Electrical Motor Nameplate Details
An electrical motor nameplate details provide important information to understand the construction characteristics and design parameters of the motor.
The motor is the most widely used type of equipment in an industry. It is important to understand the details of a motor properly; for getting it working. The details can be understood by its nameplate.
A motor nameplate, stickled on its body, gives all the information regarding its working. An engineer is required to interpret its understanding so that he can properly choose the one required in its application.
Motors run in two electrical standards – NEMA and IEC. NEMA stands for National Electrical Manufacturers Association. IEC stands for International Electrotechnical Commission.
Basically, NEMA is majorly used in North American markets and businesses relating to North America.
But, IEC is used in most parts of the world. Both have set a certain slot of standards for an electrical motor to run in the market. Without their ratings, no one will purchase a motor. That’s because that motor has not been approved by any standard and no one knows how it will function.
Motor Nameplate Details
Depending on the manufacturer and standard used, every motor nameplate will vary in some of the other parameters. But, we will discuss the most general used ones in the nameplate, which will help us to interpret it properly. A sample motor nameplate details image is shown below.
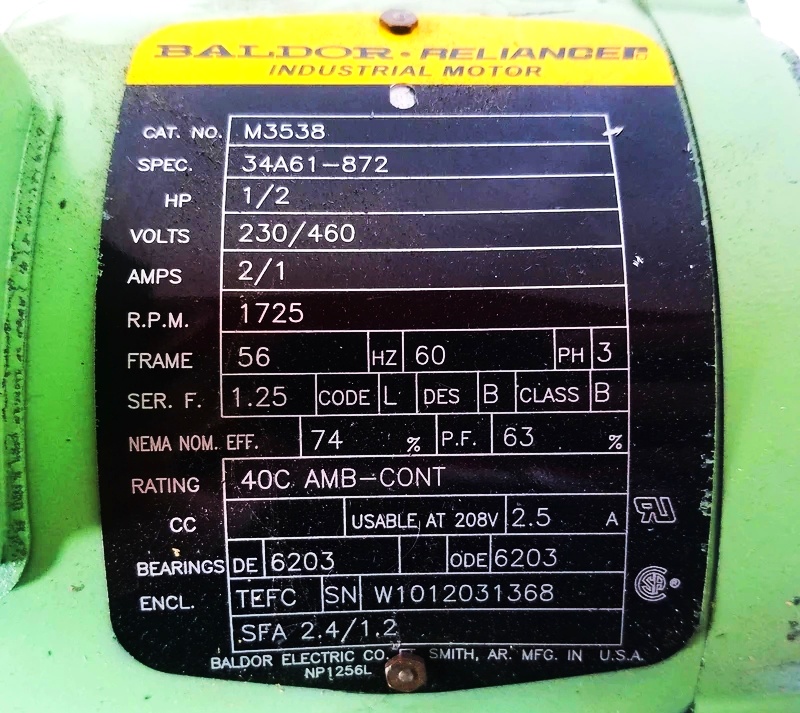
Rated Operating Voltage (VOLTS)
This specifies the rated voltage at which the motor should operate. Any deviation from this can hamper or even permanently damage the performance of the motor. The voltage specified here is the incoming voltage that it will accept.
Normally, all the motors have a tolerance of + / – 10%. That means, suppose the rated voltage is 440V; then, the motor can operate between 396V to 484V.
Number of Phases (PH)
This specifies the number of phases at which the motor should operate. The phase can be a single phase or three phases.
KW / HP Rating (PF)
The motor is used to drive a shaft load and that load will require a force from the motor for it. This force is measured in KW (Kilowatt) or HP (Horsepower).
A motor must be able to apply the specified force in the nameplate to the motor.
Connection Diagram
A motor requires to be started by various means like start-delta, direct online, reverse direct online, and other means of starter. The connection diagram shows how a motor must be started. The wrong starter method can damage the motor.
Degree of Protection
This rating specifies the motor protection rating against various hindrances like liquid entry, dust ingress, accidental contact by a human, and solid entry. IP code is specified in two numbers.
The first digit means the protection level that the enclosure provides to its internal circuit against solid ingress and the second digit means the protection level that the enclosure provides to its internal circuit against liquid ingress.
Efficiency (EFF)
It is defined as the percentage of input electrical power that will be converted to output mechanical energy. Losses occur in the motor and it is not possible to convert the whole electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is small, but not profitable.
So, it must be important to know how efficiently the motor produces mechanical power from an electrical input. The losses can be reduced and efficiency thus is increased if the manufacturer pays proper attention to it.
Frequency (HZ)
The frequency of the motor means the input frequency that will be fed to the motor. The standard ones used are 50 Hz and 60 Hz.
Rated Motor RPM (RPM)
RPM means revolutions per minute. It determines the speed of the motor at full input frequency and full load. Normally, it depends on the frequency of line voltage and the number of poles on the motor.
Insulation Class (CLASS)
Insulating materials used inside the motor have an operating temperature, exceeding which can damage them. The insulation class indicates this temperature and its types are – B, F, and H.
B class has the lowest operating temperature and H class has the highest operating temperature; with F class between them.
Rated Motor Current (FL AMPS)
It indicates the maximum current that a motor will draw when it is running at rated voltage, load, and speed.
This is an important parameter that can be used to determine the power requirements of the motor.
Ambient Temperature (RATING)
The ambient temperature of the motor at which it should operate; is determined by this parameter. If the temperature is not indicated, the default value is 40deg.C for IE2 motors and 60deg.C for IE3 motors.
If the temperature exceeds this parameter, then the insulation windings will be affected in the longer run.
Service Class (SF)
When torque demand increases, the current drawn by the motor from the incoming power supply increases. The service factor indicates the amount of overload current that a motor can withstand, without damaging its internal insulation windings.
For example, a motor with a factor of 1.2 can handle overloads of up to 20% of its rated horsepower. It means that a 10 HP motor can run maximum at 12 HP. But, one should avoid this in long run, as it causes continuous heating.
Serial Number (SN)
It is a unique identifier used to identify the motor. Normally, it is a location – year- month – day- motor code. It can be simply said that a motor will be identified by this number; as you are familiar with the serial numbers of other products.
Enclosure Type (ENCL)
The enclosure is designed to protect the motor housing against any damage. It can be a liquid spill, mechanical damage, abrasion, solid spill, etc. There are more than 20 types of enclosures generally used in motor enclosures.
In this way, we saw some general parameters which are mentioned in a motor nameplate.












