Temperature Transmitter Questions and Answers
A Temperature Transmitter is a device that plays a pivotal role in process control industries. It interprets data from temperature sensors, such as RTDs and thermocouples, and translates it into signals that can be easily read and interpreted by control units. Understanding the functions, types, and calibration of temperature transmitters is integral for professionals in instrumentation and industrial process control.
Temperature Transmitter Questions
Unlock a wealth of knowledge with our Temperature Transmitter Questions and Answers guide. Delve into key principles, operational aspects, calibration techniques, and more about these indispensable devices in process industries. This a must-read for students, engineers, and professionals seeking to enhance their understanding of temperature transmitters.
Can you explain what a temperature transmitter is?
A temperature transmitter is a device that converts the signal from a temperature sensor, like a thermocouple or RTD, into a standard signal that can be easily read and transmitted to a control system, such as a 4-20mA or digital signal.
How does a temperature transmitter improve signal quality?
Temperature transmitters improve signal quality by converting the low-level signal from the sensor into a high-level signal. This reduces the effects of electrical noise and allows the signal to be transmitted over long distances without degradation.
Can you differentiate between an RTD and a thermocouple?
RTDs and thermocouples are both types of temperature sensors. An RTD, or Resistance Temperature Detector, works by measuring the change in resistance of a metal, usually platinum, with temperature. A thermocouple generates a voltage that is proportional to the temperature difference between its two junctions.
What types of temperature transmitters are there?
There are several types of temperature transmitters, including head-mounted, DIN-rail-mounted, and field-mounted. Head-mounted transmitters are typically installed in the sensor connection head. DIN-rail transmitters are designed for mounting on standard DIN rails. Field-mounted transmitters are installed in the field near the sensor and often have a display for local reading.
How do you calibrate a temperature transmitter?
Calibration typically involves comparing the output of the transmitter with a known reference value at specific temperatures. This can be performed using a temperature calibrator. The transmitter settings can then be adjusted as necessary to match the reference.
What is the purpose of linearization in a temperature transmitter?
Linearization is the process of converting the non-linear signal from the temperature sensor into a linear signal. This is necessary because the relationship between temperature and resistance in an RTD or the voltage in a thermocouple is not linear.
Can you explain the working of a two-wire temperature transmitter?
A two-wire temperature transmitter works by supplying power to the transmitter and reading the output signal over the same two wires. The output is typically a 4-20mA current signal, where 4mA corresponds to the minimum temperature and 20mA corresponds to the maximum.
What role does a temperature transmitter play in process control?
In process control, a temperature transmitter is used to accurately measure and transmit the temperature of a process. This information can be used by the control system to maintain the process at the desired temperature, by adjusting the control elements based on the measured temperature.
What is the typical accuracy of a temperature transmitter?
The accuracy of a temperature transmitter depends on the specific model and conditions, but it can typically be in the range of ±0.1% to ±1% of the reading or span.
How does a temperature transmitter deal with cold junction compensation?
In a thermocouple, the cold junction is where the thermocouple wires are connected to the transmitter. The temperature at this junction affects the output of the thermocouple. A temperature transmitter typically has a built-in temperature sensor at the cold junction and uses this to compensate for its effect.
What is the significance of the 4-20mA signal in a temperature transmitter?
The 4-20mA signal is a standard signal used in industrial automation. It is proportional to the measured temperature, with 4mA representing the minimum and 20mA representing the maximum. This signal can be transmitted over long distances without significant loss of accuracy or susceptibility to electrical noise.
What is a smart temperature transmitter?
A smart temperature transmitter is a type of transmitter that has additional functionality beyond basic signal conversion. This can include digital communication, diagnostics, multiple inputs, and programmability.
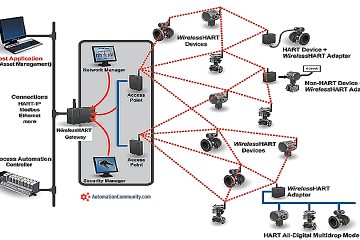
How does a temperature transmitter use a Hart protocol?
HART protocol is a communication protocol used in industrial automation. In a temperature transmitter, it allows for two-way communication between the device and a control system. This enables remote configuration, calibration, diagnostics, and access to additional information such as device status and diagnostics.
What is a thermowell and what role does it play in temperature measurement?
A thermowell is a protective tube that houses the temperature sensor, protecting it from the process media, pressure, flow-induced forces, and chemical effects. It allows for the removal of the temperature sensor without affecting the process.
How does ambient temperature affect a temperature transmitter?
Ambient temperature can affect a temperature transmitter in several ways. It can affect the electronics in the transmitter, leading to drift or changes in performance. For thermocouples, it also affects the cold junction compensation. Many transmitters have compensation mechanisms to reduce these effects.
What is the difference between temperature transmitters and temperature switches?
A temperature transmitter is a device that measures temperature and transmits the measurement as a signal to a control system. A temperature switch, on the other hand, is a device that changes state when a specific temperature is reached, usually to trigger some action, like turning on a fan or sounding an alarm.
How do you specify the range of a temperature transmitter?
The range of a temperature transmitter is specified based on the minimum and maximum temperatures that it needs to measure. This is determined by the conditions in the process and the capabilities of the temperature sensor.
What is an intrinsically safe temperature transmitter?
An intrinsically safe temperature transmitter is designed to be safe for use in hazardous areas where there may be flammable gases or dust. It does this by limiting the electrical and thermal energy in the device to a level below what could ignite the specific hazardous material.
What is the role of a temperature transmitter in a boiler control system?
In a boiler control system, a temperature transmitter is used to accurately measure the temperature of the water or steam. This information is used by the control system to maintain the desired temperature, by adjusting the firing rate of the boiler based on the measured temperature.
What are common problems that can occur with temperature transmitters?
Some common problems with temperature transmitters can include incorrect readings, loss of signal, and drift over time. These can be due to issues like sensor failure, wiring problems, environmental effects, or a need for calibration.
How would you troubleshoot a temperature transmitter that is giving incorrect readings?
Troubleshooting could involve several steps. You might first check the wiring connections and the integrity of the sensor. Then, verify the calibration of the transmitter by comparing it with a known reference. If the transmitter is still not working correctly, it might need repair or replacement.
What can cause a temperature transmitter to fail?
Temperature transmitters can fail for several reasons, such as electrical surge, physical damage, prolonged exposure to extreme conditions, failure of the sensor, or problems with the power supply.
What types of temperature sensors can be used with a temperature transmitter?
Common types of temperature sensors used with temperature transmitters include Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), thermocouples, and thermistors. The choice depends on the requirements of the application, including the temperature range, accuracy, and environmental conditions.
What are the basic components of a temperature transmitter?
The basic components of a temperature transmitter include the input circuit for the temperature sensor, the signal conversion and linearization circuitry, and the output circuit. There may also be additional components for functions like digital communication, display, and diagnostics.
How do you configure a temperature transmitter?
Configuration of a temperature transmitter typically involves setting the type of sensor, the range of temperatures, and the output signal. This can be done using buttons on the device, with a handheld communicator, or through a computer interface.
What are the effects of sensor failure on a temperature transmitter?
Sensor failure can cause the temperature transmitter to give incorrect readings or no reading at all. Many transmitters have diagnostics that can detect sensor failures and alert the user.
What is the difference between a two-wire and a four-wire temperature transmitter?
A two-wire transmitter uses the same wires for the power supply and signal output, while a four-wire transmitter uses separate wires for the power supply and output signal. Four-wire transmitters can offer advantages in terms of response time and accuracy, but they require more wiring.
What can cause drift in a temperature transmitter?
A drift in a temperature transmitter can be caused by the aging of components, temperature changes, or electrical noise. Regular calibration can help to minimize drift.
How do you verify the calibration of a temperature transmitter?
Calibration can be verified by comparing the output of the transmitter at specific temperatures with a known reference. If the output is within the specified accuracy of the reference, then the calibration is verified.
What are the methods for temperature transmitter calibration?
Temperature transmitter calibration can be done using a temperature calibrator, which generates precise temperature values for comparison with the transmitter output. Another method is by comparing the transmitter output with a reference sensor in a temperature-controlled bath.
Can a temperature transmitter be used in a hazardous area?
Yes, there are temperature transmitters designed for use in hazardous areas. They have special safety features, such as intrinsic safety or explosion-proof housings, to prevent sparking or excessive heat generation that could ignite flammable materials.
How can you increase the lifespan of a temperature transmitter?
Regular maintenance and calibration can help to increase the lifespan of a temperature transmitter. It’s also important to use the transmitter within its specified operating conditions and protect it from extreme environments, electrical surges, and physical damage.
What does it mean if a temperature transmitter is giving a 4mA signal?
In a 4-20mA signal used by many temperature transmitters, a 4mA signal usually represents the lower end of the measurement range. If the transmitter is constantly outputting 4mA, it could mean that the process is at its minimum temperature or that there’s a problem with the sensor or transmitter.
How does a temperature transmitter compensate for wire resistance in a 3-wire RTD connection?
In a 3-wire RTD connection, two wires are connected to one end of the RTD and one wire to the other end. The transmitter measures the resistance of two wires and subtracts it from the total, leaving the resistance of the RTD, which is proportional to temperature.
What is a fieldbus temperature transmitter?
A fieldbus temperature transmitter is a type of transmitter that uses digital fieldbus communication protocols, such as Foundation Fieldbus or Profibus. This allows for two-way communication between the transmitter and the control system, providing more information and greater flexibility.
What are the advantages of using a temperature transmitter over a direct sensor connection?
A temperature transmitter can offer several advantages over a direct sensor connection. These include improved signal quality, long-distance signal transmission, linearization of the sensor signal, cold junction compensation for thermocouples, and compatibility with industrial control systems.
What is a temperature transmitter with a built-in sensor?
Some temperature transmitters have a built-in sensor, providing an integrated solution for temperature measurement. These can be used when it is convenient to have the sensor and transmitter in a single package, but they may not be suitable for all applications.
Read Next: