Process Control Loop – Basic Instrumentation Questions
A process control loop is a fundamental concept in industrial automation and control systems. It refers to the continuous monitoring and adjustment of a process variable to maintain a desired output within specific limits. Process control loops are widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, chemical processing, power generation, and more.
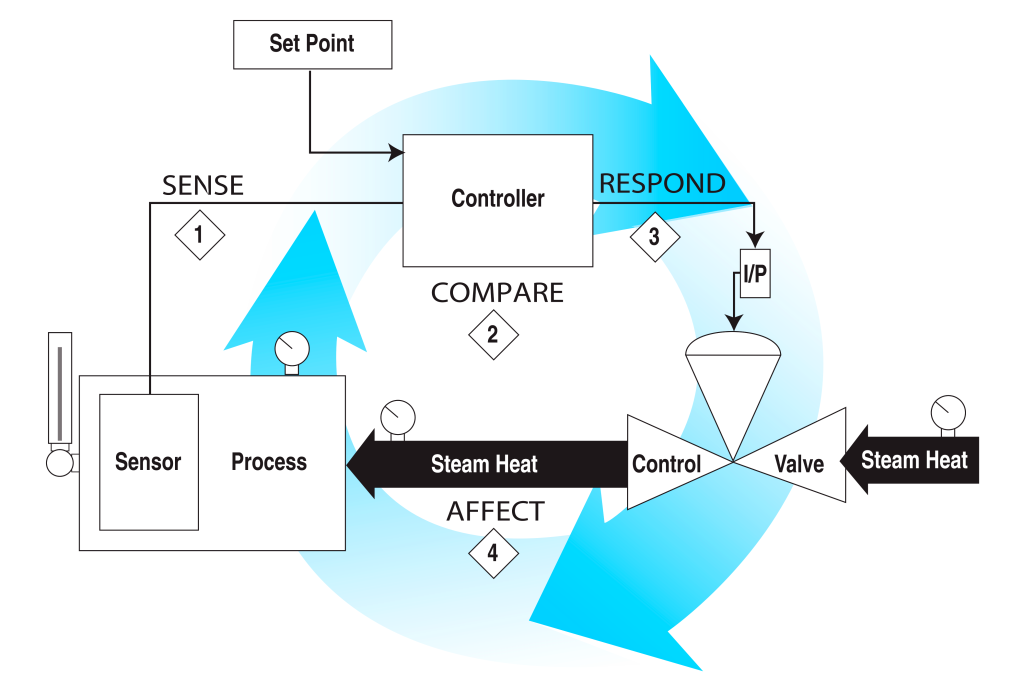
The primary components of a control loop include a measurement device (sensor or transmitter), a controller, and a final control element (actuator or control valve). The measurement device senses the process variable, such as temperature, pressure, level, or flow rate. The controller receives this measurement and compares it to a desired setpoint, determining the necessary corrective action. The final control element adjusts the process to bring the output back to the desired setpoint.
Process control loops can be classified into two types: open-loop control and closed-loop control. Open-loop control does not utilize feedback from the process variable and relies solely on the programmed instructions. Closed-loop control, on the other hand, continuously monitors the process variable and adjusts the control output based on the feedback, ensuring accurate and stable control.
Process Control Loop
Explore a set of basic instrumentation questions related to process control loops. Learn about the components of a control loop, the difference between open-loop and closed-loop control, the role of sensors, controllers, and actuators in process control, and the importance of effective control loop tuning. Enhance your understanding of the fundamental concepts of process control and instrumentation in industrial automation.
Can you explain what a Control Loop is?
A Control Loop is a process management system designed to maintain a process variable at a desired set point. Each component in the loop works together to manage the system.
What are the key components of a Control Loop?
The main components of a Control Loop are the process, sensor or input device, controller, and the final control element or output device.
What is the purpose of a Process Variable (PV)?
The Process Variable (PV) is the current value that is being controlled in a process control loop. It represents the current state of the process.
What is a Set Point (SP) in a control loop?
A Set Point (SP) is the desired value for the process variable. It’s where you want your process to be.
Could you explain the role of the controller in a control loop?
The controller’s role is to receive the process variable, compare it with the set point, and adjust the output to bring the process variable as close as possible to the set point.
What is the function of the Final Control Element in a control loop?
The Final Control Element is the device that directly manipulates the process variable. Based on the controller’s output, it adjusts the process to maintain the process variable near the set point.
What are the types of control loop schemes available?
Control loop schemes can be categorized into two main types: Open Loop and Closed Loop. Open-loop controls act without considering the output’s effect, while closed-loop controls adjust based on the output.
What is a Feedback Control Loop?
A Feedback Control Loop is a type of Closed Loop control system that adjusts its output based on feedback from the process variable. It helps to reduce errors and maintain the process variable close to the set point.
What is a Feedforward Control Loop?
A Feedforward Control Loop is a type of control system that reacts to changes in the set point or disturbances before they affect the process variable. It is proactive and often used in conjunction with feedback control.
Can you explain what PID control is?
PID stands for Proportional, Integral, and Derivative. It is a type of feedback control where the controller adjusts its output based on current error (Proportional), accumulated past error (Integral), and prediction of future error (Derivative).
What is a cascade control loop?
A cascade control loop is a control scheme with two (or more) controllers, where the output of one controller (master) acts as the set point for another controller (slave). This structure is often used when a single controller can’t adequately control the process.
Can you explain the Proportional (P) component of a PID controller?
The Proportional component of a PID controller adjusts the output based on the current error, which is the difference between the set point and the process variable. The amount of adjustment is determined by the Proportional Gain.
What is the role of the Integral (I) component in a PID controller?
The Integral component of a PID controller considers the accumulation of past errors. It works to eliminate the residual steady-state error that the Proportional component can’t remove.
How does the Derivative (D) component work in a PID controller?
The Derivative component of a PID controller predicts future errors based on the rate of change of the error. It provides damping or anticipatory control, helping to minimize overshoot and system oscillations.
What is ‘tuning’ in the PID controller?
Tuning in a PID controller involves adjusting the Proportional Gain, Integral Time, and Derivative Time parameters to achieve the best control performance, such as the fastest response with minimal overshoot and oscillation.
What are some common methods of PID tuning?
Common methods of PID tuning include trial-and-error, Ziegler-Nichols, Cohen-Coon, and software-based optimization techniques.
What are Gain Margin and Phase Margin in a control loop?
Gain Margin and Phase Margin are measures of stability in a control loop. Gain Margin is the change in open loop gain required to make the system unstable, while Phase Margin is the change in phase shift required to make the system unstable.
What is a Bode plot and how is it used in control loop analysis?
A Bode plot is a graph of the magnitude and phase of a system’s frequency response. It’s used in control loop analysis to evaluate system stability and performance.
What is a Nyquist plot and how is it used in control loop analysis?
A Nyquist plot is a graphical representation of a system’s frequency response. It plots the gain and phase shift of a system as a function of frequency. It’s used to assess the stability and performance of control loops.
What is ‘Loop Oscillation’ and how can it be mitigated?
Loop Oscillation refers to the persistent periodic fluctuation of the process variable in a control loop. It can be mitigated by tuning the control loop, usually by reducing the controller gain or increasing the damping.
What is the role of a control valve in a control loop?
A control valve, typically acting as the final control element, regulates the flow of material (fluid, gas, granules) by varying the size of the passage through which the material passes. This directly influences the process variable.
What are some common types of sensors used in control loops?
Some common types of sensors include temperature sensors (like RTDs and thermocouples), pressure sensors, flow sensors, and level sensors. The choice of sensor depends on the specific process variable being controlled.
What does “loop checking” mean?
Loop checking is a process of verifying that a control loop is functioning correctly. It includes checking each component of the loop (sensor, controller, and final control element), as well as the communication between them.
What are some common problems that might occur in a control loop?
Some common problems include sensor failure or calibration drift, controller tuning issues, and problems with the final control element like valve stiction or hysteresis. Also, communication issues might disrupt the performance of the control loop.
What is a “dead time” in a control loop, and why is it important?
Dead time is the delay between when a change occurs in the system (such as a change in set point or a disturbance) and when the effects of that change start to be observed. Too much dead time can make control difficult and potentially destabilize the loop.
What are some control strategies that can deal with dead time?
Some strategies include using a Smith Predictor, which explicitly accounts for dead time in its control algorithm, or implementing model predictive control, which can handle dead time by predicting future outputs.
What is a “split range” control loop?
In a split range control loop, two or more final control elements (like valves) are controlled by a single controller. The control elements operate in sequence or overlap, allowing finer control over a wider range of operations.
What is “ratio control”?
Ratio control is a strategy where the set point of a control loop is determined by the measurement from another control loop. It’s commonly used in situations where the ratio of two process variables needs to be maintained.
What is a “PLC”, and how is it used in control loops?
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a ruggedized digital computer used for the automation of industrial processes. In control loops, a PLC can serve as the controller, processing inputs from sensors and adjusting outputs to final control elements.
What are some advantages of digital controllers over analog controllers?
Digital controllers offer advantages like easier tuning, more complex control algorithms, better disturbance rejection, easier integration with other systems, and data logging capabilities.
What is a “lead-lag” controller and when is it used?
A lead-lag controller is a type of compensator used in control systems that can anticipate the future behavior of the process (lead) and also consider the past behavior (lag). It’s typically used to improve system stability and response time.
What is a “two-step” or “on-off” control?
Two-step or on-off control is the simplest type of control where the output is either fully on or fully off with no intermediate states. This type of control is commonly used where precise control is not required.
What is an “override control”?
Override control is a control strategy where multiple controllers monitor different process variables, but only the controller observing the most critical condition is allowed to control the process at any given time.
What is the “process gain” in a control loop?
Process gain is the ratio of the change in the process variable to a change in the control variable. It provides a measure of how sensitive the process is to changes in the control variable.
Can you explain the concept of “process dynamics”?
Process dynamics refers to the way a process changes over time in response to inputs, disturbances, and changes in operating conditions. It’s important in control loop design to ensure stability and desired performance.
What is “self-regulation” in a process control context?
Self-regulation refers to a process’ ability to return to a steady state after a disturbance without the need for corrective action from the controller. Examples include a tank draining under gravity or a heated object cooling to room temperature.
What is a “disturbance” in a control loop?
A disturbance is an undesired input or condition that affects the process variable. It can come from within the process (like equipment wear or scaling) or from the environment (like changes in ambient temperature or supply pressure).
What is the difference between “direct” and “reverse” acting control?
In direct-acting control, an increase in the controller input causes an increase in the controller output. In reverse-acting control, an increase in the controller input causes a decrease in the controller output.
What is “hysteresis” in the control loop?
Hysteresis refers to a situation where the value of the process variable depends not only on the current value of the control variable but also on its past values. It’s often associated with mechanical systems like valves where friction or backlash can cause a lag between input and output.
What is a “servo system” and how does it relate to control loops?
A servo system is a type of control system that uses feedback to precisely control the position or speed of output. In a way, it’s a specialized type of control loop often used in robotics and CNC machinery.
What is a ‘jacketed control loop’?
A jacketed control loop refers to a setup where one control loop is ‘nested’ or ‘jacketed’ within another. For example, in a temperature control loop for a jacketed vessel, the vessel’s temperature might be controlled by adjusting the temperature of the fluid in the jacket, which is controlled by a separate loop.
What is a ‘control loop audit’?
A control loop audit is a comprehensive review and analysis of a control loop’s performance. It can help identify issues like tuning problems, sensor issues, valve problems, or process changes that might affect performance.
How does a ‘fuzzy logic controller’ work?
A fuzzy logic controller uses fuzzy logic instead of traditional Boolean logic to make decisions. Fuzzy logic allows for degrees of truth, which can make a controller more adaptable and effective when the process is complex or poorly understood.
What is ‘adaptive control’?
Adaptive control is a control strategy where the controller parameters are adjusted automatically in response to changes in the process or environment. This can help maintain control performance in the face of unknown or changing process dynamics.
What is the difference between ‘open loop’ and ‘closed loop’ control?
In open loop control, the controller output is determined solely based on the set point and does not consider the process variable. In closed-loop control, the controller output is adjusted based on the difference between the set point and the process variable, which helps compensate for disturbances and process changes.
What are ‘interacting control’ and ‘non-interacting control’ in control loops?
In interacting control, changing one controller parameter (like proportional gain) affects the other parameters (like integral time). In non-interacting control, the controller parameters can be adjusted independently.
What is a ‘decoupling controller’?
A decoupling controller is used in multi-input, multi-output (MIMO) systems where the inputs and outputs are not independent. The decoupling controller ‘decouples’ the system so that changes to one input mainly affect only one output, making the system easier to control.
What is ‘process deadband’ in control loops?
Process deadband refers to a range of control variable values within which the process variable does not change. This can be due to the physical properties of the process, like static friction in a valve.
What is a ‘tuning window’ in a control loop?
A tuning window is a range of controller parameters that provide acceptable control performance. A wide tuning window can make a control loop easier to tune and more robust to changes in process dynamics.
How can ‘overshoot’ be minimized in a control loop?
Overshoot can be minimized by careful tuning of the controller. Techniques might include reducing the proportional gain, increasing the damping via the derivative term, or adding a controller with anticipatory control like a lead-lag compensator.
What does the term ‘settling time’ mean in control loop terminology?
Settling time is the time it takes for the process variable to reach and stay within a certain range of the desired final value after a change in set point or a disturbance.
What are the components of a ‘PID controller’?
A PID controller has three components: a proportional component that responds to the current error, an integral component that responds to the accumulation of past error, and a derivative component that predicts future error based on its rate of change.
What is ‘manual control’?
In manual control, a human operator adjusts the control variable based on observation of the process variable. While less precise and consistent than automatic control, manual control can be useful in certain situations, like startup/shutdown, or when dealing with complex processes.
Can you describe what a ‘stationary process’ is?
A stationary process is a process where the statistical properties like mean, variance, and autocorrelation are constant over time. Stationarity can be a useful assumption when designing or tuning a control loop.
What is a ‘transfer function’ in a control loop?
The transfer function is a mathematical representation that characterizes the relationship between the input and output of a system in the frequency domain. It is a key concept in control theory and is used to analyze and design control systems.
How can ‘integral windup’ be prevented in a PID controller?
Integral windup can be prevented by techniques like clamping the integral term when the controller output reaches its limits, or by temporarily switching to PI or PD control when the process variable is far from the set point.
What does ‘gain scheduling’ refer to in a control system?
Gain scheduling is a technique where the controller parameters are automatically adjusted based on the current operating conditions. This allows a single controller to perform well over a wide range of conditions.
What is a “ratio control” system?
Ratio control is a system where the control variable is adjusted to maintain a set ratio to another process variable. This is commonly used in processes where the correct proportion of inputs is critical, such as blending or mixing processes.
What is meant by “process capacity” in terms of control loops?
Process capacity refers to the maximum rate at which a process can operate effectively. In control terms, it often refers to the maximum change in output that a control system can cause in a given time.
What is the significance of “phase margin” in control loops?
Phase margin is a measure of system stability in frequency domain analysis. It is the change in phase required to make the system unstable. Larger phase margins indicate greater stability.
What is “split range control” in control systems?
Split range control refers to a strategy where the output of a single controller is used to manipulate two or more control valves. This is usually done when a single control valve cannot handle the entire range of control.
Can you explain “time constant” in relation to control loops?
Time constant is a measure of the speed of response of a system. It is typically defined as the time it takes for a system to reach about 63.2% of its total change after a step input.
What is “process noise” in a control loop?
Process noise refers to random variations in the process variable that are not caused by the control variable. It can be due to a number of factors, including sensor noise, minor process fluctuations, and digital sampling noise.
What is a “hybrid control system”?
A hybrid control system is one that combines different types of control strategies. For example, it might combine discrete control (on/off) with continuous control (PID), or combine different types of continuous control like feedforward and feedback.
What is a “derivative kick” in a PID controller?
A derivative kick is a sudden change in the output of a PID controller caused by a sudden change in set point. This is because the derivative term responds to the rate of change of the error, which can be very large when the set point changes suddenly.
What is a “state-space” representation of a control system?
The state-space representation is a mathematical model of a physical system as a set of input, output and state variables related by first-order differential equations. It is used in modern control methods like optimal control or state feedback control.
Can you explain the concept of “system identification” in control systems?
System identification is a process of creating a mathematical model of a system based on experimental data. This model can then be used for control design, performance analysis, or simulation.
What is “lead-lag compensation” in control systems?
Lead-lag compensation is a control strategy where a controller adds phase lead or lag to a system in order to improve performance. A phase lead compensator can improve system speed and stability, while a phase lag compensator can reduce steady-state error.
What is a “bumpless transfer” in a control system?
Bumpless transfer is the smooth transition from manual to automatic control (or vice versa) without causing a disturbance to the process. This is usually achieved by ensuring the controller output matches the manual output at the time of the transfer.
What is a “control valve” and what role does it play in control loops?
A control valve is a power-operated device used to modulate or control the flow of fluid. In a control loop, the control valve is the final control element that adjusts the process based on the controller output.
What is a step controller?
A two-step controller, or step controller, is a simple type of controller that has only two outputs. It switches from one output to the other when the process variable crosses the set point. This is often used in on-off control systems.
What is “overshoot” in a control loop?
Overshoot is the amount by which the process variable exceeds its final steady-state value in response to a change in the set point or a disturbance. It is often caused by excessive controller gain or insufficient damping.
What is “underdamping” in a control loop?
Underdamping in a control loop leads to oscillatory behavior, where the process variable exceeds and then undershoots the set point repeatedly. This can be caused by too high controller gain or too low damping ratio.
What is a “zero” in control system terminology?
In control system terminology, a zero is a value of the input variable that results in a zero output. In a transfer function, a zero is a value of the frequency variable that makes the transfer function zero.
What is “anticipatory control” in a control loop?
Anticipatory control is a strategy where the controller predicts future disturbances and adjusts the control variable in advance to counteract them. Feedforward control is a type of anticipatory control.
What is the “control algorithm” in a control loop?
The control algorithm is the mathematical logic used by the controller to determine its output based on the current error. The most common control algorithm in industrial applications is the PID algorithm.
What is the role of a “transmitter” in a control loop?
A transmitter in a control loop is a device that measures a process variable and sends a standardized signal (usually 4-20 mA or 0-10 V) to the controller. It’s an essential part of the sensing phase of the control loop.
What is “nonlinearity” in control systems?
Nonlinearity refers to a system behavior where the output is not directly proportional to the input. Many real-world processes are nonlinear to some degree, which can make control more challenging.
What is the “Nyquist criterion” in control systems?
The Nyquist criterion is a graphical method for determining the stability of a control system. It involves plotting the system’s frequency response and checking whether it encircles a certain point in the complex plane.
What is “adaptive control” in control systems?
Adaptive control is a strategy where the controller parameters are automatically adjusted in real-time based on changes in the process characteristics. This allows the control system to maintain good performance even when the process is changing.
What is a “pole” in control system terminology?
In control system terminology, a pole is a value of the frequency variable that makes the system’s transfer function go to infinity. The poles of a system can have a significant effect on its stability and response characteristics.
What is a “correction factor” in control systems?
A correction factor is a multiplier used to adjust a measurement or control output to account for some known deviation. For example, a temperature sensor might need a correction factor to account for calibration errors or sensor drift.
What is a “single-loop control system”?
A single-loop control system is a system with one controller and one feedback loop. The controller adjusts the control variable based on the error between the set point and the process variable. Most control systems in industry are single-loop systems.
What is “positive feedback” in a control loop?
Positive feedback in a control loop means that when the process variable deviates from the set point, the controller adjusts the control variable in the same direction as the deviation. This can lead to instability and is usually not desired in control systems.
What is the significance of the “Laplace transform” in control systems?
The Laplace transform is a mathematical tool used extensively in control system analysis and design. It transforms differential equations, which describe the system dynamics in the time domain, into algebraic equations in the complex frequency domain.
What is the “root locus method” in control systems?
The root locus method is a graphical technique used in control systems for analyzing the locations of the poles of the system as a controller parameter (usually the gain) is varied. It provides insight into system stability and transient response.
What is “fuzzy logic control”?
Fuzzy logic control is a type of control strategy that uses fuzzy set theory to handle situations where the system is complex or uncertain. Instead of requiring precise inputs and producing a definite output, it deals with ranges of values, providing a more flexible and adaptive control approach.
What is a “Smith predictor” in control systems?
A Smith predictor is a type of control structure that’s used to control processes with a significant amount of dead time. It includes a model of the process that predicts the effect of the control actions, which helps to compensate for the dead time.
What does “robust control” mean in control systems?
Robust control refers to the ability of a control system to maintain acceptable performance despite variations or uncertainties in the process parameters or disturbances. Robust control techniques are designed to achieve this property.
Read Next: