power consumption of each device and the power supply.
What is an FDI Device Package in the context of Foundation Fieldbus?
An FDI (Field Device Integration) Device Package is a software component that describes a field device in terms of its communication characteristics, user interface, and device parameters for a Foundation Fieldbus network.
What are Function Blocks in Foundation Fieldbus?
Function Blocks in Foundation Fieldbus are pre-defined modules of code that perform a specific function in a device, such as PID control, analog input, or discrete output.
How is control implemented in Foundation Fieldbus?
Control in Foundation Fieldbus is implemented by linking the Function Blocks in different devices. This enables distributed control, where processing is shared across multiple devices in the field.
What kind of cable is used for Foundation Fieldbus H1?
Foundation Fieldbus H1 typically uses a shielded twisted pair cable, similar to the cable used in PROFIBUS PA.
How does Foundation Fieldbus handle device failures?
Foundation Fieldbus includes mechanisms for fault detection and isolation. If a device fails, it can be replaced with a similar device, and the system will automatically reconfigure to continue operation.
What is the purpose of Link Active Scheduler (LAS) in Foundation Fieldbus?
The Link Active Scheduler (LAS) is a device in a Foundation Fieldbus H1 network that coordinates the communication between devices. It ensures the deterministic nature of the network.
What is a “Fieldbus Brick” in Foundation Fieldbus?
A Fieldbus Brick is a type of field-mounted device that provides physical layer interfaces and power to Foundation Fieldbus networks. It’s typically used in harsh environments.
What kind of topology is used in Foundation Fieldbus networks?
Foundation Fieldbus networks typically use a daisy-chain (bus) topology, though tree, star, and hybrid topologies can also be used depending on the application.
What is the role of a “Backup LAS” in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A Backup LAS (Link Active Scheduler) in a Foundation Fieldbus network is a device that can take over the functions of the primary LAS if it fails, ensuring continuous operation of the network.
What is the purpose of a “Device Description” (DD) in Foundation Fieldbus?
A Device Description (DD) in Foundation Fieldbus provides a detailed description of a device’s functions and how to access them. It’s used by host systems to interpret device data and control device operations.
What is “Fieldbus Intrinsically Safe Concept” (FISCO) in Foundation Fieldbus?
FISCO is a concept for powering intrinsically safe devices in hazardous areas in a Foundation Fieldbus network. It defines the parameters for power supply and cable length to ensure safe operation.
Can Foundation Fieldbus and PROFIBUS PA devices coexist in the same network?
No, while both Foundation Fieldbus and PROFIBUS PA are used for process automation and use similar physical layer specifications, they use different communication protocols and are not interoperable.
How does Foundation Fieldbus handle synchronization between devices?
The Link Active Scheduler (LAS) in a Foundation Fieldbus network manages synchronization between devices. It schedules the execution of function blocks in devices based on the macrocycle, which is the total communication cycle time.
What is a “Control in the Field” (CIF) concept in Foundation Fieldbus?
CIF is a concept in Foundation Fieldbus where control loops are executed in the field devices rather than in the controller. This distributed control approach can improve process performance and reliability.
What kind of power supply is used for Foundation Fieldbus H1 devices?
Foundation Fieldbus H1 devices typically use a 24V DC power supply, which is also used to carry the communication signals.
What is the maximum distance of a Foundation Fieldbus H1 segment?
The maximum distance of a Foundation Fieldbus H1 segment is 1900 meters (about 6200 feet) when using standard Fieldbus cable. Repeaters can be used to extend the distance if needed.
Can Foundation Fieldbus be integrated with other industrial networks?
Yes, Foundation Fieldbus can be integrated with other industrial networks like Ethernet, Modbus, and HART through gateways, linking devices, or network interface cards.
What is Interoperability in Foundation Fieldbus?
Interoperability in Foundation Fieldbus refers to the ability of devices from different manufacturers to work together on the same network. This is ensured by the standardization of communication protocol and function blocks.
What is an “ITK” in Foundation Fieldbus?
ITK stands for “Interoperability Test Kit”. It’s a software tool used by manufacturers to test and ensure the interoperability of their Foundation Fieldbus devices.
What is the role of the “Fieldbus Foundation”?
The Fieldbus Foundation is the organization that manages the Foundation Fieldbus technology. It develops and maintains the protocol standards, oversees product certification, and promotes the technology.
How is diagnostic information handled in Foundation Fieldbus?
Foundation Fieldbus devices can provide extensive diagnostic information as part of their standard operation. This data can be accessed by the host system for predictive maintenance and troubleshooting.
What are “transducer blocks” in Foundation Fieldbus?
Transducer blocks in Foundation Fieldbus provide an interface between the Fieldbus network and the physical process. They convert physical parameters into digital signals that can be processed by the function blocks.
How is safety implemented in Foundation Fieldbus systems?
Safety in Foundation Fieldbus systems can be implemented using safety instrumented systems (SIS) with FF-SIS technology. It allows safety and process control to be integrated into the same network.
What is a “macrocycle” in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A macrocycle in a Foundation Fieldbus network is the total time taken for all scheduled communications in the network. The Link Active Scheduler (LAS) ensures that all devices operate within the macrocycle to maintain synchronization.
How is redundancy achieved in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Redundancy in a Foundation Fieldbus network can be achieved through redundant power supplies, redundant communication interfaces, and redundant Link Active Schedulers (LAS).
What types of signals can be transmitted over a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Foundation Fieldbus can transmit various types of signals, including process variables, setpoints, status information, alarms, and device diagnostics.
What does the “Control Loop” mean in Foundation Fieldbus?
A Control Loop in Foundation Fieldbus refers to the execution of a process control function by the Function Blocks within a device, like a temperature or pressure regulation.
Can a Foundation Fieldbus network operate without a host system?
Yes, once configured, a Foundation Fieldbus network can operate without a host system because of its distributed control capability. However, a host system is required for configuration, supervision, and advanced process control functions.
How does Foundation Fieldbus achieve energy efficiency?
Foundation Fieldbus achieves energy efficiency by enabling the execution of control functions within field devices, reducing the processing load on host systems and network traffic.
What are the components of a Foundation Fieldbus HSE (High-Speed Ethernet) system?
A Foundation Fieldbus HSE system includes HSE linking devices, Ethernet switches, and HSE devices. It also includes a host system for configuration, control, and data management.
What is the importance of the “Nearest User Application” (NUA) in Foundation Fieldbus?
The NUA concept in Foundation Fieldbus allows the execution of control functions in the device nearest to the process, reducing communication delays and improving process control efficiency.
Can Foundation Fieldbus support wireless communication?
While Foundation Fieldbus itself does not support wireless communication, it can be integrated with wireless networks using gateways or linking devices.
How is device commissioning performed in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Device commissioning in a Foundation Fieldbus network is performed using a host system. It includes assigning addresses to devices, loading the device descriptions, configuring the function blocks, and checking the device’s operation.
Can Foundation Fieldbus support device calibration?
Yes, Foundation Fieldbus can support device calibration by providing access to the device parameters and diagnostic data. The calibration can be performed remotely using the host system.
What is a “Physical Layer Diagnostic” in Foundation Fieldbus?
Physical Layer Diagnostic in Foundation Fieldbus refers to the diagnosis of the physical layer of the network, including the quality of communication signals, power supply voltage, and termination.
Can Foundation Fieldbus networks be used in hazardous areas?
Yes, Foundation Fieldbus networks can be used in hazardous areas by using intrinsically safe (IS) or explosion-proof devices, and following the appropriate installation standards.
What is the purpose of a “Segment Protector” in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A Segment Protector in a Foundation Fieldbus network is used to connect spur lines to the main trunk. It provides short-circuit protection for each spur, preventing a fault in one spur from affecting the rest of the network.
What is the “Fieldbus Access Sublayer” (FAS) in Foundation Fieldbus?
The Fieldbus Access Sublayer (FAS) in Foundation Fieldbus is part of the communication stack. It provides an interface between the Fieldbus message specification (FMS) and the physical layer.
What is “Live Work” in Foundation Fieldbus?
“Live Work” in Foundation Fieldbus refers to the ability to perform tasks like device replacement, configuration changes, and calibration without interrupting the operation of the network.
How does a Foundation Fieldbus device handle alarms?
A Foundation Fieldbus device can generate alarms based on its internal condition or process variables. The alarms are transmitted to the host system for display and acknowledgment.
How is security handled in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Security in a Foundation Fieldbus network can be handled through access control, data encryption, and use of secure network infrastructure. The Fieldbus Foundation also provides guidelines for network security.
What is a “Device Revision” in Foundation Fieldbus?
A Device Revision in Foundation Fieldbus is a number assigned by the manufacturer that indicates the version of the device’s firmware and functionality.
How does Foundation Fieldbus handle software updates for devices?
Software updates for Foundation Fieldbus devices are typically handled by the device manufacturers. The updated software can be loaded into the device using the host system.
What are “Standard Function Blocks” in Foundation Fieldbus?
Standard Function Blocks in Foundation Fieldbus are function blocks that are defined by the Fieldbus Foundation and supported by all Foundation Fieldbus devices. Examples include AI (Analog Input), AO (Analog Output), PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative), etc.
What is a “Device Coupler” in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A Device Coupler in a Foundation Fieldbus network is a device that provides a connection point for field devices to the network. It typically provides short-circuit protection for the connected devices.
What is the benefit of using Foundation Fieldbus in process automation?
The benefits of using Foundation Fieldbus in process automation include improved process control, simplified wiring, extensive device diagnostics, interoperability between devices, and cost savings in installation and maintenance.
How does Foundation Fieldbus support multi-vendor interoperability?
Foundation Fieldbus supports multi-vendor interoperability by standardizing the communication protocol, function blocks, and device descriptions. Any certified Foundation Fieldbus device can be used in any Foundation Fieldbus network.
How is a Foundation Fieldbus network started up?
Starting up a Foundation Fieldbus network involves powering up the devices, verifying network communication, commissioning the devices, configuring the control strategy, and starting the process control.
What is “Parameterization” in Foundation Fieldbus?
Parameterization in Foundation Fieldbus refers to the setting of device parameters for process control. It includes setting up the function blocks, alarms, and control loops.
What are the considerations for cable selection in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Cable selection for a Foundation Fieldbus network should consider electrical characteristics like resistance, capacitance, and impedance, as well as environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, and chemical exposure.
Can Foundation Fieldbus networks be monitored remotely?
Yes, Foundation Fieldbus networks can be monitored remotely using the host system. It can provide real-time data on process variables, device status, and network performance.
How is “Asset Management” achieved with Foundation Fieldbus?
Asset Management with Foundation Fieldbus is achieved by using the extensive diagnostic data provided by the devices. The host system can use this data for predictive maintenance, fault diagnosis, and performance analysis.
Can Foundation Fieldbus networks be simulated?
Yes, there are software tools available that can simulate Foundation Fieldbus networks for training and testing purposes.
How is time synchronization achieved in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Time synchronization in a Foundation Fieldbus network is achieved through the Link Active Scheduler (LAS), which assigns time slots to the devices for communication.
What is the function of the “User Layer” in the Foundation Fieldbus communication stack?
The User Layer in the Foundation Fieldbus communication stack is responsible for processing the data received from the Fieldbus message specification (FMS) layer. It includes the function blocks that perform process control functions.
Can Foundation Fieldbus be used for batch process control?
Yes, Foundation Fieldbus can be used for batch process control. Its distributed control capability and flexible configuration make it well-suited for batch processes.
How does Foundation Fieldbus handle device failure?
In case of device failure, Foundation Fieldbus can provide extensive diagnostic information to help identify the issue. Furthermore, redundant devices can be used to maintain control in case of a device failure.
What is the role of a “Link Master” in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A Link Master in a Foundation Fieldbus network is a device that takes over the role of the Link Active Scheduler (LAS) in case of a LAS failure, ensuring the continued operation of the network.
What is the significance of the “Link Active Scheduler” (LAS) in Foundation Fieldbus?
The Link Active Scheduler (LAS) in Foundation Fieldbus is responsible for managing communication between devices. It assigns time slots to devices for data transmission, ensuring synchronization across the network.
What is the “Fieldbus Message Specification” (FMS) in Foundation Fieldbus?
The Fieldbus Message Specification (FMS) in Foundation Fieldbus defines the structure of messages and the protocol for data exchange between devices. It forms part of the communication stack of Foundation Fieldbus.
How does Foundation Fieldbus facilitate predictive maintenance?
Foundation Fieldbus devices can provide extensive diagnostic data, including device health and process information. This data can be used by the host system to identify potential issues and perform maintenance before a failure occurs.
What role does a “gateway” play in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A gateway in a Foundation Fieldbus network is used to connect the Fieldbus network to other networks or systems. It translates between the Fieldbus protocol and the protocol of the other network.
What is a “Field Device” in Foundation Fieldbus?
A Field Device in Foundation Fieldbus is a device that interfaces directly with the process, such as sensors, actuators, and controllers. These devices can perform process control functions and communicate with other devices on the network.
What is the “Host Interface” in a Foundation Fieldbus system?
The Host Interface in a Foundation Fieldbus system is part of the system that enables communication between the Fieldbus devices and the host system. It could be a software interface in the host system or a hardware interface like a network interface card.
What kind of power supply is needed for a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A Foundation Fieldbus network requires a DC power supply with a voltage typically between 9 and 32 volts. The power supply must be able to deliver sufficient power for all devices on the network, taking into account the voltage drop along the cable.
What is the purpose of a “Terminator” in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A Terminator in a Foundation Fieldbus network is used at both ends of the cable to match the impedance of the cable and prevent signal reflections. This is important for maintaining good signal quality and network performance.
What is the relevance of a ‘Function Block’ in Foundation Fieldbus?
A Function Block in Foundation Fieldbus encapsulates a specific control function, such as input/output handling, control algorithms, or mathematical functions. They are the building blocks of a control strategy in a Foundation Fieldbus device.
What is the purpose of a “Fieldbus Power Conditioner” in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A Fieldbus Power Conditioner in a Foundation Fieldbus network is used to provide power to the network while isolating the communication signal from power noise, which helps to maintain the integrity of the network communication.
Can a Foundation Fieldbus device operate independently?
Yes, once configured, a Foundation Fieldbus device can execute its control function independently, communicating directly with other devices on the network. This is due to the distributed nature of control in Foundation Fieldbus.
What is “Redundancy” in Foundation Fieldbus?
Redundancy in Foundation Fieldbus refers to the use of multiple devices, power supplies, or networks to maintain operation in case of a component failure. This increases the reliability and availability of the control system.
Can the configuration of a Foundation Fieldbus device be changed while it is operating?
Yes, Foundation Fieldbus allows for “Live Work”, meaning that the configuration of a device can be changed while it is operating, without interrupting the process control.
What is the role of the “Data Link Layer” in the Foundation Fieldbus communication stack?
The Data Link Layer in the Foundation Fieldbus communication stack is responsible for managing communication between devices. It organizes data into frames for transmission and handles error checking and retransmission.
What is a “Macro Cycle” in Foundation Fieldbus?
A Macro Cycle in Foundation Fieldbus is the cycle time for the execution of control functions and communication in the network. It is determined by the Link Active Scheduler (LAS) based on the control requirements.
Can a Foundation Fieldbus network be extended?
Yes, a Foundation Fieldbus network can be extended by adding more devices, up to the limit of the network’s power supply and communication capacity. It can also be extended using repeaters or linking devices.
How are software faults handled in a Foundation Fieldbus device?
Software faults in a Foundation Fieldbus device can be diagnosed using the diagnostic data provided by the device. The software can be reset or updated to resolve the issue. If the fault persists, it may require manufacturer support or replacement of the device.
How are Foundation Fieldbus devices configured?
Foundation Fieldbus devices are configured using a host system, such as a control system or configuration tool. The device parameters are set, function blocks are configured, and control loops are established based on the control strategy.
What’s the process of calibrating a Foundation Fieldbus device?
Calibration of a Foundation Fieldbus device involves comparing its output with a known reference value under specific conditions, then adjusting the device’s output to match the reference value. The calibration process can often be performed remotely via the host system.
How are control loops configured in Foundation Fieldbus?
Control loops in Foundation Fieldbus are configured by linking function blocks in a device or across multiple devices. The input and output of the function blocks represent process variables and control actions, respectively.
How are alarms configured in a Foundation Fieldbus device?
Alarms in a Foundation Fieldbus device are configured by setting alarm limits on process variables. When the process variable exceeds the alarm limit, the device generates an alarm message that is sent to the host system.
Can the configuration of a Foundation Fieldbus device be copied to another device?
Yes, the configuration of a Foundation Fieldbus device can often be copied to another device, provided the devices are of the same type. This feature is useful for replacing a device or setting up multiple devices with the same configuration.
Can Foundation Fieldbus devices be configured to communicate with devices on other networks?
Yes, with the use of a gateway or linking device, Foundation Fieldbus devices can communicate with devices on other networks, such as Modbus, PROFIBUS, or Ethernet networks. The gateway translates between the Foundation Fieldbus protocol and the protocol of the other network.
What factors need to be considered when configuring the Macro Cycle in Foundation Fieldbus?
When configuring the Macro Cycle in Foundation Fieldbus, the control requirements, network communication capacity, and the performance of the devices should be considered. The Macro Cycle should be short enough for the control function, but long enough to allow for all devices to communicate.
What is the role of the “Device Description Language” (DDL) in the configuration of Foundation Fieldbus devices?
The Device Description Language (DDL) is used to create the Device Description (DD) for a Foundation Fieldbus device. The DD describes the device’s parameters, functions, and user interface, which are used by the host system for device configuration.
How are function blocks linked in Foundation Fieldbus?
Function blocks in Foundation Fieldbus are linked by defining the output of one function block as the input of another function block. This can be done within a device or across multiple devices.
What parameters can be calibrated in a Foundation Fieldbus device?
The parameters that can be calibrated in a Foundation Fieldbus device depend on the type of device. For a sensor, it might be the measurement range, zero and span, or compensation parameters. For a controller, it might be the control parameters like gain, integral time, or derivative time.
How is a Foundation Fieldbus pressure transmitter calibrated?
Calibration of a Foundation Fieldbus pressure transmitter involves applying a known pressure to the transmitter and adjusting the transmitter’s output to match the known pressure. The zero and span parameters in the transmitter are set to define the range of measurement.
What tools are required to configure a Foundation Fieldbus device?
To configure a Foundation Fieldbus device, you typically need a host system with a configuration tool, a Fieldbus interface card, and the Device Descriptions (DDs) for the devices. The configuration tool allows you to set parameters, configure function blocks, and establish control loops.
How is a Foundation Fieldbus network configured?
Configuration of a Foundation Fieldbus network involves setting up the devices, defining the communication schedule, and establishing the control strategy. This is typically done using a configuration tool in a host system.
Can Foundation Fieldbus devices be remotely calibrated?
Yes, Foundation Fieldbus devices can be remotely calibrated via the host system. The device’s parameters can be adjusted based on a comparison with a known reference value.
What’s the process of configuring the Link Active Scheduler (LAS) in Foundation Fieldbus?
Configuring the Link Active Scheduler (LAS) in Foundation Fieldbus involves setting the Macro Cycle time, assigning the devices to time slots, and defining the communication schedule. The LAS ensures synchronized communication in the network.
How is a control loop tuned in a Foundation Fieldbus device?
Tuning a control loop in a Foundation Fieldbus device involves adjusting the control parameters like gain, integral time, and derivative time. This is done based on the dynamics of the process to achieve stable and optimal control performance.
Can the configuration of a Foundation Fieldbus device be saved for future use?
Yes, the configuration of a Foundation Fieldbus device can be saved in a file for future use. This is useful for backing up the configuration, duplicating the configuration on another device, or restoring the configuration after a device replacement.
How is a linking device configured in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
A linking device in a Foundation Fieldbus network is configured by setting its network parameters, defining the mapping of data between the fieldbus network and the other network, and establishing the communication schedule. The linking device translates between the Fieldbus protocol and the protocol of the other network.
How are safety functions configured in a Foundation Fieldbus device?
Safety functions in a Foundation Fieldbus device are configured by setting safety parameters and defining safety actions. This could include setting safety limits on process variables and defining actions to be taken when the limits are exceeded, such as shutting down a process or activating an alarm.
What could be the reason if a Foundation Fieldbus device is not communicating?
Several reasons could cause a Foundation Fieldbus device to stop communicating. These include a physical disconnection, power failure, device failure, incorrect configuration, or network interference. Troubleshooting typically involves checking each of these potential causes.
How can you troubleshoot a power supply issue in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Troubleshooting a power supply issue in a Foundation Fieldbus network involves checking the voltage level, looking for short circuits, ensuring proper grounding, and checking for damage to the power supply unit. A multimeter can be used for these checks.
How would you identify a faulty device in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Identifying a faulty device in a Foundation Fieldbus network involves checking for unusual device behavior, such as erratic readings, lack of response, or error messages. Diagnostic tools provided by the host system or third-party software can be used to identify and isolate faulty devices.
What steps can you take to resolve communication conflicts in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Communication conflicts in a Foundation Fieldbus network can often be resolved by checking the configuration of the devices and the Link Active Scheduler (LAS). Ensuring that devices have unique addresses and that the communication schedule does not cause conflicts, are important steps.
How would you troubleshoot network noise in a Foundation Fieldbus system?
Network noise in a Foundation Fieldbus system can be diagnosed by using a network analyzer to identify the source of the noise. This could be electrical interference, physical damage to the cable, or improper grounding. The corrective measures depend on the source of the noise.
How can you resolve device configuration errors in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Device configuration errors in a Foundation Fieldbus network can be resolved by using the host system to check and correct the configuration. This includes checking device parameters, function block configuration, and control strategy.
What should you do if a Foundation Fieldbus device fails to calibrate?
If a Foundation Fieldbus device fails to calibrate, first check the device’s manual for calibration procedures and follow them accurately. If the problem persists, check the device’s health status using diagnostic tools or contact the device manufacturer for support.
How can you determine if there’s a problem with the Link Active Scheduler (LAS) in a Foundation Fieldbus network?
Problems with the Link Active Scheduler (LAS) in a Foundation Fieldbus network can often be identified by symptoms such as erratic network behavior, communication conflicts, or devices failing to communicate. Diagnostic tools or the host system can be used to check the status and configuration of the LAS.
What might cause a Foundation Fieldbus network to slow down?
A slowdown in a Foundation Fieldbus network can be caused by several factors, including network overload, communication conflicts, device malfunction, network noise, or issues with the Link Active Scheduler (LAS). Troubleshooting involves identifying and addressing these potential causes.
How can you troubleshoot issues with function blocks in a Foundation Fieldbus device?
Troubleshooting function block issues in a Foundation Fieldbus device involves checking the configuration of the function blocks, ensuring that they are linked correctly and that their parameters are set properly. Diagnostic tools or the host system can be used for these checks.
Read Next:















Comments
2
i want to calibrate a pressure transmitter in lab. i connected the device to fieldbus barrier and power on the barrier but the device does not indicate the press. value
but if i connect the 475 communicator the device start to indicate
i do not know why this happened. and what i can do to remove this problem as device work without 475 communicator
valuable information in forms of questions and answers.