Difference Between Fuse and Relay
A fuse protects the electrical devices and a relay is an electrical switch. In this article, you will learn the difference between a fuse and a relay.
What is a Fuse?
A fuse is an electrical safety device that is designed to protect electrical devices, wiring, and equipment from damage caused by an overcurrent.

Fuses are typically made of a metal alloy that melts when the current flowing through it exceeds a certain level, which interrupts the flow of electricity and prevents further damage. This is known as “tripping” the fuse.
The purpose of a fuse is to protect against dangerous conditions such as electrical fires and equipment damage caused by overcurrents.
What is a Relay?
A relay is an electrical switch that is activated by an electrical current. It is used to control a circuit by a separate low-power signal, or to switch power between multiple circuits.

Relays are commonly used to control high-voltage or high-current circuits with a low-voltage or low-current signal, such as a switch or a computer.
Difference Between Fuse and Relay
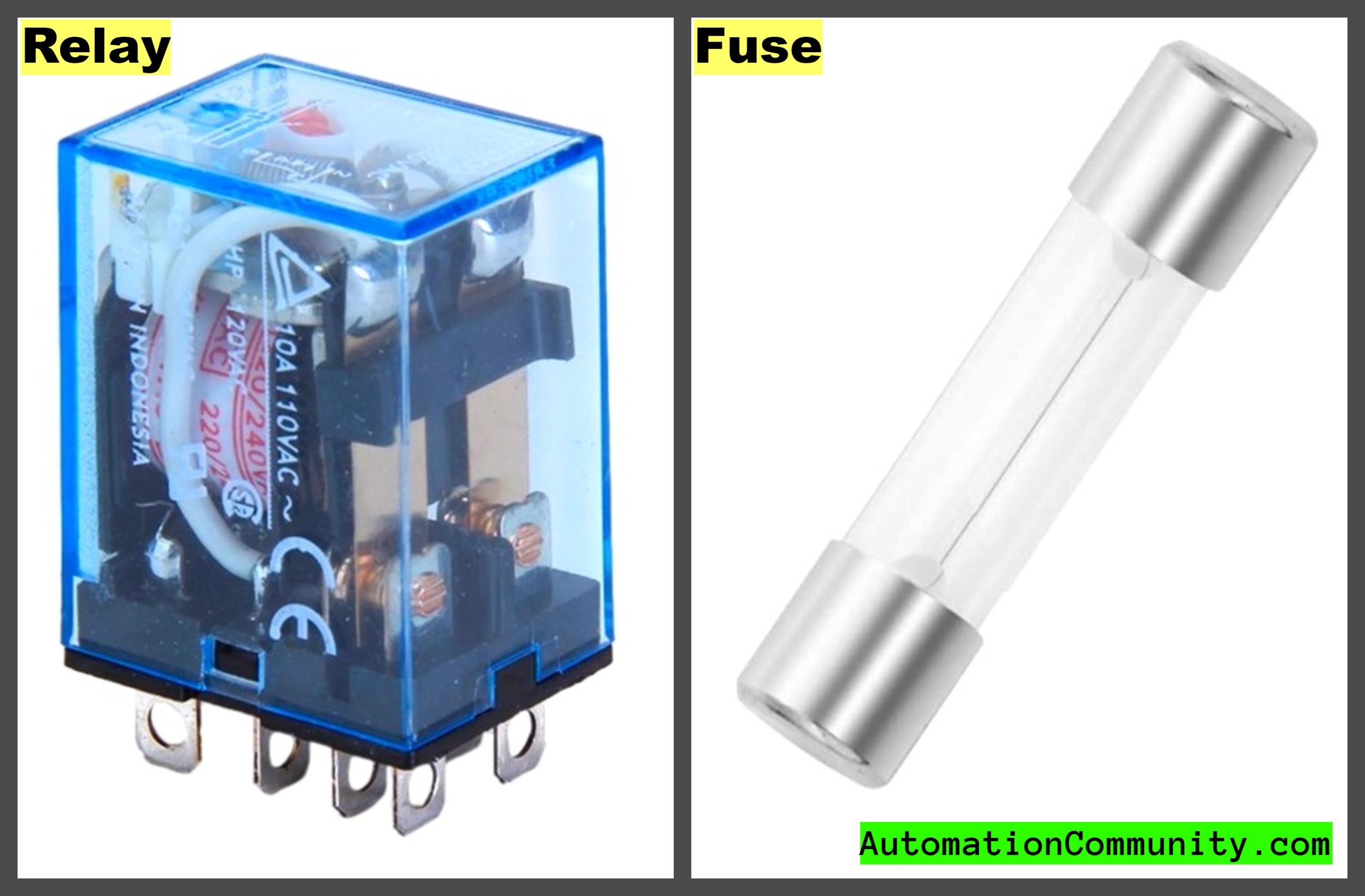
Fuses and relays are both used for overcurrent protection in electrical systems. However, there are some key differences between the two that are summarized in the table below:
| Fuse | Relay |
|---|---|
| A Fuse is an electrical safety device that is designed to protect electrical devices, wiring, and equipment from damage caused by an overcurrent | A Relay is an electrical switch that is activated by an electrical current. It is used to control a circuit by a separate low-power signal, or to switch power between multiple circuits. |
| Fuses are typically made of a metal alloy that melts when the current flowing through it exceeds a certain level, which interrupts the flow of electricity and prevents further damage | Relays are commonly used to control high-voltage or high-current circuits with a low-voltage or low-current signal, such as a switch or a computer |
| The purpose of a fuse is to protect against dangerous conditions such as electrical fires and equipment damage caused by overcurrents | Relays are used in a wide range of applications, such as automotives, industrial control systems, home appliances and security systems, and in many other devices where there is a need to control a high-power circuit with a low-power signal |
| Once the fuse is blow it needs to be replaced | Relays can be reset and reused multiple times |
| Fuses are typically rated for a specific current and voltage | Relays can be rated for a wide range of voltage and current levels |
| Fuses are typically one-time use devices, once a fuse is blown it needs to be replaced | Relays can be reset and reused multiple times |
| Fuses are typically slower in response time compared to relays | Relays have faster response time as they operate on electromagnetic principles |
| Fuses are less complex in design and operation compared to relays | Relays are more complex in design and operation |
| Fuses are typically smaller in size compared to relays | Relays are typically larger in size compared to fuses |
Conclusion
In general, fuses are simple, reliable, and inexpensive, but they are one-time-use devices and they are less flexible in terms of controlling the circuit. Relays, on the other hand, are more complex and expensive, but they can be used multiple times, provide faster response time, and can be controlled with electricity to open or close the circuit.
In summary, the choice between using a fuse or a relay depends on the specific application and the requirements of the system. Fuses are typically used in simple systems where response time is not critical, while relays are commonly used in more complex systems where faster response time and remote control are needed.
Read Next: