Solenoid Valve Testing Procedure
What is a Solenoid Valve?
A solenoid valve is an electrically operated device, whose function is essential in circuits that regulate the flow of all types of fluids.
A wide range of solenoid applications makes it necessary to know its characteristics and operation in order to handle it properly.
Basics of Solenoid Valve
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device designed to on/off flow control that circulates through a conduit. Normally, it only has open and closed positions.
Solenoid valves are made up of an assembly consisting of a coil, a plunger, an electrical connector, and a guide tube. It converts electrical energy into a mechanical pull/push action.
In normally closed valves, a return spring keeps the plunger pressed against the orifice, preventing the passage of flow. When the solenoid coil is energized, the resulting magnetic field causes the plunger to rise, thus allowing flow.
Solenoids are operated by either DC or AC coils.
Types of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves are available in wide varieties in the market and can be ordered based on individual application requirements. They are DC or AC voltage-operated. They are directly operated or pilot-actuated. Available with 2way, 3-way, and 4-way ports.
2-way solenoid – has two pipe connections, in which one is the inlet, and another one is an outlet. The 3-way solenoid has three pipe connections and two orifices. These valves are used either to divert the flow or mix fluids. The 4-way solenoid consists of five ports- one for inlet air supply, two outlets (cylinder) ports, and one exhaust port.
Tools Required for Solenoid Valve Test
- Air filter regulator (AFR)
- 24 V/110V/230V electrical supply
- Test pressure gauge
- Multimeter (optional)
- Ball valve at SOV outlet
Solenoid Valve Testing Procedure
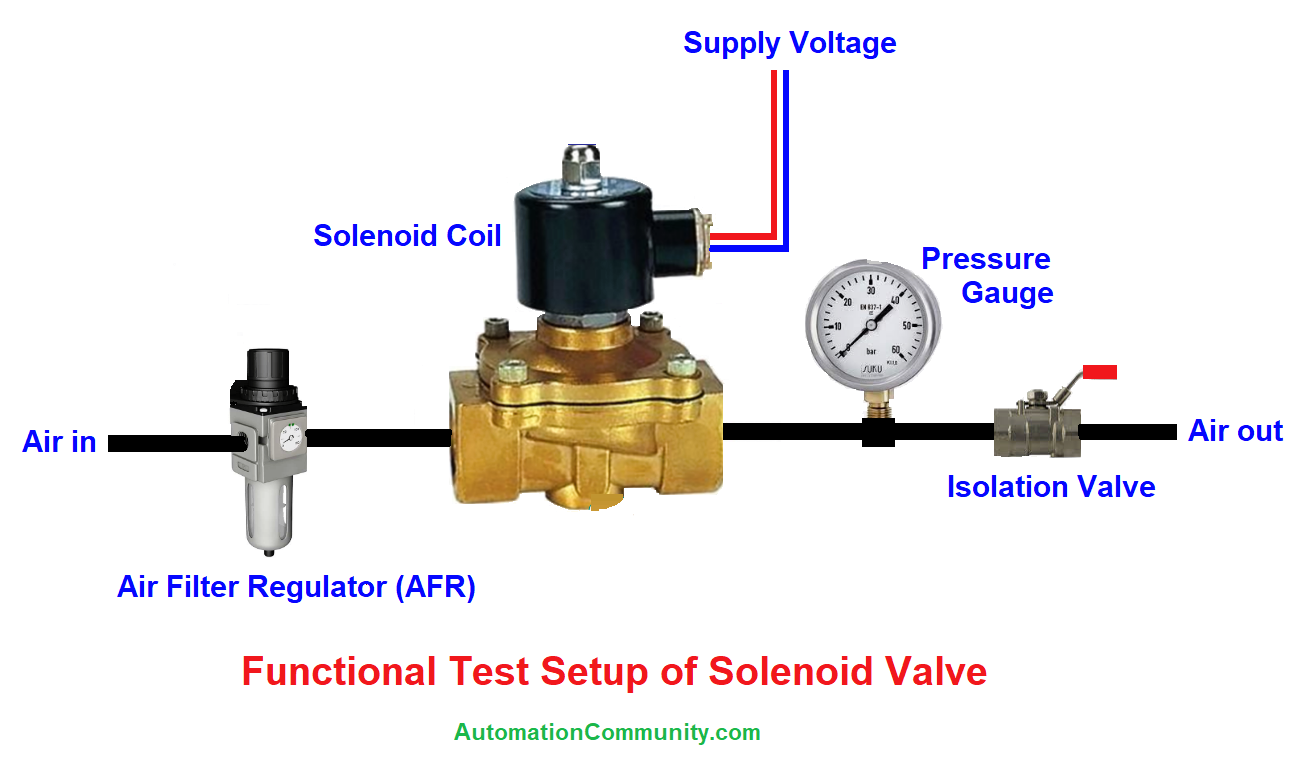
1. The solenoid valve inlet port is connected to the upstream flow and outlet to the downstream line as shown in the above figure.
2. To carry out an operation test on a solenoid valve, it is necessary to make sure that the solenoid is in good condition and working. Check the voltage rating on the label of the coil.
3. The coil is checked installed in the valve and applying a voltage to it to make the plunger actuation work, which will perform the function of opening or closing the valve as the case may be.
4. As shown in the following figure in a normally closed valve, we can test its operation by applying fluid to it, either water or air.
5. The pressure of the media that is to pass through the solenoid valve should not exceed the maximum pressure rating of the valve.
6. Once the flow is applied to a normally closed NC valve, it will not open until the coil is energized. The solenoid must be energized by supply voltage to perform this function.
7. Once we apply voltage to the solenoid, the valve opens and lets out the flow, we remove the voltage again and it should completely close the flow path.
If any of the steps mentioned above does not come out as described, it means that there is something wrong with either the diaphragm or the solenoid. To check it, it would have to be completely disassembled and checked piece by piece.
Keywords
Coil rating – DC coil power levels are measured in Watts, and AC coils are measured in VA.
Coil burnout – If the coil temperature limit is crossed, the coil becomes hot and burnout if continues for a longer time.
Chattering or humming noise – In AC solenoids, the possibility of chattering. This is because of the little gap between the coil and plunger mechanism due to wear out.