What is a Marshalling Cabinet? Design, Types, Advantages
In this article, you will learn the basics of a marshalling cabinet, design considerations, types, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is a Marshalling Cabinet?
A marshalling cabinet is a type of electrical enclosure that is used to organize and terminate field wiring in an industrial process control system. A marshalling cabinet is typically used in systems that have a large number of input and output (I/O) points, such as programmable logic controllers (PLC) and distributed control systems (DCS).
The purpose of a marshalling cabinet is to provide a central location for connecting field devices, such as sensors and actuators, to the control system. A marshalling cabinet allows the field wiring to be organized and protected, and it makes it easier to troubleshoot and maintain the system.
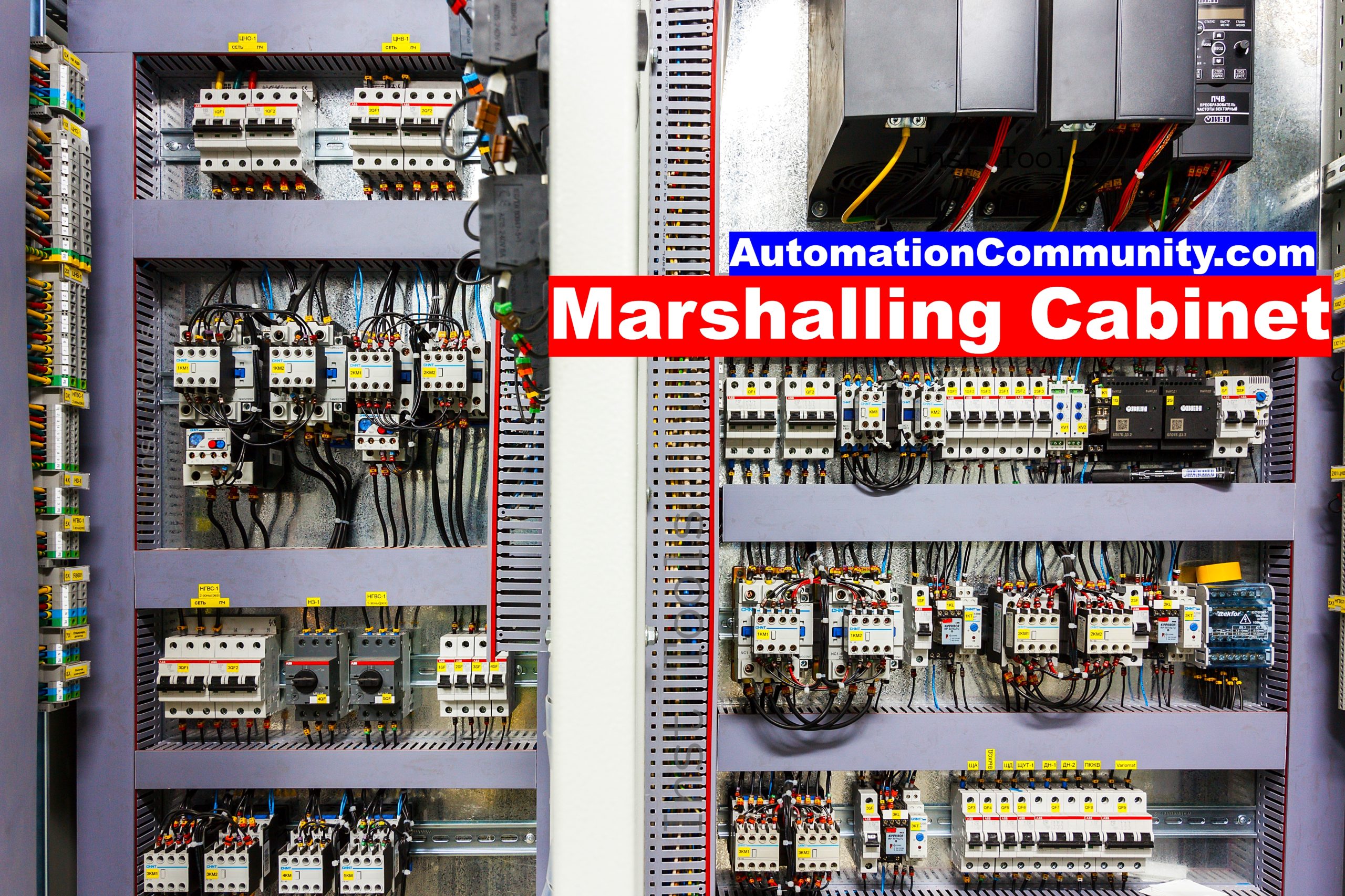
A marshalling cabinet typically contains a series of terminal blocks or connectors that are used to terminate the field wiring.
A marshalling cabinet may also include devices such as fuses, circuit breakers, and grounding points. Marshalling cabinets are typically located close to the field devices (such as local control rooms) they serve, and they are often located in areas that are easily accessible for maintenance and repair.
Design of Marshalling Panel
The main purpose of a marshalling cabinet is to organize and connect the field instrumentation signals, such as process sensors and actuators, to the control system.
Some key skills and considerations for designing marshalling cabinets include:
- Familiarity with the types of field instrumentation and the corresponding signal types, such as 4-20mA, 0-10V, etc.
- Knowledge of the control system and the types of input/output (I/O) modules required for connecting to the field instrumentation.
- Understanding of the electrical and electronic principles involved in signal transmission, such as grounding and shielding.
- Familiarity with the relevant industry standards, such as IEC 60664, NEMA 250, and UL 508, which govern the design and construction of marshalling cabinets.
- Experience with computer-aided design (CAD) software, such as AutoCAD, to create and edit detailed technical drawings of the cabinet layout and wiring.
- Knowledge of the physical requirements of the marshalling cabinet, such as size, weight, and environmental conditions.
- Strong problem-solving and analytical skills to troubleshoot and debug issues that may arise during the design and implementation phases.
- Strong communication and collaboration skills to work with other engineers, technicians, and stakeholders to ensure that the marshalling cabinet design meets the project requirements and specifications.
Components of a Marshalling Cabinet
A marshalling cabinet typically includes a number of different components that are used to organize, protect, and connect the field instrumentation signals to the control system.
Some common components found in a marshalling cabinet include:
- Terminal blocks: These are used to connect the field instrumentation signals to the control system. They typically include screw terminals for connecting wires and may include built-in jumpers for easy cross-wiring.
- Wiring ducts: These are used to organize and protect the wires that run between the field instrumentation and the control system. They typically include a cover to protect the wires from damage and to reduce the risk of accidental contact.
- Relays and contactors: These are used to switch high-voltage or high-current signals in the marshalling cabinet. They are typically controlled by low-voltage signals from the control system.
- Fuses and Circuit breakers: These are used to protect the control system and the field instrumentation from electrical damage in case of an overcurrent.
- Signal isolators and signal conditioners: These are used to convert or isolate different types of signals in the marshalling cabinet. For example, a signal isolator can be used to electrically isolate two sections of the marshalling cabinet, while a signal conditioner can be used to convert a low-level signal from a sensor into a higher-level signal that can be read by the control system.
- Power Supplies: The marshalling cabinet includes power supplies that convert the incoming electrical power into the necessary voltage and current for the control system and the field instrumentation.
- PLC or DCS I/O modules: These are used to connect the field instrumentation signals to the control system. They typically include connectors for connecting to the field instrumentation and may include built-in signal conditioning and isolation. (These modules may be provided in a separate panel such as a system cabinet)
- Seismic and vibration isolation mounts: These are used to isolate the cabinet and its contents from seismic and vibration forces, to help protect the cabinet and its contents during an earthquake or other seismic event.
- Enclosures: Marshalling cabinets typically include an enclosure that protects the internal components from dust, moisture, and other external factors.
Types of Marshalling Cabinet
Marshalling cabinets come in a variety of types, each designed to meet specific needs and requirements. Some common types of marshalling cabinets include:
- General purpose marshalling cabinets: These are the most common type of marshalling cabinets, and are used in a wide range of applications. They typically include terminal blocks, wiring ducts, and other basic components for connecting and organizing the field instrumentation signals.
- Intrinsically safe marshalling cabinets: These are designed to be used in hazardous locations, where there is a risk of explosion or fire. They include intrinsic safety barriers that isolate and limit the electrical energy in the cabinet to prevent ignition of flammable gases, dusts or fibers.
- Seismic marshalling cabinets: These are designed to withstand seismic forces and are typically used in areas where earthquakes are common. They include seismic isolation mounts and other components that help to protect the cabinet and its contents during an earthquake or other seismic event.
- Ex-proof marshalling cabinets: These are designed to be used in explosive environments, such as oil and gas production facilities. They include explosion-proof enclosures and other components that help to prevent explosions from occurring inside the cabinet.
- Compact marshalling cabinets: These are designed to be small and lightweight, making them easy to transport and install. They are typically used in applications where space is limited, such as offshore platforms or mobile equipment.
- Modular marshalling cabinets: These are designed to be easily expandable and customizable, making them well-suited for use in applications where the process or instrumentation may change over time. They typically include modular terminal blocks, wiring ducts, and other components that can be easily added or removed as needed.
- Remote marshalling cabinets: These are designed to be used in remote locations, where access to the cabinet may be difficult. They typically include features such as remote monitoring and control capabilities, and may include additional protection against harsh environmental conditions.
- Intelligent marshalling cabinets: These are designed to include intelligent electronics and communication interfaces, such as PLC, DCS, Ethernet, etc. They are used to provide a higher level of control and monitoring of the process, and to provide more advanced diagnostics and troubleshooting capabilities.
Advantages of Marshalling Cabinet
There are several advantages to using a marshalling cabinet in an industrial process control system:
- Improved organization: Marshalling cabinets provide a central location for organizing and terminating field wiring, making it easier to troubleshoot and maintain the system.
- Reduced installation time: Marshalling cabinets can significantly reduce the time and effort required to install a process control system by providing a central location for connecting field devices.
- Improved reliability: Marshalling cabinets help to protect the field wiring and control components from damage, improving the overall reliability of the system.
- Enhanced safety: Marshalling cabinets can help to improve safety by providing a secure location for electrical connections and by protecting against electrical hazards such as short circuits and ground faults.
- Simplified maintenance: Marshalling cabinets make it easier to access and maintain the control components and field wiring, reducing the downtime and maintenance costs of the system.
Marshalling cabinets offer a cost-effective and efficient means of organizing and protecting the field wiring and control components in an industrial process control system.
Disadvantages of Marshalling Cabinet
While marshalling cabinets offer many benefits, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider:
- Cost: Marshalling cabinets can be expensive, particularly for large systems with many I/O points.
- Size and weight: Marshalling cabinets can be large and heavy, making them difficult to install in some locations.
- Heat generation: Marshalling cabinets can generate heat due to the electrical components they contain, which may require the use of cooling systems or fans.
- EMI/RFI: Marshalling cabinets can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI), which can interfere with other electronic equipment.
- Voltage transients: Marshalling cabinets can produce voltage transients, which can cause damage to the control components or other equipment.
Read Next:














